File
advertisement

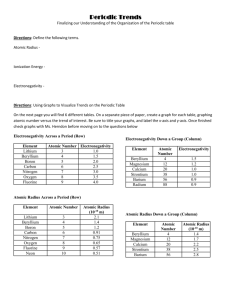
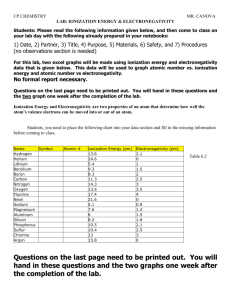
Name : ______________________________________ Periodic Table Graphing Lab Purpose: Determine how density, radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity changes on the table. Materials: graduated cylinder, balance, weighing dished, lead, silicon, tin, reference tables, graph paper, rulers. Pre-Lab: 1. Explain how you plan to find the density of silicon, tin, and lead. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Where can you find the actual densities of silicon, tin, and lead? List them here: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Procedure: 1. Find the density of the tin, lead and silicon. Be sure to record all measurements and show all work. Silicon Tin Lead 2. Graph density versus atomic number for the three substances you measured. 1 3. Calculate the percent error of your densities using table S. Silicon Tin Lead 4. On your graph, estimate the density of carbon and germanium. Place marks on the graph and label with symbol and estimated density. Then calculate you percent error. Carbon Germanium 5. Using your reference table S, graph the following: *Be sure to label the axis and name of the graph! Use appropriate scales. Atomic Number should always be labeled on the x axis. a. Atomic Number versus Radius for the Halogens. 2 b. Atomic Number versus Radius for Period 2. c. Atomic Number versus Ionization Energy for the Alkali Metals. 3 d. Atomic Number versus Ionization Energy for Period 3. e. Atomic Number versus Electronegativity for the Alkaline Earth Metals 4 f. Atomic Number versus Electronegativity for Period 2. 6. Fill in the blank with increase or decrease based on your graphs: a. Along a period, atomic radius __________________ b. Along a group, atomic radius __________________. c. Along a period, ionization energy __________________. d. Along a group, ionization energy__________________. e. Along a period, electronegativity __________________. f. Along a group, electronegativity __________________. 5 6