Sept. 8 Daily Catch
advertisement
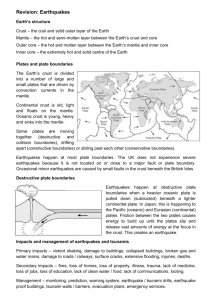
Lopez’s Daily Catch Date_____________ Name ____________________________________ Class _______________ 3 Target: Standard 3.1 Major geologic events such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, mid-ocean ridges, and mountain formation are associated with plate boundaries and attributed to plate motions. a. Gather, analyze and communicate data that explains Earth's plates, plate motions, and the results of plate motions. b. Identify, interpret, and explain models of plates motions on Earth. c. Use maps to locate likely geologic "hot spots", using evidence earthquakes and volcanic activity. d. Use web-based or other technology tools to show connections and patterns in data about tectonic plate boundaries and earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain formation. Mon: Warm UP: Explain 2 reasons why you think taking good notes can contribute to your success as a student in middle school? Summary How did marking the text and taking Cornell notes improve your comprehension Tues: If Geologists can not drill all the way to the center of the Earth how do you think they know what is inside the Earth? Summary Identify three new understandings about the earths Layers you have learned from the Wed: Circle the correct answers Summary Identify how atoms move when they have tremendous energy then explain what you think (remembering the information) about fleas? reading. happens to the energized atoms inside the earth. 1. What is the deepest layer of the Earth a person has ever gotten to? Crust, mantle, outer core. 2. What are the chunks of crust called? Continents, Crust , Tectonic Plates 3. What is caused by tectonic plates shifting? Thunder, Volcanoes, Earthquakes, tornadoes 4. What best describes the mantle? Solid, liquid viscous, gas 5. Where are oceans located? On the top of oceanic plates, on top of continental plates, In holes in the crust. 6. What is the thickest layer of the Earth? Crust, mantle, outer core, inner core 7. What is the Inner Core made of? Steel, iron , aluminum, Iron and Nickel 8. What best describes the outer core? Solid, liquid, viscous, gas 9. How hot is the Inner Core? As hot as an oven, as hot as a fire, as hot as the sun 10. Why is the Inner Core a solid? It’s unknown, It is colder than the outer core, the pressure Thurs: Underline the correct answer 1. 2. How many centimeters are in one meter? 100, 10, 1000, 10000 How long is one millimeter (mm)? about as long as the width across your fingernail, about as long as a baseball bat, about as long as the width of your pencil lead. 3. ________________________ how long is this line? 4. The height of most doors is closest to…. 2 centimeters, 2 meters, 2 millimeters 5. The diameter (width) of a quarter would be closest to…. 2.5 kilometers, 2.5 meters, 2.5 centimeters 6. How many millimeters are in one centimeter? 10, 20, 50, 100 7. The height of your science teacher would be closest to: 173mm, 173 cm, 173 m 8. About how many meters are in a mile? 1609 m, 1000m, 10 m 9. What is longer a meter stick or a yard stick? Meter stick, yard stick 10. How many centimeters are in one inch? 2.54 cm, 2 cm, 3.54 cm Fri: Which layer has the greatest differences in temperature, pressure and density? Explain Summary Identify why we are studying the inside of the earth when the science standard above ask us to understand major geologic events such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, mid-ocean ridges, and mountain formations. Summary: Explain why your model conversion of the Earth’s layers can help you in comparing and contrasting layers. Specifically compare and contrast the mantle and the crust. Concept Map for the Week