SO questions
advertisement

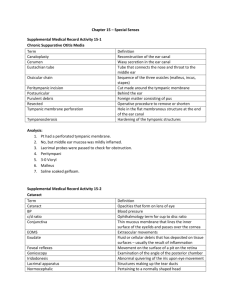
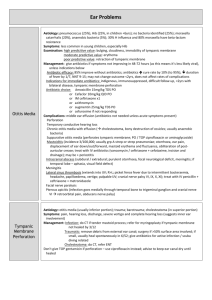
Sensory organs 1. What part of optic tract is damaged the most probably if patient reveals absence of visual perception in the medial halves of retina areas of the both eye-balls? Optic chiasm. 2. What wall of tympanic cavity is destroyed if patient with purulent process in it developed spread of pus into posterior cranial fossa? Posterior wall of tympanic cavity. 3. From what nuclei of cranial nerves smooth muscles of eye-ball are innervated, and which take part in realization of pupil’s reflex? Accessory nuclei of oculomotor nerve. 4. In which lingual papillae receptors the general sensitivity are located predominantly? Filiform papillae. 5. In what direction incisions of mammary gland are made in surgical interventions to reduce traumatization of its lobules? In radial direction. 6. In what part of auditory organs earwax may appear and sharply reduce hearing perceptions? External ear. 7. What structure of eye-ball will suffer the most probably in case of its burn? Cornea. 8. Through what anatomic formation purulent infection from internal ear may cause inflammation of dura mater? Aqueduct of vestibule. 9. Through what wall of tympanic cavity pus may get into it in case of subcutaneous phlegmon in the area of mastoid process of temporal bone? Through posterior wall. 10. Function of what muscle is blocked if patient presents disorder of pupil’s reflex, accompanied by dilatation of pupils’ diameter Muscles constricting pupil. 12. Function of what muscle is blocked if patient presents disturbance of process of lens accommodation? Ciliary muscle. 13. Function of what muscle of eye-ball is damaged if patient presents convergent strabismus? Direct lateral muscle of eye. 14. Through what anatomic formation infection may penetrate from nasopharynx into tympanic cavity of middle ear? Semicanal of the auditory tube. 15. Damage of what wall of tympanic cavity may be supposed if infection from it extended onto internal jugular bulb? Posterior wall. 16. What part of conduction tract of visual analyzer is damaged if patient presents disturbance of perception in the medial visual field of the right eye-ball and in lateral visual field of the left one? Left visual tract. 17. With peculiarity of structure of what anatomic structures is linked technique of surgical interventions on mammary gland, when radial incisions are preferred by surgeons? Convergence of apexes of lobules in the nipple area. 18. What anatomic formation of the eye-ball is damaged if in patient with glaucoma outflow of aqueous humor from anterior chamber of eye is disturbed? Venous sinus of the sclera (Shlemm’s canal). 19. From what visual fields of retina nerve impulses will not be conducted to cortical visual center, if in patient with tumor left visual tract is destroyed? From medial field of the right eye-ball and lateral field of the left. 20. Into what cranial fossa may suppuration spread from tympanic cavity in case of destruction of its upper wall? Into middle cranial fossa. 21. Function of what smooth muscles of eye-ball is damaged if patient has disorder of lens accommodation and stable dilatation of pupil? Papillary sphincter and ciliary muscle. 22. What ligament of eye-ball is fixed to the lens capsule and hangs it? Ciliary zonule of lens. 23. In what part of eye-bulb mucosa one of pathologies of its structure – coloboma (cleft formation) may be located? Iris of the eye. 24. Pathology of what part of the eye-ball mucosa may lead to astigmatism? Cornea. 25. Pathology of what eye-ball structure may lead to disorder of outflow of fluid from anterior chamber of eye-ball? Venous sinus of sclera. 26. Activity of what smooth muscles of the eye-ball is blocked if in patient present different diameter of pupils (anisocoria)? Sphincter of pupil. 27. What structure of internal ear is damaged the most probably if after fall and head trauma patient complains of dizziness, balance disorder and nausea? Vestibular organ. 28. Disorder of conductivity function along what nerve of gustatory analyzer may be supposed if patient suffers from loss of gustatory perceptions of anterior 2/3 of tongue mucosa? Chorda tympany. 29. Disorder of conductivity function along what nerve of gustatory analyzer may be supposed if patient suffers from disturbance of pain and temperature sensitivity of anterior 2/3 of tongue mucosa? Trigeminal nerve. 30. In what canal of temporal bone does osseous part of auditory tube pass? In musculo-tubular canal. 31. Destruction of what canal of temporal bone is possible in surgical intervention on inner wall of tympanic cavity? Tympanic canaliculus. 32. Through what canal of temporal bone infection may penetrate from nasopharyngeal cavity into tympanic cavity? Musculo-tubular canal. 