ROCK-n-ROLL

ROCK-n-ROLL
• rocks are primarily composed of minerals
• the oldest are 3.5-4.0 billion years old
• rocks originated from molten material (lava or magma)
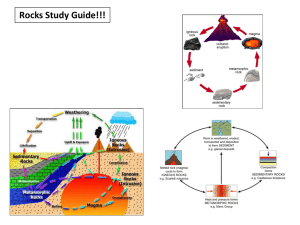
• Rock Cycle: how rocks change over long periods of time
IGNEOUS ROCK
• most abundant
• 2 categories
• intrusive - magma cools slowly, mineral crystals grow large
(course-grained)
• extrusive - lava cools quickly, minerals form small crystals (finegrained, too small to be seen)
• glasses - sub-category of extrusive, cool so fast that no crystals form (ex: obsidian and pumice)
SEDIMENTARY ROCK
• 75% of the surface rocks
• 3 categories
• clastic - “broken” bits of rock
• chemical - precipitates that harden out of solution
• organic - sea shells, decaying plants (limestone, coal)
• fossils almost only found in sedimentary rock
METAMORPHIC ROCK
• minerals recrystallize due to heat and pressure
• regional metamorphism - mountain building
• contact metamorphism - magma is squeezed through preexisting rock
• 2 categories:
• foliated - layers or bands are visible
• non-foliated - no layering or banding