Guided reading questions_answers - Troxel
advertisement
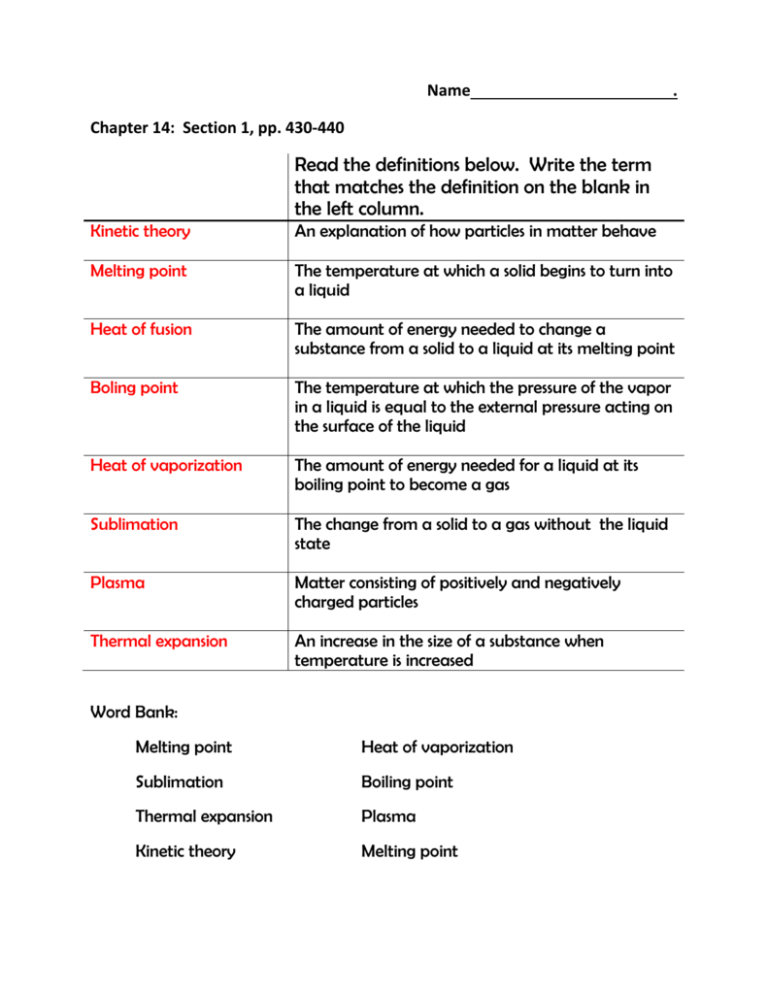
Name . Chapter 14: Section 1, pp. 430-440 Read the definitions below. Write the term that matches the definition on the blank in the left column. Kinetic theory An explanation of how particles in matter behave Melting point The temperature at which a solid begins to turn into a liquid Heat of fusion The amount of energy needed to change a substance from a solid to a liquid at its melting point Boling point The temperature at which the pressure of the vapor in a liquid is equal to the external pressure acting on the surface of the liquid Heat of vaporization The amount of energy needed for a liquid at its boiling point to become a gas Sublimation The change from a solid to a gas without the liquid state Plasma Matter consisting of positively and negatively charged particles Thermal expansion An increase in the size of a substance when temperature is increased Word Bank: Melting point Heat of vaporization Sublimation Boiling point Thermal expansion Plasma Kinetic theory Melting point Complete the outline as you read about the states of matter. I found this on page: p. 433 States of Matter A. Solid 1. Example ice 2. Particle kinetic energy unable to overcome their attractions to each other 3. Particle behavior closely packed together 4. Other fact(s) most have geometric arrangement, chemical and physical properties often due to geometric arrangement B. Liquid 1. Example water 2. Particle kinetic energy enough to partially overcome attractive force 3. Particle behavior can slide past each other 4. Other fact(s) liquids can flow and take the shape of their container C. Gas 1. Example water vapor 2. Particle kinetic energy enough to partially overcome attractive force 3. Particle behavior can spread far apart to fill their container 4. Other fact(s) do not have a fixed volume or shape D. Plasma 1. Example stars 2. Particle kinetic energy high collision forces strip electrons from atoms 3. Particle behavior positively and negatively charged particles 4. Other fact(s) overall charge is neutral, most common state of matter in the universe Sequence the kinetic energy, temperature, and density of most solids, liquids, and gases. Use 1 to represent the lowest amount and 3 to represent the highest. Constant Kinetic energy Temperature Density Solid 1 1 3 Section 2; pp. 441-446 Liquid 2 2 2 Gas 3 3 1 Section 3; pp. 447-451 Define: Temperature a measure of the average kinetic energy of all the particles in an object . Units of Measurement: SI unit - Kelvin: Zero on the Kelvin scale is the coldest possible temperature (absolute 0), roughly equal to -273˚C, Kelvin temperature can be found by adding 273 to the Celcius reading, so water freezes at 273 and boils at 373˚ Celcius: water freezes at 0˚ and boils at 100˚ Boyle’s law decreasing the volume of a container at a constant temperature increases the pressure PiVi = PfVf . Charles law the volume of a gas increases with increasing with increasing temperature at a constant pressure . Vi = Vf Ti = Tf A 4.0-L balloon at room temperature (20.0˚C) is placed in a refrigerator at 1.0 ˚C. What is the volume of the balloon after it cools in the refrigerator? Vi = Vf Ti = Vf 4.0 L = x ;x= 20.0˚C 1.0˚C