Lithosphere Vocabulary: Earth Science Terms
advertisement

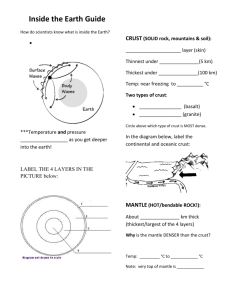
LITHOSPHERE UNIT VOCABULARY Lithosphere- rigid outer shell of Earth including the crust and solid uppermost part of the mantle Metamorphic rocks-form from changes in temperature and pressure; examples are slate and marble Igneous rocks- crystallize from magma; examples are obsidian and basalt Sedimentary rocks- form from cemented sediments; examples are sandstone and shale Erosion- movement of weathered materials from one location to another Deposition- final stage of erosion process when sediments are laid down on the ground or settle to the bottom of a body of water Foliation- process of minerals aligning in bands due to pressure; found in metamorphic rocks Weathering- chemical or mechanical process that breaks down and changes rocks on or near Earth’s surface; influenced by precipitation and temperature Mass movement- movement of loose sediments and weathered rock due to the force of gravity Oxidation- chemical reaction of oxygen with other substances Convergent boundary- where two tectonic plates are moving toward each other; form trenches, island arcs, folded mountains; destroy Earth’s crust Divergent boundary- where two tectonic plates are moving away from each other; form volcanoes, earthquakes, high heat flow; create Earth’s crust Transform boundary- where two tectonic plates slide horizontally past each other; form long faults, shallow earthquakes; conserve Earth’s crust Rift valley- long narrow depression that forms when the crust separates at a divergent boundary Subduction zone- place where one tectonic plate slides beneath another; slab pull Mantle convection- transfer of thermal energy by movement of heated matter Plate tectonics- theory that explains the structure of Earth’s crust as rigid plates that move slowly over the underlying mantle Focus- place along a fault line from which an earthquake originates Sustainable- able to be maintained at a certain rate or level Urbanization- process of rapid development of areas that were previously more rural Natural resources- materials such as minerals, forests, water etc. that occur in nature and can be used for economic gain