Course Syllabus
advertisement

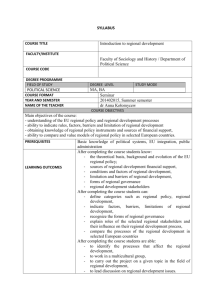
Ilia State University Faculty__[Indicate the name of the Faculty]_________ Level_[Indicate which level is this course intended for – Bachelor’s, Master’s or PhD]_____________________ Note: A syllabus must be composed in Sylfaen font Course Syllabus 1. 2. 3. COURSE TITLE COURSE DURATION ECTS CREDITS [The title of the course should reflect the content of the course.] [A syllabus should be submitted for each one-semester course. A student will be assigned a credit after completion of each one-semester course.] [Indicate the number of ECTS credits allocated to the course. One credit corresponds to 25 hours of workload. It includes not only contact hours (i.e. hours spent by students on activities guided by teaching staff) but also embraces time spent on independent work, preparation for assessment and the time necessary for the assessment. In case of 6 credit course the number of hours (contact hours plus time spent on independent work and assessment) will be 150. 4. DISTRIBUTION OF HOURS (video-lectures, lectures, seminars, lab-work, practical work, mid-term assessments, final exam, time spent on independent work, …) The courses on Bachelor’s level can be allocated 3-6 credits, on Master’s and PhD level 6-12 credits. ] [One semester consists of 15 weeks. Typically there can be 2-3 hour class meeting/sessions per week. Class meetings can have different format, they can be videolectures, lectures in the class, seminars, lab-work or other. It should be clearly stated how many hours are spent on each learning activity. Ex: Lecture -15 hr Video- lecture – 11 hr Seminars – 13hr Mid-term Exam – 4hr 1 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. INSTRUCTOR PREREQUISITES INSTRUCTION METHODS AIMS OF THE COURSE MAJOR TOPICS COURSE OBJECTIVES: LEARNING OUTCOMES AND COMPETENCES (GENERAL AND SUBJECTSPECIFIC) Final Exam – 2 hr Independent work – 105 hr] [Indicate the name, qualification and job title of the instructor, contact information and the office hours.] [List previous courses or knowledge that students should have in order to be successful in this Course. If there is no prerequisite, please state “Not applicable”.] [Specify each method of instruction applied within the course for each lesson e.g. Lecture, video–lecture, casestudy, seminars, tutorials, group discussions, brainstorming, etc.] [Clearly state the aims of the course. Aims are broad statements identifying the general educational outcomes you want a graduate of your course to be able to display. The aims and objectives should relate to level descriptors in the Higher Education Qualifications Framework http://new.eqe.ge/uploads/3_EN.pdf] [List the major topics; give the content of the course.] [Identify the most important educational outcomes a graduate of this course would be able to display. List all expected learning outcomes, define the scope of knowledge, skills and values to be attained by the completion of this course. Ex: By the completion of this course, students should be able to demonstrate general /transferable skills: Gather, integrate, synthesize, and analyze written and oral information in a critical manner; Use information objectively for solving problems and arriving at alternative solutions; Have communication skills; Write a logical and coherent argument of their own. Subject-specific outcomes/competences: Ex: Advanced knowledge of the field of study, including critical analysis of theories and principles; understanding of complex matters of the field of study. Each outcome should be formulated according to the 2 descriptor of relevant cycle of higher education. (see: The Higher Education Qualifications Framework http://new.eqe.ge/uploads/3_EN.pdf ) The learning outcomes should be expressed in measurable terms – that is, in terms of some action that students can perform and that you can evaluate. Examples of good action-oriented verbs include: describe, explain, calculate, write, evaluate, analyze, develop, create, outline, display, report, interpret, organize, explain and so on. 11. EVALUATION AND GRADING Note that each of these should be paired to an activity students can carry out on an exam, in an exercise, or in a project. They lead to measurable activities to which a grade can be assigned.] [State the grading system and the evaluation criteria according which the student will be assessed. This is the grading scale excepted on the National level: (A) 91-100 Excellent (B) 81-90 Very Good (C) 71-80 Good (D) 61-70 Satisfactory (E) 51-60 Sufficient (FX) 41-50 Unsatisfactory - meaning a student needs more effort to pass an examination and is given an extra chance to pass an additional examination through independent work. (F) Failure - 40 and less of the maximum of grades, meaning the student’s effort is not enough and he has to learn the subject anew. To earn a credit a student must accumulate the range of 51 -100 points. List the components of assessment you plan to use to evaluate your students’ performance along with the respective weight and percentage of the total grade corresponding to each component. Generally, we prefer to see not less than three different kinds of assessment components. You can use the categories listed in the example or specify your own 3 ones. Here are several examples: Tests Colloquia Project Presentation Comprehensive essay Weekly writing assignments Homework problem sets Final Exam Please note, that according to the University policy no grade can be assigned to the “attendance” component. Final assessment component cannot be assigned more than 30 points. Ex. Test – 25 points Colloquia – 25 points Project presentation – 20 points Final exam – 30 points. 12. TEXTS AND ADDITIONAL RESOURCES 13. COURSE SCHEDULE Give the assessment criteria and assessment rubrics for each component. [List any textbooks that will be used for the course (specify the author, title, date, publisher, and ISBN number) along with online resources such as websites, articles, etc.] [Give a weekly course outline specifying reading assignments, topics to be covered, major projects and exams.] Identify the competences developed by this course (Mark X in corresponding cell) Knowledge and Applying Making Communications Learning skills Values understanding knowledge judgments skills [Does the course [Will the [Does the course [Does the course [Does the course [Does the develop the graduate be able develop the skills develop the develop the course develop theoretical to apply the for making communications ability to define the values knowledge] gained judgments ] skills] the future characteristic learning needs] for professional theoretical knowledge in activity] practice] 4