Blood Unit – Exam Review Guide
advertisement

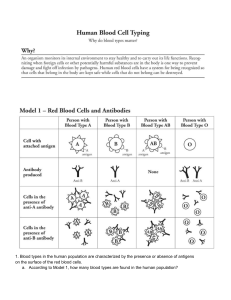
Blood Unit – Exam Review Guide - Know the bicarbonate buffer system as an example: (i.e. H2CO3 is a weak acid that can buffer a strong base and HCO2 is a weak base that can buffer a strong acid) - Know the basics of what buffers do (Weak acids buffer bases and become weak bases, Weak bases buffer acids and become weak acids; replaces a large change in pH with only a small change in pH). - Differentiate between plasma and formed elements and list substances found in each - Know what erythropoietin does - What is the relationship between megakaryocytes and platelets? - What is hemostasis? List the three main steps. - Define embolus and thrombus - What is the name for a substance that stimulates the immune system to release antibodies? - Know the definition of agglutination (i.e. the process whereby the binding of antibodies to antigens causes RBCs to clump). - Know the basics of blood typing: - blood types named by the antigens present - absence of antigen means the presence of an antibody - in a transfusion RABs attack DANs (recipient antibodies will attack donor antigens). - What blood type is the universal donor? What blood type is the universal recipient? - How do you indicate the presence or absence of the Rh- antigen when you write out the blood type? (ex: A- means that the blood cell has A antigens, B antibodies, and possibly Rh antibodies depending on whether or not the person has been exposed to Rh+ blood). - Define osmosis - Define diapedesis Not to concentrate on as much: - different types of WBCs - lots of details with hemostasis – know the 5 basic steps - blood doping