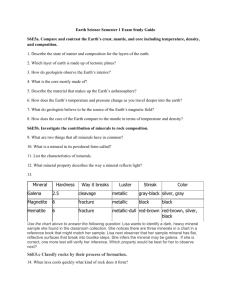
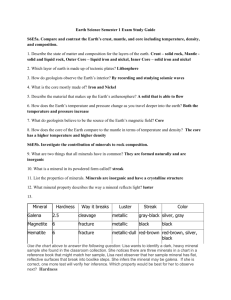
Minerals
advertisement

Unit 4 The Earth’s Crust Date:_________________________ Name:________________________ Chapter 10 Minerals, Rocks, and Soils Date:_________________________ Name:________________________ Lesson 1 Minerals A Rock is made of one or more pure naturally occurring, non-living solid materials called Minerals. What minerals make up the rock granite? Quarts, hornblende, feldspar, mica What sport uses a type of granite that is only found on one island near Scotland? ____________________________________ All Minerals are Crystals. This means that minerals are formed naturally into six basic shapes all having straight edges, flat sides, and regular angles. (Reading activity crystals) Most minerals are (rare / common)circle one. Two common minerals found in the earth’s crust are quartz and mica. A mineral can be an element (made of one type of particle) or a compound (Made of two types of compounds. A mineral that is a compound is quartz. It is made of the elements silicon and oxygen. Four minerals that are made of a single element are Sulfur, copper, gold, and diamond. Properties of Minerals Explain why it is important for someone trading their life savings in for gold should know the properties of gold? Pyrite is a mineral that looks almost identical to gold. If you are not careful someone could give you pyrite which is worth nothing. If you know the properties of the two you would be able to tell them apart and not be fooled. Video Questions: Gold 1. In the intro, the guy was talking in the third person pretending he was? Gold 2. 3. 4. 5. Where did they find the gold? The airport The gold was worth approximately? $250 000 Why did he change all his money to gold? Because Zambia wouldn’t let him take money out. Why did he not get in any trouble? The Gold was fake Property 1: Hardness Hardness is really just how hard it is to scratch a mineral. Scientist Friedrich Mohs developed a scale in the year 1812. The Mohs Hardness Scale Use the table to answer the following. The hardness is rated with the numbers from 1 to 10. The hardest mineral is Diamond. Which mineral could your fingernail scratch? Talc (or gypsum) Which mineral could scratch corundum? Diamond Property 2: Lustre The “Shininess” of a mineral. This depends on how light is reflected off its surface. _______________ often appear shiny. _________________ often appear dull. Property 3: Colour Colour can be a clue to identity, but cannot alone identify a mineral. An example of two minerals that have identical colour are? Pyrite and gold Corundum is made of aluminum and oxygen and is the colour white when pure. It dramatically changes colour when mixed. Explain what happens when Iron and titanium is added. It is the colour blue and is called a sapphire Chromium is added. It is the colour red and is called a ruby. (reading activity gemstones) Property 4: Streak A streak is the powdered form of a mineral. We often test a minerals streak on a white porcelain tile. Explain how you can tell the difference between pyrite and gold. Gold leaves a yellow streak while pyrite leaves a greenish-black or brownish black streak. Minerals harder than porcelain can be crushed. Surprise! Many minerals (usually black) will have powders that are not black. Property 5: Cleavage and Fracture Cleavage and fracture explain how minerals break apart. Cleavage is the ability to break or peel off in smooth flat surfaces/sheets. Example: Mica Fracture is when minerals break in rough of jagged edges. Example: Obsidian Uses of Minerals Explain how each of the following minerals are useful. Practical uses of diamond: Diamonds are so hard. They are used in drill bits to cut steel and rock. Diamonds are also used in scalpels, razor blades, dental drills, diamond-tipped phonograph needles, and diamond-coated computer parts. Metals: We use metals in cars, appliances, and many household utensils. Iron in your body: helps blood carry oxygen. Calcium in your body: helps keep bones and teeth strong. Crops need minerals to stay healthy. How do farmers keep minerals in their soils? 1. Apply fertilizer that contains minerals. 2. crop rotation is done so that crops that use certain minerals one year are replaced with crops that replace those minerals the following year. Quartz: Quartz vibrates regularly when electricity passes through it. This allows it to be used in watches to keep time. (Reading activity Rocks and Minerals) Interesting: Define Alchemy: a form of chemistry and speculative philosophy practiced in the Middle Ages and the Renaissance and concerned principally with discovering methods for transmuting baser metals into gold and with finding a universal solvent and an elixir of life. Video Alchemy 1 Video Alchemy 2 Questions Page 288 1. Define the following: Rock: A Natural material which is made of one or more minerals. Mineral: An inorganic, naturally occurring solid materials made of crystals. Minerals can either be elements or compounds. Element: A type of pure substance that is made of only one type of particle. 2. List the properties that are used to identify minerals Hardness, Lustre, Colour, Streak, Cleavage/Fracture 3. Name three minerals that have practical uses. Describe how they are used. Metals: We use metals in cars, appliances, and many household utensils. Iron in your body: helps blood carry oxygen. Calcium in your body: helps keep bones and teeth strong. Crops need minerals to stay healthy. How do farmers keep minerals in their soils? 