File
advertisement

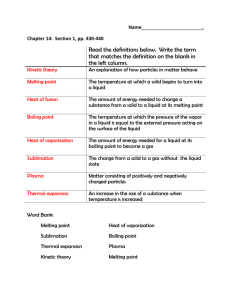
Name: ________________________ Date: ________ Homework: Heating Curves Heating Curves: TEMPERATURE vs. TIME is graphed while a substance is being HEATED at a constant rate. As a substance is heated, its particles begin to move faster and spread apart. The speed of the particles is related to their kinetic energy. The relative position of the particles is related to their potential energy. As solids, liquids, and gases are heated, most of the energy that is absorbed is converted to kinetic energy, and the temperature goes up. But as a substance melts or vaporizes, the particle attractions weaken. As a result, the energy absorbed produces changes in the potential energy of the particles, so the temperature does not change as the phase changes. The freezing point and the melting point of a substance are the same. Cooling Curves: TEMPERATURE vs. TIME is graphed while a substance is being COOLED at a constant rate. MELTING, or “FUSION”: We can represent phase changes with particle diagrams. The following particle diagram represents melting. Melting is also known as fusion, so chemists refer to the amount of energy needed to make a substance melt as the “heat of fusion”. melting/fusion The added energy decreases the attractions between particles, causing them to be less orderly, but still attracted to one another. BOILING: We can represent phase changes with particle diagrams. The following particle diagram represents boiling. Boiling is a form of vaporization, so chemists refer to the amount of energy needed to make a substance boil as the “heat of vaporization”. vaporization In this case, the added energy completely overcomes the attractions between particles, causing them to become totally dis- orderly in their conduct, with no attractions to one another. Phase Changes are classified as ENDOTHERMIC or EXOTHERMIC. E NDOTHE RMIC: System absorbs energy E XOTHE RMIC: S ystem gives off heat energy Bolls Freeies SOLID Heat Energy Check your understanding: Determine the line segment(s) that represents the information below. a. Gas, only b. Liquid, only c. Solid, only d. Solid and Liquid, only e. Liquid and Gas, only f. Melting Point g. Boiling Point h. Kinetic energy is increasing i. Potential energy is increasing Practice: From this diagram identify the following: 1. The melting point temperature: 2. The boiling point temperature: 3. The line segment where heat is being added, causing a change in the temperature of the solid phase: 4. The segment where heat is being added, causing a change in the kinetic energy of the particles when they are in the liquid phase: 5. The segment where heat is being added, causing a change in the speed of the particles when they are in the gas phase: 6. The segments where added heat causes an increase in potential energy: &_ 7. The segment where heat is added, and might be called the “Heat of Fusion”: So… Let’s compare Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy one more time. (Answer the following blanks with KE/PE and circle either increasing or decreasing.) On the flat segments: And on the diagonal segments: is constant and is constant and is increasing / decreasing. is increasing / decreasing. Practice: 1. As ice melts, its temperature remains at 0°C until it has completely melted. Its potential energy: (1) ) decreases (2) increases (3) remains the same 2. Which change of phase represents fusion? (1) gas to liquid (2) gas to solid gas 3. Which change of phase represents sublimation? (1) H2O(g) → H2O(l) (2) H2O(l) → H2O(s) CO2(l) 4. Which change of phase is exothermic? (1) gas to liquid (2) solid to liquid gas (3) solid to liquid (3) CO2(s) → CO2(g) (3) solid to gas (4) liquid to (4) CO2(s) → (4) liquid to 5. The heat of fusion for ice is 333.6 joules per gram. Adding 333.6 joules of heat to one gram of ice at STP will cause the ice to (1) increase in temperature (3) change to liquid water at a higher temperature (2) ) decrease in temperature (4) change to liquid water at the same temperature 6. Which term can be used to describe the change of a substance from the solid phase to the liquid phase? (1) condensation (2) vaporization (3) evaporation (4) fusion 7. Which sample contains particles arranged in regular geometric pattern? (1) CO2(l) (2) CO2(s) (3) CO2(g) (4) CO2(aq) 8. The energy required to change 1 gram of a solid to a liquid at constant temperature is called its “heat of ” value. It is a (physical or chemical?) property. Base your answers to questions 9 and 10 on the diagram below which represents a substance being from a solid to a gas, the pressure remaining constant 9. The substance begins to boil at point (1) E (3) C (2) B (4) D 10. Between points B and C the substance exists in (1) the solid state, only (2) the liquid state, only (3) both the solid and liquid states (4) neither the solid nor the liquid state