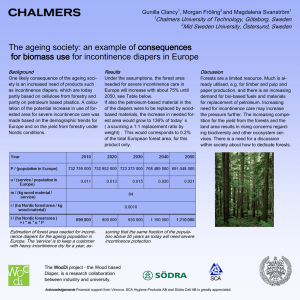
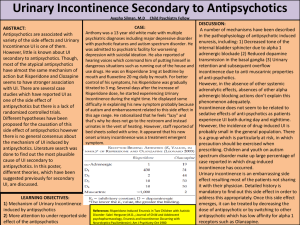
問題導向學習教案設計表(範例)
advertisement

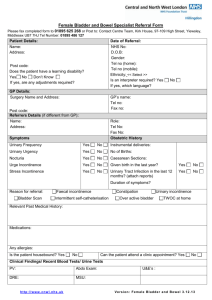
問題導向學習教案設計表(範例) 學習主題(Topic):Urinary Incontinence 課程目的(Curricular Goals) To understand the causes and treatment options for urinary incontinence in female patients 具體學習目標(Learning Objectives) 1. Identify the anatomy of the bladder, ureters, and urethra and describe their relationships to other pelvic organs 2. Describe the innervation of the bladder 3. Describe the role of collagen in the pathogenesis of incontinence 4. List and describe the anatomic, physiologic, and pathologic causes of incontinence 5. Describe the differences between frequency, urgency, dysuria, and urge and stress incontinence 6. Identify the age-specific causes of urinary incontinence 7. Take a sensitive history about incontinence 8. Recognize how incontinence affects the ability to perform activities of daily living 個案病史 Ms. Emily Johnson is a 38-year-old patient [6] of yours who has come for her yearly well-check appointment. Ms. Johnson is married and has two children, ages 14 and 10. Both pregnancies were normal, with vaginal deliveries. She is an elementary school teacher in a suburban school district. Despite trying to quit smoking on several occasions, she has not been successful and still smokes about 15 cigarettes a day. Upon review of her interval history, she indicates that she had been using a mini-pad because of urine dribbling [5]. Further inquiry indicates that she has stress and urge incontinence and that it has been increasing in the past year [5]. She says that she is quite embarrassed and is afraid that she will not have the time to go to the bathroom while teaching and will have an “accident”[8]. In discussion, she tells you that she keeps an extra set of clothing in her classroom [8]. Upon questioning, she informs you that she has had no episode of fecal incontinence [7]. Menstrual history: LMP two weeks ago, periods are regular approximately every 28-30 days, uneventful with a few clots. 理學檢查 [4] General: 160 cm, 75kg, BP 140/80, P 84, RR 16 HEENT: normal Neck: supple, no goiter Chest: clear breathing sound Breast: no mass palpable, no axillary adenopathy Heart: RHB, no murmur or gallop Abdomen: good bowel sound, soft, non-tender, no organomegaly Back: no scoliosis, nor costovertebral tenderness Pelvic: vagina: mucus discharge, urine leakage with cough cervix: no erosion uterus: antiverted, no mass palpable Rectal: external and internal hemorroid Extremities: no clubbing cyanosis or edema After you finish the exam, Ms. Johnson asks you about possible choices of birth control. She would like to consider what options are available to her and her husband because, as she tells you, “Using my diaphram is so messy, and I don't want to get pregnant.” You order the following laboratory studies, including blood glucose, due to Ms. Johnson's family history of type II diabetes. 實驗室檢查 [4] Urinalysis: within normal limits T-chol, LDL, HDL are within normal limits Homocysteine levels within normal limits Mammogram: normal Pap smear: normal Stool: no occult blood After you review the laboratory results, you contact Ms. Johnson. You assure her that all the tests were normal. You have a discussion with her about the need to stop smoking and arrange for her to be oriented about smoking cessation through your office's health education programs. You refer Ms. Johnson to an urologist specializing in pelvic floor disorders to further evaluate her urinary incontinence [1,2,3,4]. [ ]代表引導討論學習目標的地方