Cell nucleus
advertisement

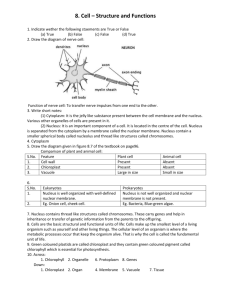
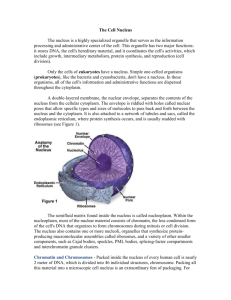
Medical Biology Lec -3- Shorooq Wessam Cell nucleus In cell biology,the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cells genetic material,organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins,such as histones to form chromosomes . the genes within these chromosomes make up the cells nuclear genome . the function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression , the nucleus is the largest cellular organelle in animals ,in mammalian cells the average diameter typically varies from 11 to 22 micrometers (µm) and occupies about 10% of the total volume . the viscous liquid within it is called nucleoplasm and is similar to the cytoplasm found outside the nucleus . The main structural elements of the nucleus are the nuclear envelope,a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and keeps its contents separated From the cellular cytoplasm,and the nuclear lamina,a meshwork within the nucleus that adds mechanical support much like the cytoskeleton supports The cell as a whole.Although the interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-delineated bodies ,its contents are not uniform and a number of subnuclear bodies exist made up of unique proteins , RNA molecules and DNA conglomerates . the best known of these is the nucleolus ,which is mainly invoved in assembly of ribosomes .after being produced in the nucleolus , ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA . 1 1- Nuclear envelope and pores The nuclear envelope consists of two cellular membranes , an inner and an outer membrane arraged parallel to one another and separated by 10 to 50 nanometers (nm) . the nuclear envelope completely encloses the nucleus and separates the cells genetic material from the surrounding cytoplasm , serving as a barrier to prevent macromolecules from diffusing freely between the nucleoplasm and cytosplasm . the outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the membrane of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and is similarly studded with ribosomes . the space between the membranes is called the perinuclear space and is continuous with the RER lumen . Nuclear pores which provide aqueous chnnels through the envelope are composed of multiple proteins collectively referred to as nucleoporins . the size of pores allows the free passage of small water – soluble molecules while preventing larger molecules such as nucleic acids and proteins . ribosomal subunits and some RNAs are transported through the pore complexes in process mediated by transport factors known as karyopherins. 2- Chromosomes 2 The cell nucleus contains the majority of the cells genetic material in the form of multiple linear DNA molecules organized into structures called chromosomes . during most of the cell cycle these are organized in a DNA – protein complex known as chromatin and during cell division . asmall fraction of the cells genes are located instead in the mitochondria . 3- Nucleolus The nucleolus is a sub-organelle of the cell nucleus , it is roughly spherical and is surrounded by a layer of condensed chromatin . no membrane separated the nucleolus from the nucleoplasm. The main role of the nucleolus is considred to be ribosome biogenises , since its fundamental component rDNA codes for preribosomal RNA .additionally recent research pointed out that the nucleolus is also responsible for the trafficking of varios prominent small RNA species . 4- Centrosome The centrosome is the main microtubule organizating center (MTOC) of the cell as well as a regulator of cell – cycle progression . although the centrosome has a key role in efficient mitosis , centrosomes are composed of two orthogonally arranged centrioles surrounded by an amorphous mass of pericentiolar material . centrosomes are often associated with the nuclear membrane during interphase of the cell cycle . in mitosis the nuclear membrane breaks down and the centrosome nucleated microtubules can interact with the chromosomes to build the mitotic spindle , also it has a central role in making cilia and flagella . 3 4