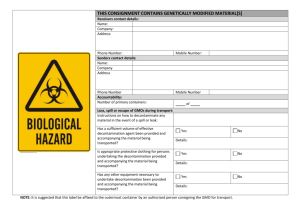
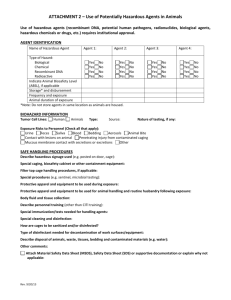
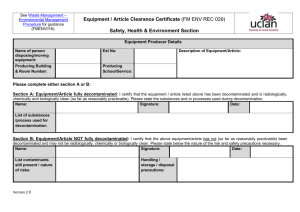
Hazardous Materials: Decontamination Techniques
advertisement

Fundamentals of Fire Fighter Skills, Third Edition Chapter 34: Hazardous Materials: Decontamination Chief Concepts Decontamination makes personnel, equipment, and supplies safe by removing or reducing hazardous materials or WMDs. Proper decontamination is essential at every hazardous material/WMD incident to ensure the safety of both personnel and property. Cross-contamination is the process by which a contaminant is carried out of the hot zone and contaminates people, animals, the environment, or equipment. Cross-contamination may occur in several ways: • A contaminated victim comes into physical contact with an emergency responder. • A bystander or other emergency responder comes into contact with a contaminated object from the hot zone. • A decontaminated responder comes into contact with another contaminated responder or object. Fire fighters are often responsible for establishing a decontamination corridor. There are four major categories of decontamination: • Emergency decontamination—Aims to reduce the amount of surface contaminant. Involves dousing the victim with water via a hose line outside of a decontamination corridor. Formal decontamination is performed later. • Gross decontamination—Uses a large shower system in a decontamination corridor. This type of decontamination is used for a brief and rapid contamination reduction. • Technical decontamination—Performed after gross decontamination and may involve several steps. • Mass decontamination—Used to decontaminate large groups of people in the field. Victims will need to undergo further and more thorough decontamination. Alternative decontamination procedures include the following options: • Absorption—Use of a spongy material to soak up the hazardous material. This technique is used to decontaminate equipment and property. • Adsorption—Binding of the contaminant to the surface of an added material, which is disposed of. • Dilution—Use of soap and water to flush the hazardous material off a person or object. • Disinfection—Process used to destroy disease-carrying organisms. • Disposal—Two-step removal process for items that cannot be decontaminated properly. • Solidification—Chemical process of treating a hazardous liquid to become a solid. • Emulsification—Process of neutralizing or reducing the harmful effects of a hazardous material by changing its chemical properties. • Vapor dispersion—Process of separating and diminishing harmful vapors, often with a water spray. 1 © 2014 Jones & Bartlett Learning • • Removal—Process of removing contaminated soil from a hazardous materials site. Vacuuming—Removal of dusts, particles, and liquids by sucking them up into a container. 2 © 2014 Jones & Bartlett Learning