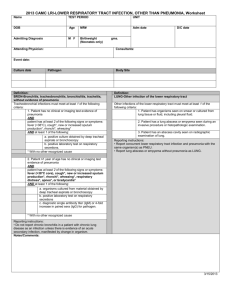
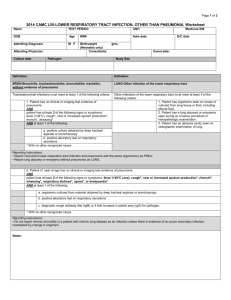
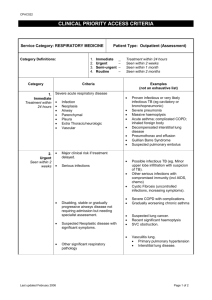
National Commission for Academic Accreditation and
advertisement

COLLEGE OF MEDICINE RESP-312 1435-1436 [2014-2015] Course specifications 1 National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment Course Specifications Institution: ALMMAREFA COLLEGE College/Department: DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE A. Course Identification and General Information 1. Course title and code: The Respiratory Block – RESP-312 2. Credit hours: 7 Credit Hours 3. Program(s) in which the course is offered: MBBS (If general elective available in many programs indicate this rather than list programs) 4. Name of faculty member responsible for the course: Dr. Abdelaty Shawky (Boys Section) Dr. Haneeen Mahmoud (Girls Section) 5. Level/year at which this course is offered: Year 3 – Level 5 6. Pre-requisites for this course (if any): ANAT214 – PHSL215 – PATH216 BLOCKS 7. Co-requisites for this course (if any): 8. Location if not on main campus: 2 B. Objectives 1. Summary of the main learning outcomes for students enrolled in the course Recall the anatomical structure and histological features of the upper respiratory tract Discuss the developmental formation of the upper respiratory tract & related congenital anomalies List the types of pathogenic bacteria that cause upper respiratory tract infection. Recognize medications used to control upper respiratory tract diseases symptoms. Recall the anatomical the structure, functional anatomy and histological features of the trachea, bronchial tree, pleura, lungs, respiratory wall, chest muscles & diaphragm. Discuss the developmental formation of the trachea, bronchial tree & lungs & related congenital anomalies Explain the main physiological & biochemical aspects of breathing & respiration with focusing on mechanics & control of breathing in addition to concepts of lung volume, capacities & compliance. Recognize the various infectious microbes & viruses that can affect the respiratory system with their impact on pathological features with special focus on pneumonia & tuberculosis. Discuss the main pathological aspects concerning different common respiratory diseases including chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPDs) & lung tumors. Recall medications used for COPDs Discuss the mechanisms of the cellular respiratory chain & its role in generating cellular energy. Verify the concepts of pulmonary ventilation & gas exchange & transport system Apply the physiological & biochemical mechanisms concerning acid-base balance & respiratory type of its disorders. 2. Briefly describe any plans for developing and improving the course that are being implemented. (e.g. increased use of IT or web based reference material, changes in content as a result of new research in the field): Continuous updating of the course contents. Improving the integration of disciplines of the course. Encourage student centeredness strategies for learning. 3 C. Course Description: (Note: General description in the form to be used for the Bulletin or Handbook should be attached) 1- Topics to be Covered List of Topics 1- Anatomy of Nose and Pharynx 2- Anatomy of Larynx 3- Practical Anatomy of chest wall and Respiratory Muscles 4- Anatomy of the Diaphragm 5- Anatomy of Trachea, Bronchial Tree and Pleura 6- Anatomy of the lung 7- Histology of the Respiratory System 8- Practical Anatomy of Lower Respiratory Tract (Lab.1) 9- Practical Anatomy of Lower Respiratory Tract (Lab.2) 10- Development of respiratory System 11- Practical Histology of Respiratory System (Lab.) 11- Function of the Respiratory System 12- Mechanics of Breathing 13- Physiology Lab. 14- Lung Volume and Capacity 15- Lung Compliance 16- Pulmonary Ventilation and Gas Exchange 17- Gas Transport 18- Control of Breathing 19- Factors Affecting Respiration 20- Respiratory Chain 21- Oxygen Binding Proteins 22- Acid-base Balance-1 23- Acid-base Balance-2 24- Upper Respiratory Tract Infection 25- Tuberculosis 26- Organisms causing-pnemonia-1 27- Organisms causing-pnemonia-2 28- Viral Infection of the Respiratory Tract 4 No. of Weeks Contact hours 1 1 1 2 2 2 4 1 6 3 6 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 5 3 4 5 5 6 6 2 3 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 5 2 5 3 4 6 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 29- Pathology of Pulmonary Tuberculosis 30- Pathology of Bronchial asthma 31- Pathology of COPD 32- Pathology of bronchiectasis 33- Pathology of pneumonia 34- Tumors of Lungs 35- Pathology Lab 36- Drugs Used