Continental Drift
advertisement
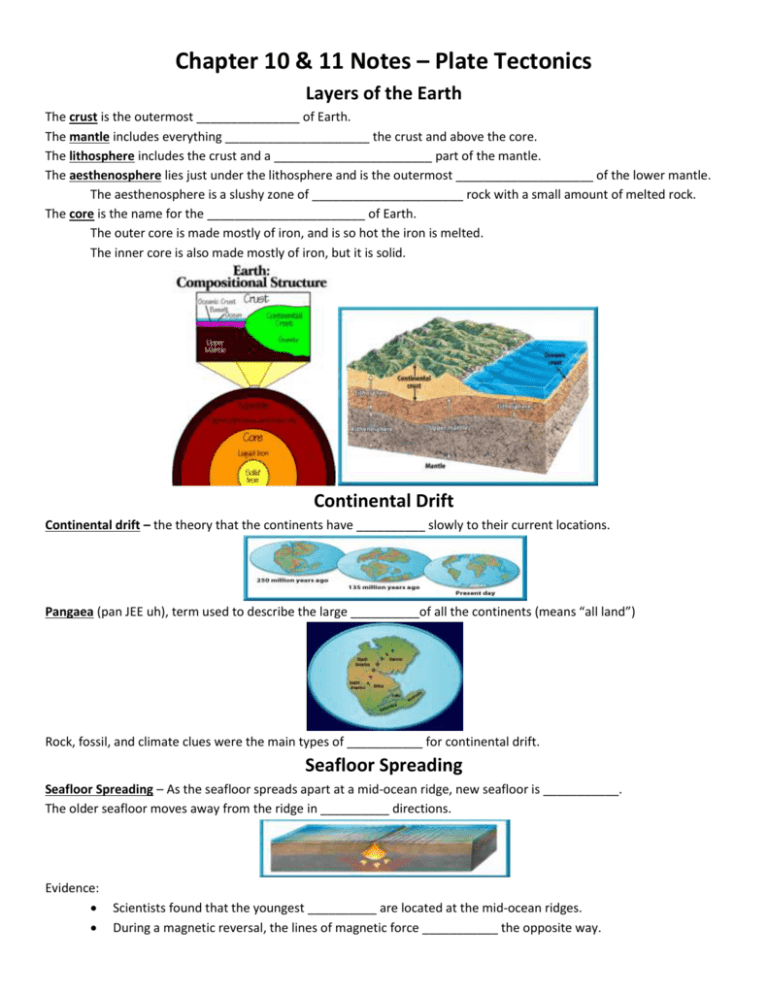
Chapter 10 & 11 Notes – Plate Tectonics Layers of the Earth The crust is the outermost _______________ of Earth. The mantle includes everything _____________________ the crust and above the core. The lithosphere includes the crust and a _______________________ part of the mantle. The aesthenosphere lies just under the lithosphere and is the outermost ____________________ of the lower mantle. The aesthenosphere is a slushy zone of ______________________ rock with a small amount of melted rock. The core is the name for the _______________________ of Earth. The outer core is made mostly of iron, and is so hot the iron is melted. The inner core is also made mostly of iron, but it is solid. Continental Drift Continental drift – the theory that the continents have __________ slowly to their current locations. Pangaea (pan JEE uh), term used to describe the large __________of all the continents (means “all land”) Rock, fossil, and climate clues were the main types of ___________ for continental drift. Seafloor Spreading Seafloor Spreading – As the seafloor spreads apart at a mid-ocean ridge, new seafloor is ___________. The older seafloor moves away from the ridge in __________ directions. Evidence: Scientists found that the youngest __________ are located at the mid-ocean ridges. During a magnetic reversal, the lines of magnetic force ___________ the opposite way. Theory of Plate Tectonics • • The theory of plate tectonics – Earth’s crust and part of the upper __________ are broken into sections, and move around on the mantle. The sections, called plates, are made of the ___________ and the upper mantle. Causes: • • The cycle of ____________, rising, cooling, and sinking is called a convection current. This is the driving force behind plate tectonics. The sinking of cooling magma within the ______________________ or the sliding of one tectonic plate under another plate is call subduction. When plates move: They can move ___________ each other and converge, or collide. They also can ___________ apart. They can ___________ alongside one another. Plate Boundaries: 1. The boundary between two plates that are moving ___________ is called a divergent boundary. Mid-ocean ridges are formed ____________ two oceanic plates move apart. Divergent boundaries can also be found on continents as rift valleys. 2. A Convergent boundary is when two plates collide or __________ into each other. a. Continent – Oceanic, is when an oceanic plate converges with a less dense continental plate; the denser oceanic plate sinks under the continental plate. This creates a deep-sea trench where one plate bends and sinks beneath the other. b. Oceanic – Oceanic, is when two oceanic plates collide. A subduction zone also can form where two oceanic plates converge. This forms a valley in ___________ ocean floor called a trench. c. Continent – Continent, when two continental plates collide. The two plates collide and crumple up, forming mountain ranges. 3. Transform boundaries occur where two plates ___________ past one another. a. They move in opposite directions or in the same direction at different rates. b. When one plate slips past another suddenly, earthquakes occur. Vocabulary: Crust Plates Mantle Convection Current Lithosphere Subduction Aesthenosphere Divergent Boundary Core Convergent Boundary Continental Drift Transform Boundary Pangaea Rift Valley Seafloor Spreading Trench Plate Tectonics Mid-Ocean Ridge