RTI data, terms and explanantions

Pioneer Central School Response to Intervention RTI
Response to Intervention: A new approach to identifying students with specific learning difficulties, which represents a major change in educational law. (RT,12/08, Mesmer and Mesmer p.280.
The change shifts the emphasis of the identification process toward providing support and intervention to struggling students early. It was developed because of the problems with the discrepancy model of identifying students with learning disabilities. In 1977 a learning disability was described as “a severe discrepancy between achievement and intellectual ability”, US,D.of Ed.1977.
Level Data: Compares how students are doing in relation to peers at a specific time.
Slope Data: Compares how students are doing over time in relation to his or her previous learning.
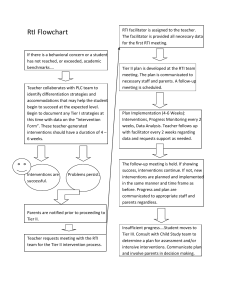
Progress monitoring: Assessment technique required by RTI. Teachers administer quick assessments (1-5 ) minutes frequently to gauge improvement. This captures rate of learning and growth rate. This provides information about a student’s progress and the success of the intervention.
Literacy Screening: Process of assessing the most basic and predictive literacy skills for all students in a school. The goal is to select learners whose reading achievement is significantly below students who require additional help.
Step 1: Establish universal literacy practices that include screening grades K-3.
Step 2: Valid intervention practices for identified students. Small Group
Step 3: Progress monitoring See tools. www.studentprogress.org/chart/chart.asp
This chart lists Early STAR and STAR Literacy has acceptable methods of progress monitoring as well as
DIBLES, etc.
Step 4: Individualize interventions for students who are not progressing. Additional assessments may be required.
Step 5: Decision making process for to determine eligibility for special education services. A team of school based professionals and the student’s parents review the data. If a students lack of response may be caused by some other factor not explained by a LD, then additional assessment may be required for social, emotional, intellectual and adaptive functioning.
The Law: In 2004, IDEA, PL 108-446 introduced RTI language. (A learning disability may be present when a student’s performance is not adequate to meet grade level standards when provided with appropriate instruction and research –based interventions.) In the RTI model, the “tests” of whether student’s possesses learning disabilities are not standardized measures, but students’ measured responses to interventions. Students responding to interventions are less likely to possess a disability than students responding more slowly or not at all. The term appropriate refers to instruction in the classroom that matches a student’s skill level. The term research based indicates that interventions should be based on practices verifiable through researched based studies.
Target Areas of Underachievement:
Oral expression, listening comprehension, written expression, basic reading skills, reading fluency skills, reading comprehension, mathematics calculation, mathematics problem solving
Other problem areas of concern:
RTI Response to Intervention Planning
A visual, hearing or motor disability, mental retardation, emotional disturbance, cultural factors, environmental or economic disadvantage, or limited language proficiency
Ensure proper documentation of underachievement:
Ongoing data that verifies a student received appropriate instruction in a regular education setting delivered by qualified personnel and documentation of repeated assessment at regular intervals of student progress monitoring that was provided to the child’s parents.
Use chart below to collect baseline data for the District.
(1)
Student Groups
Average students performance
Total Number of students =
Students receiving academic intervention services
N=
Inclusion students
English Language Learners
N=
N=
Gifted & Talented students N=
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
(2)
Less than expected
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
(3)
As expected
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
(4)
Better than expected
Elem
MS
HS
Elem
MS
HS
Response to Intervention (RTI): What teachers of Reading Need to Know, The Reading
Teacher, Vol. 62, NO 4 Dec. 2008/January 2009
RTI Response to Intervention Planning
4
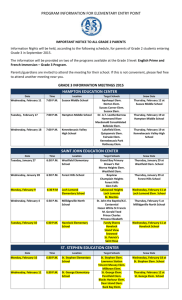
Tier 1 All students grades UPK to 4
Grade
UPK to K
Assessment
Initial screening using DIAL
K to 1 Marie Clay Observation Survey
STAR Early
Frequency spring and summer
3 times per year.
1 to 2 On the Mark Assessment
Running Records
STAR Early quarterly benchmark monthly
3
4
NY State ELA
NY State ELA
Annual
Annual
**District may consider DIBLES, PALS or other Screening Tool for grades K-4
Tier 2 Student not performing to grade level expectations (15-20%)
1
2
3
UPK
K
1.
Small group direct instruction in the regular classroom by qualified staff
2.
AIS is required for deficits in achievement
3.
Progress monitoring of interventions and assessments
4.
CST review if requested by classroom teacher
5.
Parent notification
Interventions Progress Personnel
Target
Cut off
Follow-up
Level 3
Level 3
Response to Intervention (RTI): What teachers of Reading Need to Know, The Reading
Teacher, Vol. 62, NO 4 Dec. 2008/January 2009
RTI Response to Intervention Planning
2
3
K
1
4
Tier 3 Students targeted for further diagnosis and assessment (lowest 5%)
Grades
UPK
1.
Appropriate instruction and interventions one on one have not been successful
2.
CST referral to CSE
3.
Progress monitoring of interventions and assessments provide evidence and data to support referral
4.
Further diagnosis and testing as indicated
5.
Parent notification
Interventions Progress Personnel Follow-up
Response to Intervention (RTI): What teachers of Reading Need to Know, The Reading
Teacher, Vol. 62, NO 4 Dec. 2008/January 2009