Volcanoes and Earthquakes Test Fall 2010 Study Guide
advertisement
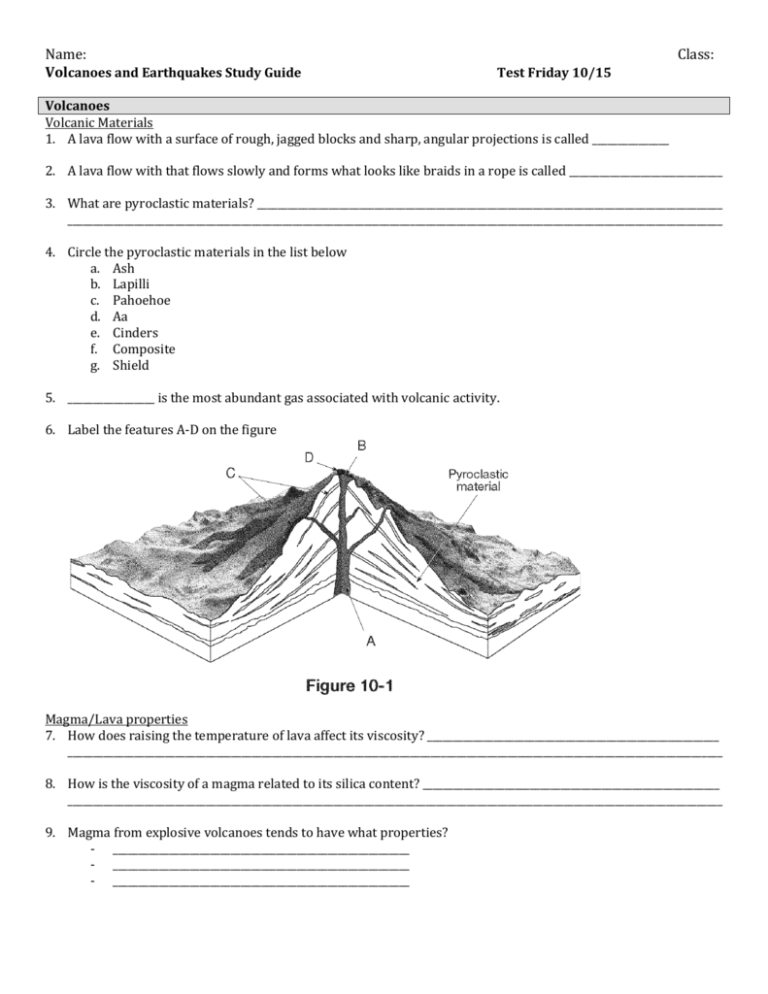
Name: Volcanoes and Earthquakes Study Guide Class: Test Friday 10/15 Volcanoes Volcanic Materials 1. A lava flow with a surface of rough, jagged blocks and sharp, angular projections is called _______________ 2. A lava flow with that flows slowly and forms what looks like braids in a rope is called ______________________________ 3. What are pyroclastic materials? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Circle the pyroclastic materials in the list below a. Ash b. Lapilli c. Pahoehoe d. Aa e. Cinders f. Composite g. Shield 5. _________________ is the most abundant gas associated with volcanic activity. 6. Label the features A-D on the figure Magma/Lava properties 7. How does raising the temperature of lava affect its viscosity? _________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. How is the viscosity of a magma related to its silica content? __________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Magma from explosive volcanoes tends to have what properties? - __________________________________________________________ - __________________________________________________________ - __________________________________________________________ Name: Class: 10. Magma forms when ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ and rises to the surface because __________________________________________________________________________________________ 11. What affects the melting point of a rock a. b. c. d. Types of volcanoes 12. What plays a major part in determining the form of a volcano? ______________________________________________________ 13. How are shield volcanoes formed? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. How are composite volcanoes formed? __________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 15. How are cinder cones formed? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Volcano/Plate Interactions 16. What type of plate boundary results in volcanic island arcs? ___________________________________________________________ 17. What type of plate boundary results in continental volcanic arcs? ____________________________________________________ 18. How were the Hawaiian Islands formed? ________________________________________________________________________________ 19. Where are most active volcanoes located? _______________________________________________________________________________ a. Why are they located here? _______________________________________________________________________________________ 20. Diagram an oceanic- continental convergent boundary and what it produces. Earthquakes Earthquake waves 21. Name the 3 earthquake waves. a. b. c. 22. Which of these waves is the most destructive? ___________________________________ 23. Which of these waves is the slowest? _____________________________________________ Name: Class: 24. Which of these waves is the fastest? ______________________________________________ 25. Which wave travels through solids only? ________________________________________ 26. Put the three earthquake waves in order from slowest to fastest. a. b. c. Earthquake features 27. What is the focus of an earthquake? ______________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 28. What is the epicenter of an earthquake? _________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 29. How are the two related? __________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 30. What is the intensity of an earthquake? __________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 31. How is the Richter magnitude of an earthquake determined? _________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 32. Most of the information about earthquakes is obtained by studying __________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Earthquake Effects 33. What are tsunamis and how are they related to earthquakes? _________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 34. What are the smaller earthquakes that precede a major earthquake? _________________________________________________ 35. What earthquakes come after a major earthquake? _____________________________________________________________________ 36. If you had to choose in what location you would be when an earthquake struck, which of the following would you choose and WHY? - area with granite bedrock - area with loosely consolidated soil - area with structures built on a landfill - area with steep slopes of unconsolidated sediments Name: Class: Travel-Time graphs 37. According to the figure, what is the distance between the seismic station and an earthquake epicenter, if the first S wave arrives 4.0 minutes after the first P wave? (SHOW YOUR WORK) 38. Use the graph to determine the difference is the travel-times of the first P wave and first S wave if the seismic station is 4000 km from the epicenter. (SHOW YOUR WORK) 39. According to the figure, when will the first P wave arrive if an earthquake epicenter is about 1800 km from the seismic station? (SHOW YOUR WORK)







