History Taking in Fe..
advertisement

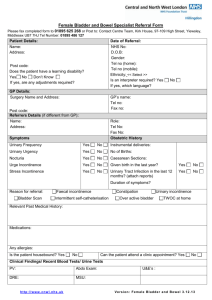
History Taking in Female Urinary Incontinence Female Urinary Incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine in the female. There are three types of urinary incontinence in women: Genuine stress incontinence - increase in abdominal pressure Urge incontinence - overwhelming desire to urinate Overflow incontinence - frequent urinating in small volumes True incontinence - no control over flow Epidemiology Incontinence is a very common problem in women. The prevalence of urinary incontinence in women differs depending on age: Young adult women - 20% Middle-aged women - 30% Elderly women - 40% Etiology Genuine Stress incontinence: Post-delivery Post-menopause Poor control of sphincter Urge incontinence: Detrusor instability Bladder infection Calculi Overflow incontinence: Hypotonic Bladder Bladder Outlet Obstruction Pelvic surgery True incontinence: Vesiculo-vaginal fistula Uretero-vaginal fistula Ectopic ureter Bladder exstrophy Presenting Complaint Urinary Incontinence History of Presenting Complaint 1. Onset - "When did it begin?" 2. Periodicity - "Is it there every time you go or is it intermittent?" 3. Duration - If episodic - "How long does each episode last?" 4. Severity - "How much urine?" 5. Aggravating factors 6. Relieving factors 7. Associated symptoms Urgency? Frequency? Nocturia? Hesitancy? Quality of flow? Menstrual History 1. Menarche and menopause 2. 1st day of last menstrual period 3. Length of bleeding (days) 4. Frequency 5. Regularity 6. Bleeding between periods 7. Bleeding after intercourse 8. Nature of periods Heavy? Clots? Flooding? Obstetric History 1. Number of pregnancies 2. Dates of deliveries 3. Induced or spontaneous labor? 4. Mode of delivery 5. Size and sex of the children 6. Complications Gynecological History 1. Gynecological symptoms 2. Gynecological diagnoses 3. Gynecological surgery 4. Abnormal smears Past Medical History 1. Current or past illnesses 2. Hospital admissions 3. Past surgeries Drug History 1. Prescribed medications 2. Non-prescribed medications/herbal remedies 3. Recreational drugs Family History 1. Medical conditions 2. Gynecological conditions 3. Malignancies Social History 1. Occupation 2. Support network 3. Smoking 4. Alcohol Examination Neurological examination Sacral reflexes Lower limb reflexes Assess cognitive awareness Abdominal Examination General Examination Pelvic examination Pelvic floor muscles Investigations Urinary Dipstick Uinalysis Urinarydynamics -- References Nitti V W. The Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence. Rev Urol. 2001;3 (S2-S6) O'Connor, J. Pathology 2nd ed. Mosby. Edinburgh. 2002. McCarthy, A & Hunter, B (2003) Master Medicine: Obstetrics and Gynaecology (2nd ed.) Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunder www.gpnotebook.co.uk