lab 10 electrochemical cells
advertisement

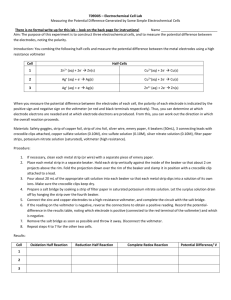
Lab 10 Electrochemical Cells Purpose: 1. 2. To predict the voltage and direction of electron flow of various electrochemical cells To construct and measure the voltage of various electrochemical cells Prelab Exercise: Complete the following diagrams for each of the cells you will be making. Materials: 1 voltmeter porous cup 250 mL beaker 4 100 mL beakers strip of aluminum strip of copper strip of zinc carbon electrode 50 mL graduated cylinder 10 mL of 6.0 mol/L H2SO4(aq) 70 mL of 0.13 mol/L K2Cr2O7(aq) 80 ml of 0.10 mol/L Al2(SO4)3(aq) 80 mL of 0.10 mol/L ZnSO4(aq) steel wool 80 mL of 0.10 mol/L CuSO4(aq) Procedure: 1. Use labeled 100 mL beakers to obtain about 100 mL of each metal solution. Also obtain about 75 mL of dichromate solution 2. Use a graduated cylinder to obtain 10 mL of sulfuric acid (CAUTION) 3. Add the acid to the dichromate solution (Handle this solution with care.) 4. Place the carbon electrode in a 250 mL beaker. 5. Pour the acidic dichromate solution into the 250 mL beaker 6. Clean the surface of a zinc strip with steel wool and place the strip in a porous cup. 7. Add the zinc sulfate solution to the porous cup until it is 2/3 full 8. Place the porous cup into the 250 mL beaker 9. Connect the positive (red) terminal of the voltmeter to the cathode of the cell and connect the negative (black) terminal of the voltmeter to the anode of the cell. 10. Record the voltmeter reading in the data table. 11. Look for signs of a chemical reaction around the anode and cathode. Record any observations in the data table. 12. Take the porous cup out of the 250 mL beaker, remove the zinc strip and pour the zinc sulfate back into the labeled 150 mL beaker 13. Rinse the porous cup with tap water 14. Repeat steps 6-13 using aluminum strip in a Al3(SO4)3(aq) solution in the porous cup 15. Repeat using a copper strip in a CuSO4(aq) solution in the porous cup. 16. Remove the carbon electrode from the 250 mL beaker and pour the dichromate solution back into the labeled beaker. 17. Rinse the 250 mL beaker with tap water 18. Repeat steps 6 – 13 using zinc and copper half cells 19. Repeat steps 6-13 using zinc and aluminum half cells 20. Repeat steps 6-13 using aluminum and copper half cells 21. Clean and dry the metal strips, dispose of solutions in the waste container in the fume hood. Rinse glassware and the porous cup. Observations: Part A: Positive Electrode Prelab Exercise Negative Predicted electrode voltage Observed Voltage Zn(s)/Zn2+(aq)//Cr2O72-(aq),H+(aq),Cr3+(aq)/C(s) Al(s)/Al3+(aq)//Cr2O72-(aq),H+(aq),Cr3+(aq)/C(s) Cu(s)/Cu2+(aq)//Cr2O72-(aq),H+(aq),Cr3+(aq)/C(s) Zn(s)/Zn2+(aq)//Cu2+(aq)/Cu(s) Zn(s)/Zn2+(aq)//Al3+(aq)/Al(s) Al(s)/Al3+(aq)//Cu2+(aq)/Cu(s) Questions: 1. Compare the predicted voltages with the observed voltages. Account for any differences. 2. Why were the instructions to use 0.13 mol/L K2Cr2O7(aq) solution when all other solutions were 0.10 mol/L? 3. What problems might be encountered in storing an acidic solution in potassium dichromate?