for Treatment of Cough 37- Pharmacology of Drugs used in Bronchial Asthma 7 4 5 3 3 7 7 4 7 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 2- Course components (total contact hours per semester): Lectures: 34 Hours Tutorial: 3 Hours Laboratory: 10 Hours Practical/Field work/Internship Other: 3- Additional private study/learning hours expected for students per week. (This should be an average: for the semester not a specific requirement in each week) Student Directed Learning: 1 Hour / Week 4- Development of Learning Outcomes in Domains of Learning For each of the domains of learning shown below indicate: A brief summary of the knowledge or skill the course is intended to develop; A description of the teaching strategies to be used in the course to develop that knowledge or skill; The methods of student assessment to be used in the course to evaluate learning outcomes in the domain concerned. a. Knowledge: (i) Description of the knowledge to be acquired: Discuss the anatomical structure of nose. Define paranasal sinuses. Describe the anatomical structure of pharynx. List the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the pharynx with their nerve supply and actions. 5 Describe anatomical structure of larynx. List the cartilages of the larynx. Define inlet of the larynx. List the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the larynx with their nerve supply and actions. Verify the difference between the olfactory and nasal mucosa. Discuss the microscopic structure of larynx Discuss the formation of the lung buds. Describe the development of larynx. Understand the conducting zone and non-conducting zone of respiratory system Define the respiratory and non-respiratory functions. Recognize the functions of alveoli, pleura, and pleural cavity Enlist the pathogenic bacteria that cause upper respiratory tract infection. Differentiate microbes of upper respiratory tract according to the different microbiologicalaspects. Identify the clinical picture of each infectious microbe. Summarize the major toxic substances produced by these bacteria and their role in inflammation and disease complications. Describe the mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, adverse effects, drug interactions & therapeutic uses of drugs used to treat cough &allergic rhinitis. Discuss the anatomical structure of the trachea with its relations. Define the term bronchial tree. Describe bronchopulmonary segments. Explain pleura. Define mediastinum. Discuss the anatomical structure of lungs. List the relations of right and left lungs. Recognize the blood and nerve supply of the lungs. Identify the sternum and ribs with their characteristic features. Define intercostal space with its contents. Describe intercostal muscles with their nerve supply and actions. Enlist the respiratory muscles with their actions. Explain the Bucket handle and pump handle movements. Discuss the origin and insertion of diaphragm. Enlist the openings (with their contents) in the diaphragm. Give the motor and sensory nerve supply of the diaphragm. Describe the microscopic structure of trachea and lungs. Differentiate between the terminal and respiratory bronchioles. Explain alveolar cells. Explain the mechanism of formation of trachea, bronchi and lungs. Differentiate between the periods of lung maturation. Discuss the congenital anomalies of the respiratory system. Intra-alveolar, intra pulmonary pressure and atmospheric pressure How lungs expand during inspiration and air comes in and out of lungs 6 Respiratory muscles of normal inspiration and forced inspiration and expiration Air way resistance Lung Volumes: TV, IRV, ERV and RV Lung capacities: VC, IC, FRC and TLC Importance of VC and FEV1 in obstructive and restrictive lung disease What physiological and pathological factors can affect lung volumes and capacities What is Compliance? What factors affect it? Surfactant and surface tension Transmural Pressure and factors which keep the alveoli open Respiratory distress syndrome, factors which can cause collapse of alveoli Recognize the physiological aspects of the control of breathing. Being oriented of the factors affecting respiration. Explain how ventilation is regulated by the CNS Explain how blood gases and pH influence ventilation Describe the changes in percent oxyhemoglobin as a function of arterial PO2 and explain how this relates to oxygen transport Describe the various conditions that influence the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve and oxygen transport Identify the infectious microbes of pneumonia according to microscopic features, cultural