Name___________________________
advertisement

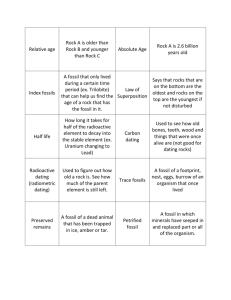
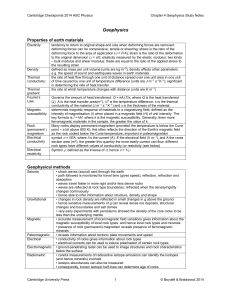
Name___________________________ Date_________________________ Hour__________________ Changing Earth’s Surface and Geologic Time (Chapters 7-10) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Where are the youngest rocks on the ocean floor located? Near mid-ocean ridges How quickly do the plates move? 1-12 cm per year What evidence do scientists have for continental drift? Matching rock structures and fossils What conditions help to make a good fossil? Hardened parts, buried quickly, protected from scavengers What does it mean if the same type of fossil is found in two separate rock layers? They are part of one deposit How do scientists determine different classifications of geologic time? By looking at the different types of organisms living at that time. Which era has extensive mountain building? Cenozoic Era What happens if an organism does not adapt to its environment? It will die out. Where does subduction take place? At convergent boundaries What dangers occur at a volcanic eruption? Lava flows, pyroclastic flows, mud slides Compare an earthquake to the stretching of a rubber band. The rocks in Earth’s crust stretch and tension builds. When the rocks break, the tension is released in the form of waves, causing an earthquake. What makes an excellent index fossil? Abundant, available for a short amount of time, geographically widespread Understand how to determine the relative age of a rock structure by looking at the different layers. Write the following vocabulary words: Lithosphere—the crust and the upper mantle Asthenosphere—the lower taffy-like part of the mantle Continental Drift—hypothesis that continents have slowly moved to their current locations Transform Fault Boundary—plates slide past each other; forms earthquakes Convergent Boundary—plates move towards each other; forms mountains Divergent Boundary—plates move away from each other; forms volcanoes Seismic Waves—earthquake waves Primary Waves—smallest and fastest waves Secondary Waves—medium sized earthquake waves Surface Waves—slowest, biggest, and most damaging waves Lava—the molten material that flows onto Earth’s surface Relative Age—a rock’s age in relation to other objects/rocks Cenozoic Era—era of recent life; life forms include humans, marine animals, and reptiles; time of mountain building Mesozoic Era—era of middle life; life forms include birds, dinosaurs, and angiosperms Paleozoic Era—era of ancient life; life forms include marine organisms Name___________________________ Date_________________________ Hour__________________ Precambrian Time—longest period of Earth’s history; life forms include cyanobacteria Cyanobacteria—blue green algae present in Precambrian time Fossil—remains, imprints, or traces of once-living organisms Mold—cavity left in rock by a decayed organism Original Remains—actual organism or parts of organism protected from decay Radiometric—method of dating rocks when the amounts of parent and daughter materials are measured Absolute Dating—method using properties of atoms in rocks and other objects to determine their ages Uniformitarianism—principle stating that Earth’s processes occurring today are similar to those that occurred in the past Carbon—element found in tissues of most organisms Half Life—time it takes for half of the atoms in a radioactive element to decay Unconformities—gaps found in rock records Radioactive—kind of decay that results in the formation of a different element