Matching review games
advertisement
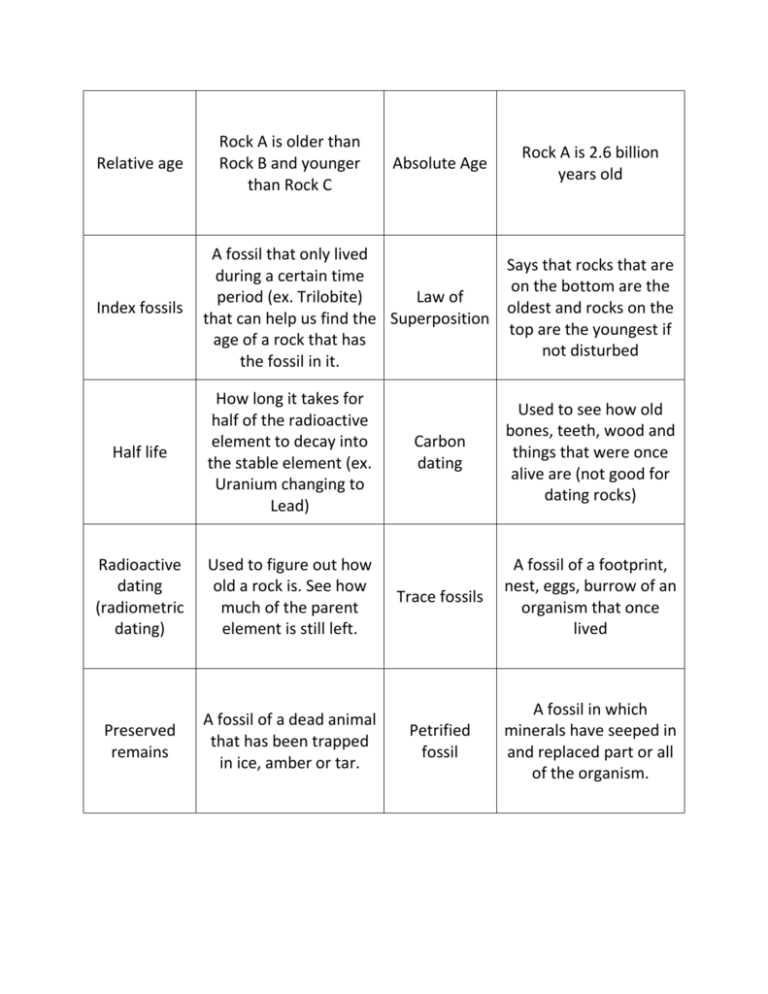
Relative age Index fossils Rock A is older than Rock B and younger than Rock C Absolute Age Rock A is 2.6 billion years old A fossil that only lived Says that rocks that are during a certain time on the bottom are the period (ex. Trilobite) Law of oldest and rocks on the that can help us find the Superposition top are the youngest if age of a rock that has not disturbed the fossil in it. Half life How long it takes for half of the radioactive element to decay into the stable element (ex. Uranium changing to Lead) Radioactive dating (radiometric dating) Used to figure out how old a rock is. See how much of the parent element is still left. Preserved remains A fossil of a dead animal that has been trapped in ice, amber or tar. Carbon dating Used to see how old bones, teeth, wood and things that were once alive are (not good for dating rocks) Trace fossils A fossil of a footprint, nest, eggs, burrow of an organism that once lived Petrified fossil A fossil in which minerals have seeped in and replaced part or all of the organism. Intrusion Magma came up and cut through a rock. It is younger than the rock it cut through. Vertebrate Animal that has a backbone Invertebrate Animal that does not have a backbone Cenozoic Age of Mammals, Era you live in Mesozoic Age of Reptiles Quaternary Time period you live in Paleozoic Era that had invertebrates, amphibians, land plants, insects and some reptiles PreCambrian Time Long period of history of where Earth was formed and Earth’s atmosphere Unconformity Gap in the geologic record where erosion wiped away some of the layers of rock Amphibians Animals that live partly in the water and partly on land Mammals Warm blooded vertebrates 4.6 billion years How old the Earth is Igneous rocks Radioactive dating works best with which types of rocks? Sedimentary rocks The Law of Superposition works best with which types of rocks? Single celled organisms The first type of things that lived on Earth during the Precambrian Time Hydrogen & Helium The gases in Earth’s first atmosphere – blown away by solar winds Comets What brought water vapor to Earth and caused rain which accumulated in our oceans Mass Extinction When all the animals or plants die Evolution How animals and plants change over long periods of time Fossils The remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Precambrian Time Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Quaternary Period Permian Period Carboniferous Period Mass extinction of ocean and land animals Reptiles, ferns, trees Devonian Period Fish, amphibians Cambrian Period Explosion of life on Earth – invertebrates in the sea Silurian Period Insects and plants on Land Ordovician Period Triassic Period First dinosaurs, reptiles Jurassic Period Dinosaurs, first birds Cretaceous Period Paleogene, Neogene Periods Mammals and grasses Extinction of dinosaurs, first flowers and fruit Humans, pets Formation of earth, atmosphere, ocean, continents invertebrates / vertebrates/jawless fish Age of Reptiles Age of Mammals First Era