Water Hardness Determination: EDTA Titration Lab
advertisement

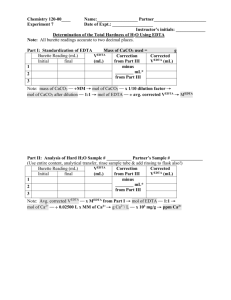
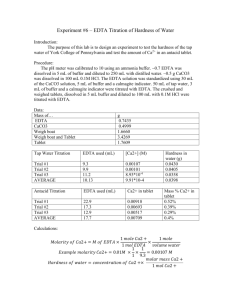
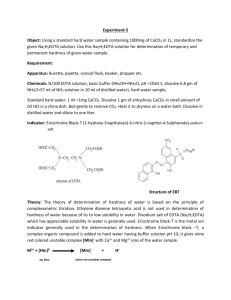
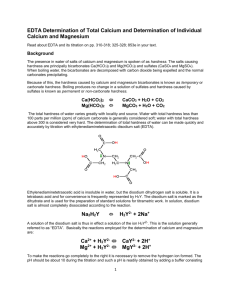
The Determination of Water Hardness Objective To perform a complexometric titration to determine the hardness water from various sources. Background Originally the hardness of water referred to the measurement of the capacity of water to precipitate soap. Water hardness is an expression for the sum of the calcium and magnesium cation concentration in a water sample. These cations form insoluble salts with soap, decreasing Soap’s cleaning effectiveness. The standard way to express water hardness is in ppm CaCO3. An excellent way to determine water hardness is to perform a complexometric titration with a standard ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) solution. Due to steric hindrances, EDTA will complex with calcium and magnesium in a one-to-one molar ratio. The endpoint in this experiment will be determined using a complexometric indicator specific for calcium and magnesium. The indicator imparts a red color to the solution while there are calcium and magnesium ions that have not complexed with EDTA. Once the endpoint has been reached and there is no more uncomplexed Ca or Mg, the indicator will give a blue color. No hint of red color will be left. The combined calcium and magnesium content is reported in units of equivalent amounts of calcium carbonate. Consequently, results obtained by this procedure are usually designated “calcium carbonate hardness” even though the method also determines magnesium. O C - H2C H2C CH2 N O C C N H2C O O CH2 O - CH2 O - C - O O EDTA4EDTA 4 + Ca 2+ CaEDTA 2 O C - H2C H2C CH2 N O H2C O C O CH2 N O O CH2 Ca C O C O - Your Lab kit includes: EDTA solution ~ 0.1 M calcium solution of known concentration 10.00 mL pipet Erlenmeyer flask 250 mL ~ 30 mL of the water hardness buffer solution ~ 1 g of the “hardness” indicator Procedure The EDTA solution must first be standardized against a calcium solution of known concentration. Dilute a 10.00 mL aliquot of the calcium standard with ~ 40 mL of deionized water in an Erlenmeyer flask. Add ~ 5 mL of the buffer solution and ~ 5 mg of the “hardness” indicator. The solution will be the colour of red wine. Titrate with the EDTA solution to a pure blue end-point. Repeat the standardization until runs agree within ±0.2 mL. Take a 50.00 mL aliquot of the cold tap water, add 5 mL of the buffer and ~ 5 mg of the indicator. Titrate with the EDTA solution to the pure blue end-point. Repeat the analysis until the titration volumes agree within ±0.5 mL. Take a 50.00 mL aliquot of a different water sample and repeat the titration. Data and Results Concentration of standard calcium solution: ______________ M Standardization of EDTA solution Volume of Ca2+ aliquot: ______________ mL In the table below, present the data for your two best titrations. Titration Initial Burette Final Burette Volume of Number Reading (mL) Reading (mL) EDTA (mL) 1 2 Concentration of EDTA soln. (M) 1. Calculate the concentration of EDTA solution using the balanced chemical equation for the process of standardization. Average concentration of the EDTA solution based on the two best titrations: __________ M Determination of "calcium" in unknown water sample #1 Volume of unknown aliquot used: ______________ mL In the table below, present the data for your two best titrations. Titration Number Initial Burette Reading (mL) Final Burette Reading (mL) Volume of EDTA (mL) Concentration of "Ca" in sample (M) 1 2 Average concentration of the calcium concentration based on the two best titrations:______________ M Sample #1: Concentration of "calcium" is ____________ M and ____________ mg CaCO3/L. Hint: to convert the mole Ca / L concentration to ppm CaCO3. a. Express (mole Ca / L) as (mole CaCO3 / L) using the 1:1 ratio (1 Ca per CaCO3) b. Convert (mole CaCO3 / L) to (g CaCO3 / L) using the molar mass of CaCO3. c. Convert (g CaCO3 / L) to (mg CaCO3 / L) using a metric system conversion. d. (mg CaCO3 / L) is the same as ppm CaCO3 for dilute aqueous solutions. Determination of "calcium" water sample #2: Volume of unknown aliquot used: ______________ mL In the table below, present the data for your two best titrations. Titration Number Initial Burette Reading (mL) Final Burette Reading (mL) Volume of EDTA (mL) Concentration of "Ca" in sample (M) 1 2 Average concentration of the calcium concentration based on the two best titrations: _________M Sample #2: Concentration of "calcium" is ____________ M and ____________ mg CaCO3/L. What is meant by the expression, hardness of water? What experimental errors are present? How could you reduce or eliminate these errors?