double-angle identities (restricted to sine, cosine, and tangent)
advertisement

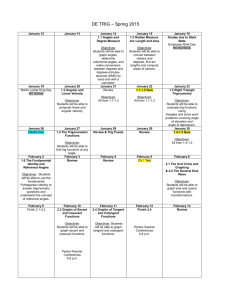
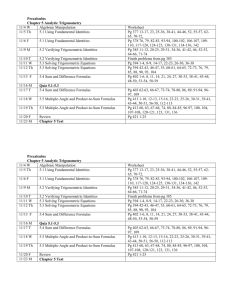
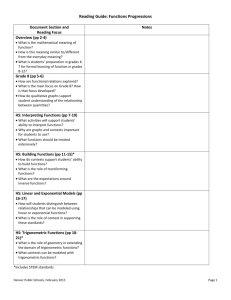
Subject: Pre-calculus 30 Outcome: PC30.5 - Demonstrate understanding of trigonometric identities including: reciprocal identities quotient identities Pythagorean identities sum or difference identities (restricted to sine, cosine, and tangent) double-angle identities (restricted to sine, cosine, and tangent) Beginning – 1 Approaching – 2 Proficiency – 3 Mastery – 4 I need help. I have a basic understanding. My work consistently meets expectations. I have a deeper understanding. With assistance, I can verify a trig statement for a given value I can verify a trig statement for a given value I can prove complex identities without errors. I can determine non- permissible values of trig identities. With assistance, I can prove “one step” trig identities algebraically. Prove “ one step” trig identities algebraically. I can prove any trig identity With assitance, I can determine the exact values of trig ratios using sum, difference and double angle identities. My process is correct, but may make simplifying errors. I can determine the exact values of trig ratios using sum, difference and double angle identities. Indicators – please select and assess as appropriate to your unit, bold text indicates possible key indicators. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Explain the difference between a trigonometric identity and a trigonometric equation. Verify numerically (using degrees or radians) whether or not a trigonometric statement is a trigonometric identity. Critique statements such as "If three different values verify a trigonometric identity, then the identity is valid". Determine, with the use of graphing technology, the potential validity of a trigonometric identity. Determine the non-permissible values of a trigonometric identity. Develop, explain, and apply strategies for proving trigonometric identities algebraically. Explain and apply strategies for determining the exact value of a trigonometric ratio by using sum, difference, and double-angle identities. Refer to the Saskatchewan Curriculum Guide Pre-Calculus 30