Balancing Redox Equations
advertisement
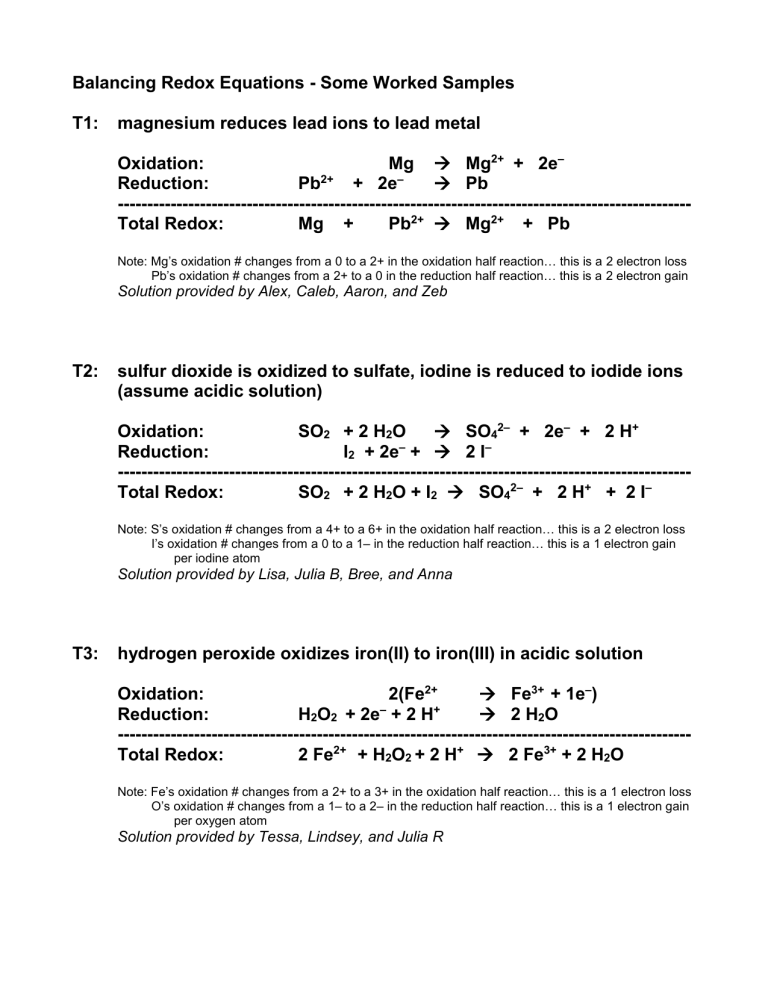
Balancing Redox Equations - Some Worked Samples T1: magnesium reduces lead ions to lead metal Oxidation: Mg Mg2+ + 2e– Reduction: Pb2+ + 2e– Pb -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Redox: Mg + Pb2+ Mg2+ + Pb Note: Mg’s oxidation # changes from a 0 to a 2+ in the oxidation half reaction… this is a 2 electron loss Pb’s oxidation # changes from a 2+ to a 0 in the reduction half reaction… this is a 2 electron gain Solution provided by Alex, Caleb, Aaron, and Zeb T2: sulfur dioxide is oxidized to sulfate, iodine is reduced to iodide ions (assume acidic solution) Oxidation: SO2 + 2 H2O SO42– + 2e– + 2 H+ Reduction: I2 + 2e– + 2 I– -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Redox: SO2 + 2 H2O + I2 SO42– + 2 H+ + 2 I– Note: S’s oxidation # changes from a 4+ to a 6+ in the oxidation half reaction… this is a 2 electron loss I’s oxidation # changes from a 0 to a 1– in the reduction half reaction… this is a 1 electron gain per iodine atom Solution provided by Lisa, Julia B, Bree, and Anna T3: hydrogen peroxide oxidizes iron(II) to iron(III) in acidic solution Oxidation: 2(Fe2+ Fe3+ + 1e–) Reduction: H2O2 + 2e– + 2 H+ 2 H2O -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Redox: 2 Fe2+ + H2O2 + 2 H+ 2 Fe3+ + 2 H2O Note: Fe’s oxidation # changes from a 2+ to a 3+ in the oxidation half reaction… this is a 1 electron loss O’s oxidation # changes from a 1– to a 2– in the reduction half reaction… this is a 1 electron gain per oxygen atom Solution provided by Tessa, Lindsey, and Julia R T4: zinc reduces acidified dichromate ions to chromium(III) Oxidation: 3(Zn Zn2+ + 2e–) Reduction: Cr2O72– + 6e– + 14 H+ 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Redox: 3 Zn + Cr2O72– + 14 H+ 3 Zn2+ + 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O Note: Zn’s oxidation # changes from a 0 to a 2+ in the oxidation half reaction… this is a 2 electron loss Cr’s oxidation # changes from a 6+ to a 3+ in the reduction half reaction… this is a 3 electron gain per atom of chromium Solution provided by Robby, Chris, Ariel, Stephanie, and Alex T5: acidified permanganate ions oxidize methanol to carbon dioxide and water Oxidation: 5(CH3OH + H2O CO2 + 6 H+ + 6e–) Reduction: 6(MnO4– + 5e– + 8 H+ Mn2+ + 4 H2O ) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Redox: 5 CH3OH + 6 MnO4– + 18 H+ 5CO2 + 6 Mn2+ + 19 H2O Note: C’s oxidation # changes from a 2– to a 4+ in the oxidation half reaction… this is a 6 electron loss Mn’s oxidation # changes from a 7+ to a 2- in the reduction half reaction… this is a 5 electron gain Solution provided by Tudor, Max, Christienne, and Sarah T6: chlorate ion (ClO3-) is oxidized to the perchlorate ion (ClO4-) and is reduced to the chloride ion Oxidation: 3(ClO3– ClO4– + 2e–) Reduction: ClO3– + 6e– Cl– -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Total Redox: 4 ClO3– Cl– + 3 ClO4– Note: Cl’s oxidation # changes from a 5+ to a 7+ in the oxidation half reaction… this is a 2 electron loss Cl’s oxidation # changes from a 5+ to a 1- in the reduction half reaction… this is a 6 electron gain Solution provided by Dan, Dominique, and Mike








