Earthquakes & Volcanoes
advertisement

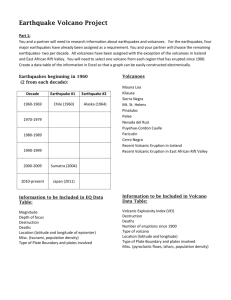
Name _____________________________ Earthquakes & Volcanoes (p. 738 – 746) I. What Are Earthquakes? 1. Define the term earthquake. Earthquake – 2. Earthquakes typically occur around plate boundaries. Circle One : True False 3. Match the following terms with the correct definitions. 1. ________ Seismic Waves A. Point on the surface directly above the focus. 2. ________ Focus B. Wave that moves at a right angle to wave direction. 3. ________ Epicenter C. Fastest type of seismic wave. 4. ________ Longitudinal Wave D. Slowest type of seismic wave. 5. ________ Transverse Wave E. Wave that moves back & forth with wave direction. 6. ________ Primary Wave F. Energy released by earthquakes. 7. ________ Secondary Wave G. Wave that is transverse; only passes through solids 8. ________ Surface Wave H. Point inside Earth where earthquakes originate. 4. The most destructive type of seismic wave is a primary wave. Circle One : True False II. Measuring Earthquakes 1. Define the term seismology. Seismology – 2. How does a seismograph record seismic wave activity? ________________________________________________________________________ 3. The closer an earthquake, the less the time between the arrival of the P-Wave and the arrival of the S-Wave. Circle One : True False 4. Geologists use circles to find the epicenters. What do the following represent? Center of Circle : _________________________________________________________ Radius of Circle : _________________________________________________________ 5. Identify the scale used to assess the magnitude strength of earthquakes. _______________________________ Name _____________________________ III. Volcanoes 1. Define the term volcano. Volcano – 2. Match the following terms with the correct definitions. 1. ________ Vents A. Opening of volcanoes; located in crater or sides. 2. ________ Ash B. Molten material located on the surface of the Earth. 3. ________ Magma C. Molten material located inside a volcano. 4. ________ Lava D. Mineral particles released from volcanoes. 3. Match the following volcanic characteristics with the correct type of volcano. 1. ________ Smallest & most abundant type of volcano. A. Shield Volcano 2. ________ Results from quiet eruptions. 3. ________ Composed of fragments called tephra. B. Composite Volcano 4. ________ Several thousands of meters high. 5. ________ Results from explosive eruptions. C. Cinder-Cone Volcano 6. ________ Largest type of volcano. 7. ________ Erupts runny & thick lava. 8. ________ Looks like a large shield on it’s side. 9. ________ Alternates between quiet & explosive eruptions. 4. Match the type of volcano with the correct representative examples. 1. ________ Shield Volcano A. Mt. St. Helens, Mt. Pinatubo, Mt. Vesuvius 2. ________ Composite Volcano B. Mt. Kilauea, Mt. Surtsey, Mt. Mauna Loa 3. ________ Cinder-Cone Volcano C. Mt. Cerro Negro, Mt. Pelee, Mt. Paricutin 5. List 3 locations where volcanoes typically form and give an example of each location. Location Example 1. __________________________ __________________________________________ 2. __________________________ __________________________________________ 3. __________________________ __________________________________________ 6. What is the Pacific Ring of Fire? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________