Here
advertisement

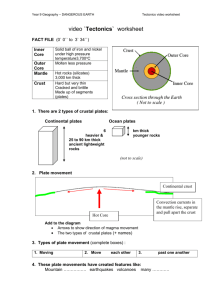
Name _________________________________________________ Period ________ Date _________________ 1st Semester Study Guide *** Your study guide MUST be Neat, Clean, Legible, and Detailed! Use your Notes, textbook, or my website to answer each question Section 1: MINERALS (pg. 62-79) 1. How to test the hardness of a mineral (pg. 69) - Include a picture of the Mohs Scale *To test the hardness of a mineral you: _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Picture of the Mohs Scale: (pg. 69) – COMPLETE THE CHART Mohs Scale Hardness 1 Gypsum 3 4 Apatite Feldspar 7 8 Corundum Diamond 2. How to perform a streak test (Pg. 71) *To perform a streak test you need to ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Describe the difference between fracture and cleavage (Pg. 71) *_________________ is when minerals break with uneven, rough, or jagged surfaces. *_________________ is when minerals break along smooth flat surfaces. 4. Minerals special properties (Pg. 72) - Magnetism attracts magnets and will pick up iron fillings - Chemical reaction with Calcite (Include a picture) *When hydrochloric acid (HLC) is dropped on calcite it will ___________________. Picture 5. Crystalline structure when magma cools fast and slow *When magma cools slow the crystals will be ________________. *When magma cools fast the crystals will be _________________. Section 2: Rocks (pg. 90-109) 1. List the 3 types of rocks and their characteristics - Igneous (difference between intrusive and extrusive) (pg. 95) *Intrusive: Located __________________ the Earth’s surface These type of rocks cool very ____________ and have ______________ sized crystals *Extrusive: Located _________________ the Earth’s surface These type of rock cool very ____________ and have ______________ sized crystals - Sedimentary (difference between compaction and cementation) (pg. 104) *Compaction is when _________________ from the upper layers pushes down on the lower layers. *Cementation: As ___________ moves through soil and rock, it picks up materials released from minerals during ___________________. These minerals act like natural ___________, and hold the sediments together like ____________. - Metamorphic (difference between foliated and nonfoliated) (pg. 101,102) * Foliated Rocks: The mineral grains line up in _____________________. * Nonfoliated Rocks: __________________ does not occur. The mineral grains grow and ______________ 2. Picture of the rock cycle (Compete the diagram with arrows and labels) pg.91 Sediments Sedimentary Rock Igneous Rock Metamorphic Rock Magma Section 3: Natural Resources (pg 120-135) 1. Renewable resources (List and describe the 5 and give examples for each) 1. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Example: _____________________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Example: _____________________________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Example: _____________________________________________________________________ 4. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Example: _____________________________________________________________________ 5. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Example: _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Nonrenerable resources (Give a description of each) - Fossil Fuels (list and describe the 3 types) (pg120-123) 1. Coal – ________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Oil –_________________________________________________________________________ Example - _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Natural gas – __________________________________________________________________ Example - _____________________________________________________________________ - Nuclear (pg.127) * Nuclear energy is an alternate energy resource produced from ________________________. Example - ________________________________________________________________________ 3. Include 1 picture for renewable and 1 picture for nonrenewable Renewable resource picture Nonrenewable resource picture This is a picture of __________________ This is a picture of ___________________ Section 4: Soil (pg. 190-191) 1. Draw and label a picture of the soil profile (pg. 191) 2. Describe the characteristics of each layer (Pg. 191) *A Horizon: Also called the __________________, and is the _________________ layer Is covered in ___________________ Very __________ and fertile Composed of ________________ which provides nutrients for the soil *B Horizon: Also called the __________________ _________________________ occurs in this layer which is the removal of minerals that have been dissolved in water. *C Horizon: Also called the ___________________, and is the ________________ layer Consists of _________________________ This horizon is most like the ____________________________. 3. What are the components of soil? (What is it made up of) (Pg. 190) *Soil is made up of _____________ and _____________________________, ___________________, _______________, and ______________________. Section 5: Weathering (Pg. 182-186) 1. Mechanical weathering - List the 3 types and describe the characteristics of each 1._______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 2._______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. ______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Chemical weathering - List the 3 types and describe the characteristics of each 1._______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 2._______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. ______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Provide 1 picture of mechanical and 1 picture of chemical weathering Picture of mechanical weathering Picture of Chemical Weathering This is a pict. of _______________ This is a pict. of ________________ Section 6: Erosion and Deposition Give examples of erosion and deposition for each erosional force. Erosion Erosional Force Gravity (pg. 210-214) Glaciers (Pg. 215-220) Deposition Wind (pg. 222-227) Section 7: Plate Tectonics (pg. 272-289) 1. Draw, label, and give characteristics of the 3 ways plate tectonics move 1. Divergent Boundary (pg. 281) Pict: These type of plates move ____________ 2. Convergent Boundary (pg. 282) Pict: 3. Transform Boundary (pg. 284) Pict: *These type of plates move __________________ *The denser plate will ____________ under the less dense plate. *The area where the plate goes under the other plate is called the _______________________, and a ____________________ can form here. *These type of plates occur when ______________ __________________________________________ 2. Using the flow chart, describe the difference between continental drift, seafloor spreading, and plate tectonics 1. Continental Drift 2. Seafloor Spreading 3. Plate Tectonics 3. List 5 supporting evidences that Alfred Wegner’s theory, continental drift, existed. 1. ______________________________________________________________________ 2. __ ____________________________________________________________________ 3. _______________________________________________________________________ 4. ______________________________________________________________________ 5. _______________________________________________________________________ 4. Label the layers of the Earth 5. Explain how convection currents occur - A convection current is the ___________________________, ___________________________, _________________________, and ____________________________ of magma. - The hot, _________________________________ magma rises, cools, and becomes _____________________________________ causing it to sink. - This cycle is what causes the ________________________________________________ to move. 6. Describe the age of rocks the closer and farther away they get from the mid ocean ridge. - The closer to the mid ocean ridge, the _____________________________________ the rock. - The farther away from the mid ocean ridge, the _________________________________ the rock. 1) When an earthquake occurs, energy is released in the form of __________. a. seismic waves c. magnitude b. faults d. tsunamis 2) What kind of a wave causes particles in rocks to move side to side at right angles to the direction of the waves? a. surface waves c. secondary waves b. primary waves d. tsunami waves 3) What kind of waves causes particles in rocks to move back and forth in compressions in the same direction? a. surface waves c. secondary waves b. primary waves d. tsunami waves 4) An earthquake’s _______________ is the point on Earth’s surface directly above the earthquake focus. a. elastic limit c. epicenter b. focus d. primary wave 5) The Richter scale measures the _________ of an earthquake. a. magnitude c. liquefaction b. intensity d. fault 6) Normal faults are created by _____________ forces. a. compression c. sliding b. tension d. exploding 7) Rocks are subject to the force of tension where Earth’s plates ____________. a. slide past each other c. move apart b. come together d. slide over another one 8) _____________________ forces are present where Earth’s plates come together. a. explosive c. tension b. elastic d. compression 9) At a ___________________ fault, the rocks above the fault surface are forced up and over the rocks below the fault surface. a. liquid c. normal b. strike-slip d. reverse 10) Earthquakes create all of these types of waves EXCEPT ___________ a. tertiary c. primary b. secondary d. surface