1. Apply fertilizer that contains minerals. 2. crop rotation is done so that crops that use certain minerals one year are replaced with crops that replace those minerals the following year. Quartz: Quartz vibrates regularly when electricity passes through it. This allows it to be used in watches to keep time. (Reading activity Rocks and Minerals) Lesson 2 The Rock Cycle The three families of rocks are 1. Igneous 2. Sedimentary 3. Metamorphic Igneous Rock Magma is melted rock that is found beneath the earth. When magma breaks above the earth’s surface commonly during a volcanic eruption it is then called lava. Igneous forms when magma cools and solidifies. Rocks that are formed from magma (below the earths surface) is called Intrusive rock. Rocks that are formed from lava (above the earth’s surface) is called extrusive rock. Granite is an igneous rock that forms very deep and very slowly in the earth’s crust. What type of igneous rock is granite? Intrusive Sedimentary Rock Sedimentary rock is made up of sediments. What does sediment mean? Loose materials such as bit of minerals, rocks, plant and animal remains. ____________ percent of rock seen on the earth’s surface is sedimentary. The formation of sedimentary rocks Sediments are piled on top of each other with usually the heavier fragments settling towards the bottom. Layers of these sediments are called beds. The weight of the layers of sediment and water on top creates a great amount of pressure which forms rock through the process of compaction. In some rocks minerals dissolve in water to form a type of cement to hold the rock together. Limestone is a very common sedimentary rock that is made of once living things called fossils. Because of this limestone is classified as an organic sedimentary rock. Describe the makeup of the following sedimentary rocks: Shale:______________________________________________________________ Sandstone:__________________________________________________________ Conglomerate:______________________________________________________ Metamorphic Rock (Means change form) Metamorphic rock is formed when sedimentary or igneous rock is exposed to extremely high pressure and heat causing the original rock to change and recrystallize. Marble is a metamorphic rock formed from limestone. Explain two ways that geologists know these two rocks are related. Both have a hardness of 3 and are made from the mineral calcite. Two other metamorphic rocks are Shale to slate to schist to gneiss Granite to gneiss The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle describes the constant action of rocks on earth changing from one form of a rock to another. Weathering The process of breaking down rocks is called weathering. Weathering creates sediments which makes up sedimentary rocks. The three types of weathering are 1. Mechanical 2. Chemical 3. Biological (Which can be Mechanical or Chemical. Mechanical Weathering Mechanical weathering refers to the physical break-up or disintegration of rocks. Examples: 1. Gravity causing rocks to fall down a cliff and break apart. 2. Heating and cooling will cause water to seep into rocks and then when it cools outside the water will freeze causing rocks to wedge apart. (This is called frost wedging) 3. Wind wearing away rock is called erosion. When the wind carries the sediment away and leaves it behind this is called deposition. Grit or sediment in the air can help the wind speed up erosion because it acts like sandpaper. Chemical Weathering Chemical weathering is the breakdown or decomposition of minerals because of a chemical reaction. This usually occurs because of chemicals dissolved in water or gases in the air. Example 1. Acid Rain is caused when pollution is in the rain. Acid will react with some rocks. This will cause the rock material to dissolve and then be washed away. Biological Weathering This can be Mechanical or chemical weathering. It can be any break down of rock by a living organism such as plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi. Example 1. Plant root wedging its way into a rock crack wedging it apart. (Mechanical) 2. Acidic fluids produced by plant roots, bacteria, fungi, and some insects and small animals will slowly dissolve rock. Lesson 3 Soil Soil is a mixture of weathered rock, organic matter, mineral fragments, water, and air. Is Dirt and soil the same thing? No. Soil is the top layer of our earth that grows plants. Dirt is not what you would consider fertile(e.g. dirt swept under the rug.) The Formation of Soil 1. Earth is covered by a layer of rock and sediment. 2. Sediments and Minerals are not soil until organic matter is added, such as leaves, twigs, and dead worms and insects. 3. The organic matter creates spaces which can be filled with air or water. 