Ecological Relationships Due: Species Interaction: Section 20.1
advertisement

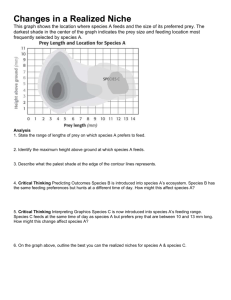
Ecological Relationships Due: __________________ Species Interaction: Section 20.1 (pages 399 – 404) KEY POINTS: Prey and predator adaptations Identify specific interspecies competition Compare parasitism, mutualism and commensalism Answers Bolded! Predation: an individual of one species (predator) eats all or some parts of another species (prey) How is predation a powerful force in a community? Predation influences size of populations and effects where each species lives. Why have predators developed adaptations over time? They must be able to adapt to find, capture, and consume prey What are 2 adaptations that have been selected for? Sharp teeth, speed, camoflauge Why would a prey also develop adaptations? Need to escape, avoid, or ward off predators What are 2 ways animal prey have adapted? Deceptive markings and chemical defenses, mimcry What are 2 ways plant prey have adapted? Physical defenses and chemical defenses Interspecific Competition: two or more species use the same limited resource Cite an animal & plant example: lions and hyenas eat zebras; plants need soil and sunlight Competitive Exclusion: when one species is eliminated from community because of competition for limited resource How does competitive exclusion tie back into species occupying a specific niche? Competition between species dictates the specific niche occupied by those species How is the fundamental niche different than the realized niche? Fundamental niche is the range of conditions and resources a species can tolerate and use; Realized niche is the part of the fundamental niche that is actually used by the species What is character displacement? Describe what has occurred on the Galapagos Islands. Differences between species due to competition. On the Galpagos Islands, finches in close proximity have the largest difference in beak size. What is resource partitioning? Describe how multiple birds can live in the same tree. Resource partitioning is when species coexist with each other to use a different part of a limited resource. Warblers can live in the same tree because they forage in different parts of the tree. Symbiosis: close, long-term relationships between 2 organisms Parasitism: relationships where one individual is harmed and the other is benefitted How has natural selection acted on parasites? Has led to more efficient ways to exploit the host Explain ectoparasites versus endoparasites (give examples of parasite and host) ecotoparasites remain outside the host; endoparasites remain inside the host Mutualism: relationship in which both organisms benefit What is one of the most important mutualistic relationships? pollination Commensalism : one organism benefits, but the other is neither helped nor harmed Cite an example from outside your textbook. Egret and cattle 1. In the relationship between cattle egrets and Cape buffaloes, if the egrets regularly removed ticks from the buffaloes, would this relationship still be considered commensal? No, because both would now benefit 2. How does predations on plants differ from predation on animals, in terms of the usual effect on the prey? The adaptations are different amongst plant and animal prey because plants cannot move away from their predators. 3. Species A and B have a very similar niche. Species A recently arrived in a location where species B previously lived and carried a disease that killed all members of species B. Is this situation an example of competitive exclusion? Explain your answer. No because they were not competing over a limited resource