Lesson Plan: 2 - Delaware Access Project
advertisement

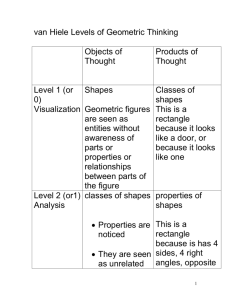
Lesson Plan: 2 Teacher(s): L. Creasy Subject: Math Unit: Graphing Grade band(s): K-2 Number of students: Setting: Lesson Objective(s): Objective 1: Given objects to graph, students will create a graph and answer questions about the data. Objective 2: Student will be able to identify and sort shapes according to their attributes. Connections to the GBEs: Standard(s): MD 2.10 Draw a picture graph and a bar graph (with single-unit scale) to represent a data set with up to four categories. Solve simple put-together, take-apart, and compare problems using information presented in a bar graph. Essence: Represent data on a graph E1: Given data, create a bar or picture graph and answer questions about the data. E2: Given data, create a bar or picture graph. E3: Given a picture or bar graph, answer literal questions about the data. G 2.1 Recognize and draw shapes having specified attributes, such as a given number of angles or a given number of equal faces. Identify triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, and cubes. Essence: Identify shapes E1: Name shapes. E2: Sort shapes. E3: Match shapes. CC K.4 Understand the relationship between numbers and quantities; connect counting to cardinality. Essence: One-to-one correspondence and concept of one more E1: Using one-to-one correspondence, count a given number of objects and identify the next number within the range of 1-20. E2: Given a number of objects, identify the number that corresponds to that quantity within the range of 1-20. E3: Count with one-to-one correspondence within the range of 1-20. CC K.5 Count to answer “how many?” questions about as many as 20 things arranged in a line, a rectangular array, or a circle, or as many as 10 things in a scattered configuration; given a number from 1-20, count out that many objects. Essence: Count to answer “how many?” E1: Given a specified number from 1-10, count the correct number of objects. Lesson Plan: 2 E2: Given a rectangular array or line containing up to 10 objects, count the total number of objects. E3: Given a line of up to five objects, count the total number of objects. CC K.6 Identify whether the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than, or equal to the number of objects in another group, e.g., by using matching and counting strategies. Essence: Compare groups of objects E1: Given two groups of objects, identify which group is greater (exclude equal sets). E2: Given two groups of objects, identify whether the groups are equal to each other. E3: Given two groups of objects arranged in a line side by side, identify whether the groups are equal to each other. Moderate support Most support Least support Given data, students will create a graph and answer questions about the data. Given data, students will create Given a graph, students will be a graph. able to answer literal questions about the data. Given a shape, student will name/identify the shape and 1 characteristic. Given 4 shapes, student will sort according to number of sides. Student will be able to match shapes when given a model. Using 1:1 correspondence, students will count a given number of objects and identify the next number within the range of 1-20. Given a number of objects, students will identify the number that corresponds to that quantity within the range of 1-20. Count with 1:1 correspondence within the range of 1-20. Given a specified number on a graph from 1-10, students will count the correct number of objects in each bracket. When looking at the objects in a graph bracket or line containing up to 10 objects, student will count the total number of objects. Given a line of up to five objects, count the total number of objects. Given two groups of objects, Given two groups of objects, identify which group is most identify whether the groups and least. are equal to each other. Materials: Data sheets Reinforcers Geometry is Everywhere Smart Board Doc Given two groups of objects arranged in a line side by side, identify whether the groups are equal to each other or not. Lesson Plan: 2 Painters tape Shape headings Classroom objects of different shapes (triangular, circular, square, rectangular) Activities: 1. Teacher facilitation: Provide students with characteristics of shapes (circle, square, triangle and rectangle). Use the Geometry is Everywhere Smart Board Doc to highlight the characteristics of each. 2. Student application 1: Introduce objects. Students will work together to sort accordingly through objects to determine what shape they are most like. Use painters tape to create a graph on the floor. Use headings provided in the kit to help create the graph. Example of floor graph: 3. Teacher Facilitation: share/report results and graphing exercise. 4. Questioning: Ask students least/less, most/more and same questions based on graphed results. Questioning Examples: 1. Were most shapes round or did they have four sides? 2. How many shapes had three sides? 3. Were there more shapes with 3 sides then round? 4. Which shape had the least number of objects? Warm-up: Tell students that all things found in the classroom and outside resemble shapes. Show them a few examples of items that are most like a circle, square, rectangle and triangle. For example: a cone for a triangle, a box of Kleenex for a rectangle, a Frisbee for a circle and a book for a square. Key Vocabulary: least/less most/more Same/equal all together “how many” Lesson Plan: 2 Barriers: Non-verbal communication Print Universal Design for Learning (UDL) brainstorm: Representation How will instructional content and materials be presented to the students (the “what” of learning)? Materials will be presented visually and verbally. Actions/ Expression How are the students able to interact with the materials and demonstrate knowledge (the “how” of learning)? Verbally, with eye gaze, pointing, with communication device, hands-on Engagement What interests and engages students in the learning process (the “why” of learning)? Students are learning in multiple modes which in return help keep them interested. Teaching Strategies: Modeling Interactive learning Graduated guidance Hands-on Think aloud Demonstration Assessments: Response mode: Completion of a graph Verbal Participation in “What Shape Am I” PowerPoint Touch Eye gaze Possible accommodations to use with this lesson: Picture representation Tangible items/tactile Closing Activity: Teacher will discuss results from graph created from shapes and will review vocabulary words. Students will share 1 thing that they learned from the lesson.