File
advertisement

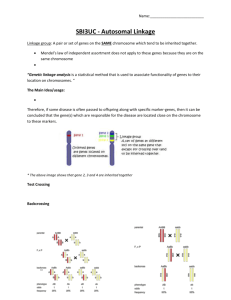
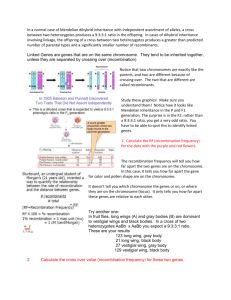
Name:__________________________ SBI3UC - Autosomal Linkage Linkage group: A pair or set of genes on the SAME chromosome which tend to be inherited together. These genes tend to show up together in the same combinations in the offspring. Mendel’s law of independent assortment does not apply to these genes because they are on the same chromosome “Genetic linkage analysis is a statistical method that is used to associate functionality of genes to their location on chromosomes. “ The Main Idea/usage: Neighboring genes on the chromosome have a tendency to stick together when passed on to offspring. Therefore, if some disease is often passed to offspring along with specific marker-genes, then it can be concluded that the gene(s) which are responsible for the disease are located close on the chromosome to these markers. * The above image shows that gene 2, 3 and 4 are inherited together Test Crossing is a cross of an unknown dominant parent with a homozygous recessive individual to help determine the genotype of the unknown parent depending on the phenotype of the offspring. Backcrossing is a crossing of a hybrid with one of its parents or an individual genetically similar to its parent, in order to achieve offspring with a genetic identity which is closer to that of the parent. F2 Name:__________________________ Making the gametes Previously we have written our genotypes as for example- TtLl. This form does not represent which alleles are linked on the same chromosome. When we represent gene linkage we write the alleles together that are found on the same chromosome. FL 𝑓𝑙 Here FL are linked and fl are linked on the same chromosome Practice: Write the gametes for the following examples; a) 𝑎𝑏 𝐴𝑏 𝑅𝑤 𝑟𝑊 c) Rw, rW GY b) 𝐺𝑌 𝐺𝑌 Stop ab, Ab Example with Linkage Ex. A flower that is homozygous for purple flowers and long flower was crossed with a pure breeding red and round flower. These traits are found on the same chromosome. Name:__________________________ Now let’s apply this knowledge to a practice problem; Long ears and blonde fur in the Rabid rabbit are dominant characteristics found on chromosome 5. The corresponding recessive characteristics are small ears and black body. A rabbit homozygous for long and blonde is crossed with a homozygous recessive rabbit. Deduce the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring of a test cross on the F1 rabbits. 1. The fact that the traits are both on chromosome 5, tell us these traits are linked 2. Designate variables; a. Let L=long, l=small; B=blonde, b=black 3. Write the parent phenotypes, genotypes and gametes; Parent phenotypes Long blonde Small black Parent genotype 𝐿𝐵 𝐿𝐵 𝑙𝑏 𝑙𝑏 Gametes LB lb 4. Write the F1 phenotype and genotype; 𝐿𝐵 𝑙𝑏 5. Test cross Parent phenotypes Long blonde Small black Parent genotype 𝐿𝐵 𝑙𝑏 𝑙𝑏 𝑙𝑏 Gametes LB, lb lb F1 genotypes and phenotypes gametes lb LB lb 𝐿𝐵 𝑙𝑏 𝑙𝑏 𝑙𝑏 Long, blonde Small, black Both of these do not have recombinants as they are the same as the parental type. The fact that we get a 1: 1 ratio indicates that there is a linkage. If they were not linked we’d get a 1:1:1:1 in the test cross. Name:__________________________ Autosomal Linkage with Crossing over Sometimes in meiosis, homologous chromosomes exchange parts in a process called crossing-over, or recombination. Note: recombinants are any combination of alleles that are not the same as the parental combinations Recombination, which occurs in prophase I of meiosis, can split the two alleles inherited from a parent, giving recombinant types. These tend to be