heat flow
advertisement

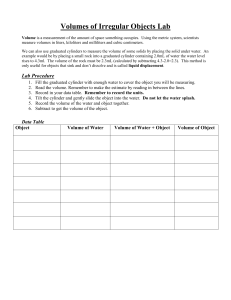
3.4A Creating Steady-State Heat Flow Conditions Name: Observations and Data Collection 1. Complete the following Data Table Data Table 1 Power Supply Voltage: VS = Power Supply Current: IS Thermocouple Reading Top of Cylinder Time (min) T Change T BOTTOM (ºC) V A Thermocouple Reading Bottom of Cylinder BOTTOM T TOP (ºC) Temperature Difference Change TTOP 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 2. Complete the following Data Table Data Table 2 Top Temperature T TOP (ºC) Bottom Temperature T BOTTOM (ºC) Temperature Difference ∆T (BOTTOM – TOP) (ºC) Input Heat-Flow Rate Q (W) Input Heat-Flow Rate Q (cal/sec) Section 3.4A Questions and Interpretations 1. When the temperature reaches the steady-state condition, what is the relationship between the heat flow into the cylinder and the heat flow out of the cylinder? 2. Does the heat conduction through the walls of the thermal container affect the results of your experiment? How? 3. In your home, the thermostat cycles the furnace on and off to keep the temperature at a preset value. How does the heat-flow rate from the furnace to your home relate to the heat-flow rate from your home to the outside of the building?