Lafayette Parish School System - Lafayette Parish School Board
advertisement

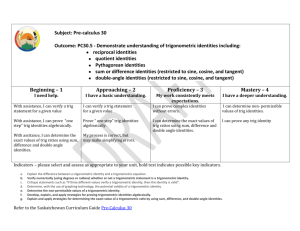
Lafayette Parish School System Advanced Math Pre-Calculus Curriculum Map Unit 3: Solving Trigonometric Equations/Identities Time Frame: CC # Common Core Evidence / Assessments of learning Instructional Notes/Strategies Enrichment/Remediation Strategies Student Understandings F.TF.6 F.TF.7 F.TF.4 F.TF.8 Understand that restricting a trigonometric function to a domain on which it is always increasing or always decreasing allows its inverse to be constructed. Use the inverse functions to solve trigonometric equations that are arise in modeling contexts; evaluate the solutions using technology and interpret them in terms of the context. Use the unit circle to explain symmetry (odd and even) and periodicity of trigonometric functions. Prove the Pythagorean identity sin2(θ) + cos2(θ) = 1 and use it to find sin(θ), cos(θ), or tan(θ) given sin(θ), cos(θ), or tan(θ) and the quadrant of the angle. F.TF.9 Prove the addition and subtraction formulas for sine, cosine, and tangent and use them to solve problems. F.TF.3 Use special triangles to determine geometrically the values of sine, cosine, Basic Trig Identities Strategies for proving Trig Identities Addition and Subtraction Identities for sine, cosine, and tangent functions Co-function Identities Double-Angular Formulas Half-Angle Formulas Find the exact value of the inverse of sine, cosine, and tangent functions Find an approximate value of the inverse of sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions What is the difference between sine function and the restricted sine function and why is it important when working with the inverse sine function? 6.1 The Inverse of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Functions 6.2 The Inverse Trigonometric Functions Shmoop (See Links) 6.3 Trigonometric Identities Hotmath: Trigonometric Identities Identify possible identities Basic Trig Identities Use Addition and Subtraction identities for sine, cosine, and tangent functions Use co-function identities Strategies for proving Trig Identities How is proving or verifying a trig identity different than solving a trig equation? Use Sum and Difference Formulas to Find Exact Values Use Sum and Difference Formulas to Establish Identities Use Sum and Difference Formulas Involving Inverse Trig Functions Can students use the sum and difference identities and the double angle identities? Regents Prep: Inverse Trig Functions Investigating Inverse Trig Functions-Activity SMART Notebook: Trigonometric Identities TI NSpire CX Activity: Precalculus: Proof of Identities 6.4 Sum & Difference Formulas Trigonometric Identities Discovery Activities (Covers several) Analyzemath: Sum and Difference Formulas in Trigonometry Algebra Lab: Sum and Difference Formulas Lafayette Parish School System Advanced Math Pre-Calculus Curriculum Map Unit 3: Solving Trigonometric Equations/Identities Time Frame: CC # Common Core Evidence / Assessments of learning Instructional Notes/Strategies Enrichment/Remediation Strategies , , and , and use the unit 3 4 6 circle to express the values of sine, cosine, and tangent for x, x , and 2 x in terms of their values for x, where x is any real number. tangent for F.TF.9 F.TF.8 Prove the addition and subtraction formulas for sine, cosine, and tangent and use them to solve problems. Prove the Pythagorean identity sin2(θ) + cos2(θ) = 1 and use it to find sin(θ), cos(θ), or tan(θ) given sin(θ), cos(θ), or tan(θ) and the quadrant of the angle. Use double angle identities Can students use double angle formulas to find exact values? Can students use half-angle formulas to find exact values? 6.5 Double & HalfAngle Formulas Algebra Lab: Half and Double Angle Formulas WyzAnt: Trigonometric Double-Angle and HalfAngle Formulas