BIO 191 Supplemental Instruction
Chapter 15
Sex Linked Inheritance
The two sex chromosomes in the human body are defined X and Y. Traits carried on the X
chromosome are said to be sex-linked. Because males have an XY genotype and females have
an XX genotype, inheritance is unlike that defined by Mendel because males only have one allele
while females have two.
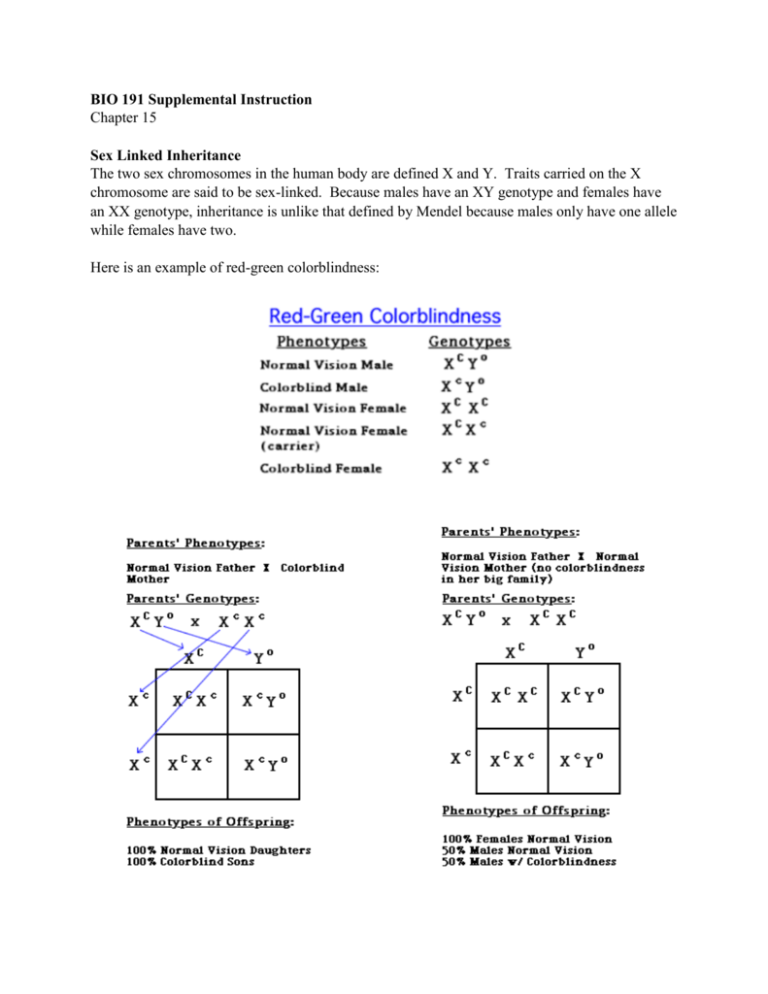
Here is an example of red-green colorblindness:
Different systems of Sex Determination
XY Males/XX Females- Humans
ZZ Males/ZW Females- Birds
XO Males/XX Females- Grasshoppers, crickets, cockroaches, insects
Haplodiploid- Females are diploid and males are haploid
Nondisjunction
Error which occurs when chromosomes fail to separate as they should, which causes a gamete to
either receive two of the same chromosome or lack a certain chromosome.
Aneuploidy- any abnormal number of chromosomes (Associated diseases- Downs syndrome,
turner syndrome)
Crossover and Linkage Mapping
Recombination is the results of crossover, in which two homologs swap certain traits to make a
new combination of genes. Genes close together on a chromosome do not have as much
recombination as genes far apart. Lastly, the frequency of recombination can be measured in
map units, defined as the distance within which recombination occurs 1% of the time. The rate
of crossover gibes no information of the physical distance of the genes, only the order of linked
genes on the chromosome.
Linkage map example: Genes A, B, and D are linked. The crossover frequencies for B and D is
5%, A and B is 30%, and D and A is 25%. Construct a linkage map.
Answer: BDA or ADB