characteristics, biotyping, biochemical activities, and serotyping. Discriminate between granulomatous pneumonia, hospital acquired pneumonia and community acquired pneumonia according to etiology and mechanism of inflammation. Enlist the clinical specimens that collected for diagnosis of pneumonia. Discriminate between laboratory methods and their significant diagnostic value for different types of pneumonia. Recall the structure, classification and general functions of phospholipids Recognize lung surfactant and respiratory distress syndrome. Understand the types and functions of phospholipases. Understanding the concept of chronic suppurative lung dis. Recognizing etiopathogenesis of bronchiectasis Describe the gross and microscopic picture of bronchiectatic lung. Be aware of the complications of bronchiectasis. Understand the concept of pneumonia. Know the types of pneumonitis. Differentiate between lobar pneumonia and bronchopneumonia. Enlist the infectious microbes that cause tuberculosis. Differentiate between Mycobacterium species according to microscopic examination, cultural morphology and biochemical activities. Identify the clinical picture and clinical diagnosis of tuberculosis. Understand the definition and mechanism of granulomatous inflammation. Recognize predisposing factors for T.B. Being oriented of types and morphological features of pulmonary tuberculosis. 7 Being aware of the complications of pulmonary T.B Identify the most common viruses transmitted by respiratory droplets. Differentiate these viruses according to their structure, clinical picture and laboratory diagnosis. Define the antigenic drift and antigenic shift characters of Influenza virus. Define Latency and know the most common latent viruses. Understand in brief the structure of respiratory acinus. Recognize the mechanism of lung tissue destruction in emphysema. Being oriented of the gross and microscopic picture of emphysematous lung. Be aware of the complications and outcome of emphysematous patients. Understanding the main concept of obstructive pulmonary disease. Recognizing pathological aspect of bronchial asthma as regard its types, morphological picture and complications. Being aware of the definition of chronic bronchitis. Understanding the pathogenesis and the morphologic changes of chronic bronchitis. Understanding the concept ofcorpulmonale and its significant. Explain the first line & alternative drugs used as antihistamincs with special emphases on bronchodilators, corticosteroids and anti-inflammatory drugs, their pharmacokinetics , pharmacodynamics, adverse effects & route of administration. Enumerate drugs used in various types of COPD. Recalling in brief classifications of lung tumors. Discussing the predisposing factors for bronchogenic carcinoma. Recognizing methods of distant spread of bronchogenic carcinoma. Understanding the morphological features of bronchogenic carcinoma. Being oriented of the complications of bronchogenic carcinoma. Recalling in brief some metastatic tumors to the lung and methods of diagnosis. Discuss the importance of mechanisms of energy production by cells. Describe the main concepts of the electron transport chain (respiratory chain) of the mitochondria. Discuss the mechanisms of oxidative phosphorylation & its role in energy production in the cells. Recognize the concepts of uncoupling proteins. Explain how inspiration and expiration are accomplished Describe lung volumes and capacities, and explain how pulmonary function tests relate to pulmonary disorders Explain how partial gas pressures are calculated, and their significance in measurements of arterial blood gases Describe the factors that influence the partial pressure of blood gases and the total content of oxygen in the blood Explain how oxygen and carbon dioxide is transported by the blood Explain the relationship between blood levels of carbon dioxide and the blood pH Recall the structure of oxygen binding proteins. Recognize the different statesof hemoglobin 8 Identify factors affecting binding of hemoglobin to oxygen Understand concepts of acid-base balance Recognize laboratory investigations for assessing acid-base status. Identify types of disturbance of acid-base balance with reference to lab investigations results. (ii) Teaching Strategies to be used to develop the knowledge: 1234- Lectures Practical laboratory classes Tutorial classes Directed Student Learning (iii) Methods of assessment of knowledge required: 1- MCQs 2- SAQs 3- OSPE 9 b. b. Cognitive Skills: 1212- (i) Description of cognitive skills to be developed: 1- Horizontal integration of information of topics of basic medical