in smaller proportions than the parental, linked types. Crossing over is rare and therefore, recombinants tend to be fewer in number than parental. The percentage of offspring showing the recombinant types can give an estimate of how close the two genes are to each other on the chromosome. The closer the genes are, the fewer recombinant types should occur. Genotypes for linked genes can be shown as: 𝐴 𝐵 𝑎 𝑏 This is an example of a parental combination This genotype would give the same phenotype as: BUT this is an example of a recombinant 𝐴 𝑏 𝑎 𝐵 Name:__________________________ Practice: Write the parental gametes and the recombinant gametes for the following examples; 𝑎𝐵 𝑅𝑤 a) 𝐴𝑏 𝑔𝑌 b)𝑟𝑊 Parental a) aB, Ab b) Rw, rW c) gY, Gy c) 𝐺𝑦 Recombinant ab, AB RW, rw gy, GY It is vital to remember that the dominant genes don’t always necessarily have to be linked!!!!!!!!!!!! Example of Linked genes: From the work of William Bateson, who studied the sweet pea. He was looking at 2 genes; flower colour (P-purple and p-red) and the shape of the pollen grain (L-long and l- round). He crossed PPLL and ppll and then self-crossed (back crossed) the resulting F1 generation to create PpLl in the F2 generation. According to Mendelian genetics the expected ratios would be 9:3:3:1. Instead he found an increased number of the parental combinations PPLL and ppll. Name:__________________________ Phenotype and Genotype Purple, long (PpLl) Purple, round (Ppll) Red, Long (ppLl) Red, round (ppll) Observed 284 21 21 55 Expected from 9:3:3:1 216 72 72 24 Name:__________________________ Recombinants are recognized by: 1. Unpredicted combinations of characterisitics. (Red Long; Purple short) 2. Low frequency of new combinations of phenotype. 3. Statistical difference from ratios expected from either dihybrid and unlinked (9:3:3:1) or monohybrid with no linkage (3:1) Example: In wild blueberries, the genes for sweetness and size are linked. The gene for sweetness is dominant to sourness and small berries are dominant to large berries. A heterozygous small sweet berry plant was test crossed and the results wereSmall, sweet 215 Large, sour 212 Small, sour 16 Large, sweet 20 Large pair of number- the parental combinations small pair of number- the recombinants 1. Let S=small , s=large; W=sweet, w=sour 2. We are told that the first parent is heterozygous and that the genes are linked. Since we have 4 phenotypes crossing over must have occurred. 3. Determine the linkage pattern via the F1 offspring. How do we know which are linked???? 𝑆𝑊 𝑆𝑤 Is it 𝑠𝑤 or 𝑠𝑊 ?? Very simply by looking at the numbers. The 215 and the 212 are the parental combinations of alleles. This means that SW are linked on one chromosome and sw are linked on the other. 4. Prove it with a Punnett square. Parent phenotypes Small, sweet Large, sour gametes sw Parent genotype 𝑆𝑊 𝑠𝑤 𝑠𝑤 𝑠𝑤 Gametes SW, sw sw SW sw Sw sW 𝑆𝑊 𝑠𝑤 𝑠𝑤 𝑠𝑤 𝑆𝑤 𝑠𝑤 𝑠𝑊 𝑠𝑤 Small, sweet Large, Sour Small, sour Large, sweet Parental Recombinant Name:__________________________ 1. Genes P, Q, R and S are located on the same chromosome. The cross over values between them are: P-Q 20% P-R 30% P-S 15% Q-R 15% Q-S 30% R-S 40% What is the sequence of genes in the gene map of the chromosome? A. S, P, Q, R B. R, P, Q, S C. P, R, S, Q D. Q, S, R, P Stop Answer is A 2. A cross is performed between two organisms with the genotypes AaBb and aabb. What genotypes in the offspring are the result of recombination? A. Aabb, AaBb B. AaBb, aabb C. aabb, Aabb D. Aabb, aaBb Stop A normal linkage cross would result in AB//ab and ab//ab (AaBb and aabb) Recombinants are then Ab//ab and aB//ab (Aabb and aaBb) Therefore, the answer is D