name: Hiep Ton
advertisement

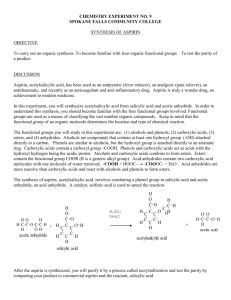
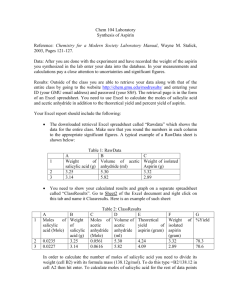
NAME: HIEP TON February 22, 2015 Exp 8 ASPIRIN SYSTHESIS I. INTRODUCTION: The purpose of this lab is to find the purity of the synthesized aspirin or a commercial aspirin tablet. Aspirin has been using as pain-killer (analgesic) and fever-reducing drug (antipyretic). Acetylsalicylic acid remains intact in the acidic stomach. Aspirin’s molar mass is 180.2 g/mol. Salicylic acid’s molar mass is 138.1 g/mol. Acetic anhydride’s molar mas is 102.1 g/mol. Aspirin is a weak monoprotic acid. From the melting point, the purity of an aspirin can be determined. Melting point is essentially independent of atmospheric pressure. The degree of lowering the melting point depends on the nature and the concentration of the impurities. Purity can be determined by acid-base titration. mole acetylsalicylic acid × % 𝑝𝑢𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑦 = II. 180.2 g = gram acetysalicylic acidic mole gram acetysalicylic acidc × 100 gram aspirin sample PROCEDURE: In the first lab day, Aspirin was prepared in the fume hood. In 125mL Erlenmeyer flask, two grams of salicylic acid was measured. 4-5mL acetic anhydride and salicylic acid were swirled. After adding 5 drops of H2SO4, the Erlenmeyer flash was put in a 400mL boiling water bath beaker. After 15 minutes, the flash was removed. The flask was added 10mL of deionized ice water, swirled, and placed in the ice bath until no crystal form. The filter paper was sealed in Buchner funnel by 0.5mL of water. The mixture in the flash was decanted onto the filter paper. The Page 1 of 5 NAME: HIEP TON February 22, 2015 amounts of added water were recorded each time added. The solid on the filter was kept for the second lab day. In the second lab day, After the solid was dry out, the crystal was transferred to a 100mL beaker. 20mL of ethanol was added to dissolve the crystal. The water was kept adding into the beaker, which was placed on the 60oC hotplate, until the mixture got absolute cloudy. The beaker was placed in the ice bath until the crystal of acetylsalicylic acid from. The filter paper was sealed in Buchner funnel by 0.5mL of water. The mixture in the flash was decanted onto the filter paper. The amounts of added water were recorded each time added. The solid on the filter was kept for the third lab day. In the third lab day, After the solid was dry out, the crystal was put in the one-open-end capillary tube for 1cm depth. The capillary was placed in the mel-temp apparatus. The temperature of the solid when started to melt and when was totally melted were recorded. Mel-temp apparatus was returned to the stockroom and chemical was disposed according to the instruction from the instructor. III. DATA & RESULT: Sample mass Volume of added ethanol Volume of added acetic anhydride Crystal mass Time of water added 1st 2.0037 gram 9.500 mL 4.300 mL 0.9980 gram Volume of water added (mL) 10 Page 2 of 5 NAME: HIEP TON February 22, 2015 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th Total Temperaturewet Temperaturesolid- 15 30 10 10 10 15 100 Trial 1 122.0oC 129.3oC Trial 2 127.0oC 132.7oC Trial 3 119.8oC 132.3oC gone IV. RESULT & DISCUSSION: The percent purity of aspirin as calculated below was 47.73%. The possible error that made the percent purity was not close to 100% might be the amount of water added during the filtering times. The amount of water might be added not enough. V. CONCLUSION: Through filtering the salicylic acid, acetic anhydride mixture and gaining the mass of the aspirin crystal, the purity of the aspirin was determined. VI. CACULATION: Page 3 of 5 NAME: HIEP TON February 22, 2015 Actual Value: gram salicylic acid sample × 2.0037g × 1 mol = mole salicylic acid sample 138.1g 1 mole = 0.01451 mol salicylic acid sample 138.1g mol salicylic acid sample × 0.01451 mol × 180.2 g = gram acetysalicylic acidic mole 180.2 g = 2.615 g acetysalicylic acidic mol 𝐏𝐮𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐞𝐝 𝐰𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐫 Experimental Value: 0.9980 gram Purity: % 𝑝𝑢𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑦 = Experimental Value × 100 Actual Value % 𝑝𝑢𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 0.9980 g × 100 = 38.17 % 2.615 g 𝐏𝐮𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐞𝐝 𝐰𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐫 Experimental Value: 𝐴𝑑𝑑𝑒𝑑 𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 1 100 1 ( × ) + 𝐶𝑟𝑦𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑀𝑎𝑠𝑠 = ( × ) + 0.9980 = 1.248 100 4 100 4 Purity: % 𝑝𝑢𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑦 = Experimental Value × 100 Actual Value Page 4 of 5 NAME: HIEP TON % 𝑝𝑢𝑟𝑖𝑡𝑦 = February 22, 2015 1.248 g × 100 = 47.73 % 2.615 g Page 5 of 5