sciences 2- Vertical integration of information of basic and clinical sciences. (ii) Teaching strategies to be used to develop these cognitive skills: 1- Discussions in tutorial classes & office hours 2- Directed student learning (iii) Methods of assessment of students’ cognitive skills: 1- MCQs 2- OSPE c. Interpersonal Skills and Responsibility: (i) Description of the interpersonal skills and capacity to carry responsibility to be developed: 1- Team work 2- Group discussion (ii) Teaching strategies to be used to develop these skills and abilities: Directed student learning (iii) Methods of assessment of students interpersonal skills and capacity to carry Responsibility: d. Communication, Information Technology and Numerical Skills: (i) Description of the skills to be developed in this domain. 1- Utilizing internet service for obtaining scientific data 2- Exploiting software programmes for writing scientific researches. (ii) Teaching strategies to be used to develop these skills: - Conducting seminar sessions to be presented by students (bronchial asthma seminar) (iii) Methods of assessment of students numerical and communication skills: 1- Discussion of students in tutorial hours. 2- Evaluating of students for seminars. e. Psychomotor Skills (if applicable) (i) Description of the psychomotor skills to be developed and the level of performance required (ii) Teaching strategies to be used to develop these skills (iii) Methods of assessment of students psychomotor skills 10 5. Schedule of Assessment Tasks for Students During the Semester Assessment 1 2 3 4 Week due Proportion of Final Assessment Exam.1 (MCQs + SAQs) 3 20 Exam.2 (MCQs + SAQs) 7 20 OSPE 8 20 End-Block Examination (MCQs) 8 40 Assessment task (e.g. essay, test, group project, examination etc.) D. Student Support 1- Arrangements for availability of teaching staff for individual student consultations and academic advice. (include amount of time teaching staff are expected to be available each week) One Staff Member / 10 Students Time available for a Staff Member: 6 Hours E. Learning Resources 1- Required Text(s): 1. Clinical Anatomy By Systems, 1st edition, 2007 (Richard S. Snell). 2. diFiore’s Atlas of Histology with functional correlation, 11th edition, 2008 (Victor P. Eroschenko). 3. Langman’s Medical Embryology, 11th edition, 2010 (T.W. Sadler). 4. Human Physiology, From cells to Systems, 7th edition, 2010 (Lauralee Sherwood). 5. Lippincott’s illustrated Reviews: Microbiology, 2nd edition (Richards A. Harvey, Pamela C. Champe, Bruce D. Fisher) 6. Robbins; Pathologic Basis of disease, 9thth edition 7. Lippincott’s illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry, 5th edition, 2011 (Richards A. Harvey, Denise Ferrier) 8. Lippincott’s illustrated Reviews: Pharmacology, 4th edition, 2009 (Richards A. Harvey, Michelle A. Clark, Richard Finkel, Jose A. Rey, Karen Whalen). 11 2. Essential References: 3- Recommended Books and Reference Material (Journals, Reports, etc) (Attach List) 4-.Electronic Materials, Web Sites etc 5- Other learning material such as computer-based programs/CD, professional standards/regulations F. Facilities Required Indicate requirements for the course including size of classrooms and laboratories (i.e. number of seats in classrooms and laboratories, extent of computer access etc.) 1. Accommodation (Lecture rooms, laboratories, etc.) 1- Lecture Rooms 2- Seminar rooms 3- Laboratories for Physiology, Histology, Pathology, Microbiology & Biochemistry 4- Dissection Rooms (for Anatomy) 2. Computing resources: 1- Smart boards 2- IT Labs connected to the internet G. Course Evaluation and Improvement Processes 1-Strategies for Obtaining Student Feedback on Effectiveness of Teaching: 1- Evaluation of course & staff members by students is conducted through Edugate of the College 2-Regular meeting of students with the Head of Department 2 -Other Strategies for Evaluation of Teaching by the Instructor or by the Department: - Feedback from staff members 3 Processes for Improvement of Teaching: 1234- Making lectures more interactive Better utilizing of IT skills & facilities Increasing time allocated for tutorials Adopting PBL & CBD strategies. 12 4. Processes for Verifying Standards of Student Achievement (e.g. check marking by an independent member teaching staff of a sample of student work, periodic exchange and remarking of tests or a sample of assignments with staff at another institution) 5. Describe the planning arrangements for periodically reviewing course effectiveness and planning for improvement. Discussing issues related to the course in the meetings of the department 13