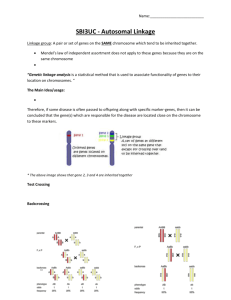
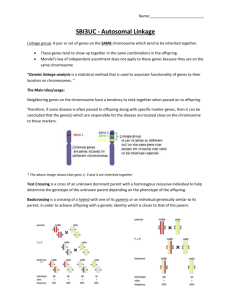
In a normal case of Mendelian dihybrid inheritance with
advertisement

In a normal case of Mendelian dihybrid inheritance with independent assortment of alleles, a cross between two heterozygotes produces a 9:3:3:1 ratio in the offspring. In cases of dihybrid inheritance involving linkage, the offspring of a cross between two heterozygotes produces a greater than predicted number of parental types and a significantly smaller number of recombinants. Linked Genes are genes that are on the same chromosome. They tend to be inherited together, unless they are separated by crossing over (recombination) Notice that two chromosomes are exactly like the parents, and two are different because of crossing over. The two that are different are called recombinants. Study these graphics! Make sure you understand them! Notice how it looks like Mendelian inheritance in the P and F1 generation. The surprise is in the F2; rather than a 9:3:3:1 ratio, you get a very odd ratio. You have to be able to spot this to identify linked genes. 1. Calculate the RF (recombination frequency) for the data with the purple and red flowers. The recombination frequency will tell you how far apart the two genes are on the chromosome. In this case, it tells you how far apart the gene for color and pollen shape are on the chromosome. It doesn’t tell you which chromosome the genes or on, or where they are on the chromosome (locus). It only tells you how far apart these genes are relative to each other. Try another oneIn fruit flies, long wings (A) and gray bodies (B) are dominant to vestigial wings and black bodies. In a cross of two heterozygotes AaBb x AaBb you expect a 9:3:3:1 ratio. These are your results 123 long wing, gray body 21 long wing, black body 27 vestigial wing, gray body 129 vestigial wing, black body 2. Calculate the cross over value (recombination frequency) for these two genes. 3. Determine the sequence of genes along a chromosome based on the following recombination frequencies. I have done the first one for you. It helps to plot them on a chromosome, but your answer will just be the order of the genes on the chromosome (see #5 and 6). • A-B = 8% Start with the genes that are the furthest apart. • A-C = 28% Use them to map the rest. • A-D= 25% Each % = 1 map unit • B-C = 20% When you have them correct, you will know it. • B-D = 33% 33 B-----------------------------D 4. There are 4 genes on a single chromosome: A, B, C and D. They exhibit the following crossing over frequencies: • A-B = 35% • B-C = 10% • C-D= 15% • C-A =25% • D-B=25% Determine the order of the genes on the chromosome. 5. 6.