support_ms_APL2
advertisement
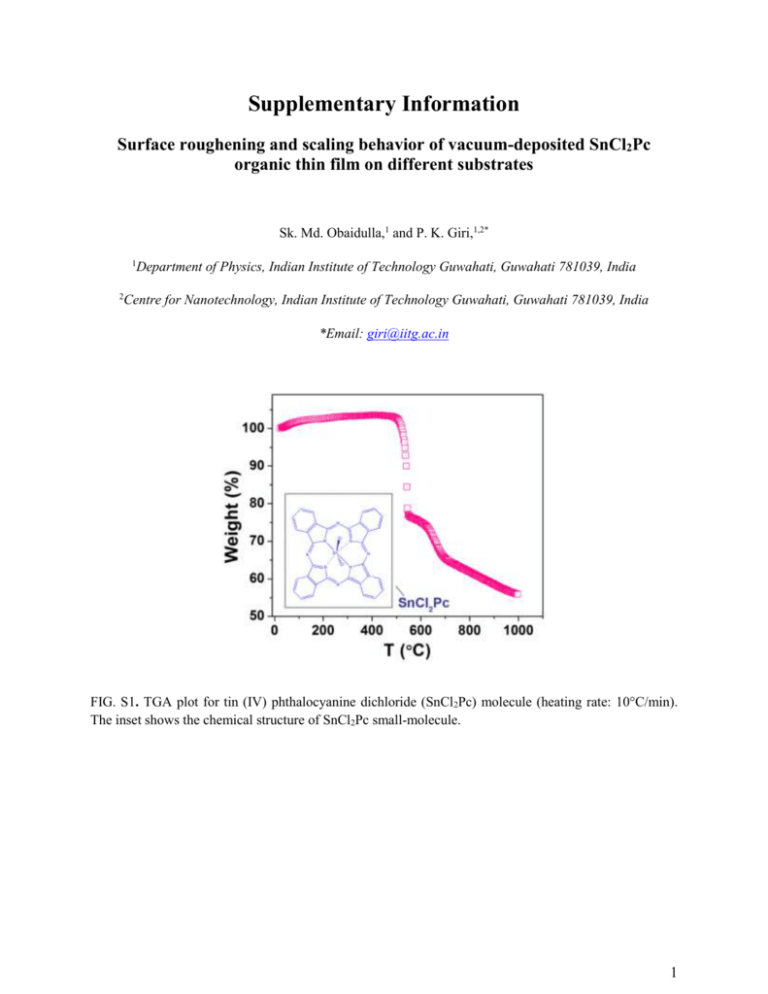
Supplementary Information Surface roughening and scaling behavior of vacuum-deposited SnCl2Pc organic thin film on different substrates Sk. Md. Obaidulla,1 and P. K. Giri,1,2* 1 Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, Guwahati 781039, India 2 Centre for Nanotechnology, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, Guwahati 781039, India *Email: giri@iitg.ac.in FIG. S1. TGA plot for tin (IV) phthalocyanine dichloride (SnCl2Pc) molecule (heating rate: 10C/min). The inset shows the chemical structure of SnCl2Pc small-molecule. 1 FIG. S2. AFM images (upper one) and surface height profile (lower panel) for ~ 87 nm SnCl2Pc thin films on (a) glass and (b) Si substrate. 2 FIG. S3. C1s XPS spectra of the SnCl2Pc organic thin film of thickness 5 nm on (a) Si and (b) glass substrate. FIG. S4. Si 2p XPS spectrum of the Si substrate showing peaks corresponding to different oxidation states of Si. The symbols represent the experimental data and the solid lines represent the fitted peaks. 3 FIG. S5. XRD patterns of SnCl2Pc thin film (thickness ~87 nm) gown on (a) glass, and (b) Si substrate at different grazing angles ω= 0.5 to 1.5 degree of incidence. FIG. S6. UV-Vis absorption spectra of SnCl2Pc thin films at room temperature for different deposition times. 4 FIG. S7. Height distribution function p(h)obtained from the AFM images of SnCl2Pc for deposition time 5 min (~8 nm) on (a) Si and (b) glass substrates. Skewness, S, is negative for Si substrate, while it is positive for glass substrate. 5