4. The above is the make up of soil. List five factors that influence the formation of soil. 1. Climate 2. Type of rock (that sediments are made from) 3. Amount of Rainfall 4. Slope of the land 5. Small living creatures in the soil speed up soil production. What will happen to soil if the slope is too steep? If the land is too steep, loose dirt will run off with each rainfall leaving only barren rock. The dark part of soil is called humus. It is a mixture compost(dead plant matter) and other matter. Humus is extremely important for fertile soil. List 4 Nutrients that humus is rich in. 1. nitrogen 4. sulfur 2. phosphorus 3. potassium Good quality soil are equal parts humus and broken down rock. Humus helps keep water in the soil. Water dissolves and keeps the nutrients which are so important for plants. Worms, insects, and rodents are responsible for mixing humus with fragments of rocks. A fertile soil can supply nutrients for plant growth. Where might you find low fertility soil? Eroded, rocky soil of steep cliffs and roads. Where may you find fertile soil? Soils that develop near rivers. Explain the three stages of soil as described by the figures on the bottom of page 300. A. Weathered Rock allows air and water to enter. B. Small hardy plants grow in broken down rock sediments creating a layer of organic material on top. (Immature Soil) C. Plants growing and leaving behind a thick layer of decaying organic matter (top soil/humus). Water Soil Profiles Soils can take thousands of years to form. Soil can be very deep (60m) or very shallow (a few cm). There are many different types of soils. The layers of soil make up the soil profile. The soil profile is divided into layers that we call horizons. Horizon A is called topsoil. Characteristics 1.dark coloured 2.rich soil 3.contains humus 4.contains small grains of rock Also possible (the most mature layer of soil) Horizon B is the next layer. Characteristics 1. lighter in coulour 2. little or no humus. 3. contains minerals leached from the top layers. Leaching is the removal of soil materials because they dissolve in water. Water will dissolve minerals and carry them to lower soil horizons. Horizon C is the next layer. Characteristics 1. Contains partly weathered rock 2. contains minerals leached from above layers. 3. Most like the original parent rock. Soil Texture Texture relates to how soil feels when it is rubbed between two fingers. The particle size of the sediments are very important in the texture of the soil. Name of Rock sediment Gravel Sand Silt Clay Average particle size Over 2mm in diameter 2.0 to .05 mm in diameter 0.05 to 0.002 mm in diameter. Less than 0.002 mm in diameter. Define: (text glossary will help) Permeate – The ability of water to drain through soil. Water holding capacity – How much water a soil can hold. Describe the water-holding capacity of the three following soils. Sandy: The particles are rather large leaving lots of space for water to permeate. Has a low water holding capacity. Water will permeate it to quickly meaning it will not keep water for long. Clay: Has very small particles meaning that clay leaves very little space for water to permeate. Water will sit on clay for a long time before it soaks in. What do you think silts water holding capacity would be like? Silt has a particle size in between sand and clay; therefore we can hypothesise that it has a good water holding capacity. Farmers actually prefer a mixture of sand, silt, and clay called loam. Farming, Soil Loss, and the Environment When crops are harvested soil can be directly exposed to rain and wind causing soil loss. Erosion and weathering can carry away nutrient-rich humus. When natural vegetation is removed from an area with little rain a desert like formation can occur called desertification. List 6 things in a large farm operation that can contribute to environmental harm. 1. Plowing long straight lines can cause topsoil loss due to water erosion. 2. Cutting trees down can expose fields to wind erosion causing topsoil loss. 3. Marshes are often drained and fields plowed to the edge of rivers. This causes the loss of many species of wildlife. 4. Fossil fuel burning from large equipment can lead to air pollution. 5.Nitrogen from fertilizer and manure can get into our rivers, lakes, streams and ground water. 6.Pesticides and herbicides to control weeds, insects and animals can dissolve in water and find its way to rivers, lakes, streams and ground water Saving our Soil List four common farming practices that farmers are using to help save our soil. 1. Farmers are planting new wind breaks to prevent soil loss due to wind erosion. 2. Farmers cover bare soils with decaying plants to help keep soil in place. 3. In dry areas farmers are not tilling land, but instead using the area as a cattle grazing region. 4. No tilling (zero tillage) is a practice where farmers leave plant stalks in the ground instead of tilling the soil. This helps keep the soil in place. Landfills and Buried Waste Urbanization leads to landfill sites, which is just another name for a place that we put garbage or waste. Much of the garbage that is sent to landfills will decompose and contribute to the humus in the soil. (Kitchen and garbage waste) Sometimes Hazardous (poisonous) material finds itself in landfills and seeps into groundwater. Some other types of waste that get into our water are gasoline tanks, septic systems and fertilizer runoff. What type of area should be selected for landfill sites? A Hard rock and clay area is best for landfill because not much leaching will occur. This helps keep hazardous materials out of our water. List two things you can do to help keep hazardous materials out of our environment. 1.Reduce the amount of harmful materials you use and throw out. 2. Seperate hazardous waste from garbage.