33. Through what wall of tympanic cavity purulent infection from it may penetrate into alveolus of mastoid process? Posterior wall. 34. Where is third neuron of olfactory organ located? In anterior perforated substance of the brain. 35. Where are receptors of gustatory organ located? Mucous membrane of the tongue, palate, posterior wall of pharynx and epiglottis. 36. What olfactory nerve gets from nasal cavity into cranial cavity? Trough cribriform foramina of perforated lamina of cribrous plate. 37. What cranial nerves innervate gustatory sensitivity of the tongue? Anterior 2/3 of tongue is innervated by chorda tympany of facial nerve, posterior 1/3 of tongue – lingual branch of glosso-pharyngeal nerve. 38. What gustatory receptors does lingual branch of glosso-pharyngeal nerve innervate? Receptors of mucous membrane of posterior 1/3 part of the tongue and soft palate. 39. What nerve innervates gustatory receptors of epiglottis mucosa? Anterior pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve. 40. Where are the first neurons of taste located? In ganglia of facial, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. 41. Where are the second neurons of taste conduction tract located? On the fundus of rhomboid fossa in the nucleus of solitary tract. 42. What tunics of eye-ball structure are distinguished? Fibrous tunica, vascular tunica and retina. 43. Name portions of vascular tunica of eye-ball: Proper vascular tunica, ciliary body, iris of the eye. 44. What fibers (by direction) is cilary muscle composed of? Circulatory fibers, radial fibers, meridional fibers. 45. What muscles of what part of vascular tunica perform papillary reflex? Muscle which dilates pupil and muscle, which constricts pupil located in the iris of the eye. 46. What peculiarities does iris of the eye have in its structure to perform papillary reflex? To regulate retinal illuminance: presence of smooth musculature: muscle which dilates the pupil and muscle which constricts it; presence of pigment. 47. Name subsequently refractive mediums of the eye-ball: Cornea, aqueous humor of anterior and posterior chambers, lens, vitreous body. 48. What structures of the eye-ball form nucleus of eye? Lens and vitreous body. 49. What portions by structure and by topography are distinguished in the eye retina? By structure two layers are distinguished: pigment and neurogenic. By topography: optic and blind portion. 50. What optic receptors of the eye are presented by? Retinal rods and cones. 52. Where are subcortical centers of vision located? Subcortical centers of vision are located: in midbrain – upper colliculus of tectal plate, in diencephalon – lateral geniculate bodies. 53. What canal lies in the point of junction of sclera and cornea? Venous sinus of sclera (Shlemm’s canal). 54. Name composition of lacrimal apparatus of eye-ball: Lacrimal gland, excretory ducts of lacrimal gland, lacrimal lake, superior and inferior lacrimal canaliculuses, lacrimal sac, nasolacrimal canal. 55. What structures form eyelid? Conjuctiva, cartilage of eyelid, orbicular muscle, skin of eyelid. 56. How is site on the eye fundus from which its vessels come out called? Blind spot (site of optic nerve exit). 57. Where from direct muscles of eye-ball origin? From tendinous ring of eye orbit which is located around optic canal. 58. What muscles origin from tendinous ring of eye orbit? From tendinous ring of eye orbit four rectus muscles of the eye origin: superior, inferior, medial and lateral; superior oblique muscle of the eye; musclelevator of the upper eyelid. 59. Name regions of osseous labyrinth of the internal ear: Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals. 61. Where is the first neuron of balance located? The first neuron of balance is located in vestibular ganglion on the fundus of inner auditory duct. 62. Where is the second neuron of hearing located? The second neuron of hearing lies in the rhomboid fossa in superior and inferior cochlear nuclei. 63. Where does chiasm of hearing conduction tract take place? In the area of pons: it is trapezoid body of pons and medullary striae of the fourth ventricle. 64. Name subcortical centers of auditory organ: Subcortical centers of hearing are located in midbrain – inferior colliculus of tectal plate; diencephalon- medial geniculate bodies. 65. What structures inter-communicate middle and inner ear? On the medial wall of the middle ear two foramina are located: oval foramen (vestibular window) and round foramen (tympany window). 66. What structures shut vestibular window and cochlear window of inner ear? Vestibular window of inner ear is shut by stapedial base, round window is shut by secondary tympanic membrane. 67. What ducts does membraneous labyrinth of inner ear have? Membraneous labyrinth of inner ear has three communications: duct of cochlear aqueduct, duct of vestibular aqueduct – provide outflow of endolymph and perilymph from the inner ear into sinuses of dura mater; utriculo-saccular duct – intercommunicates vestibular saccule and utricle and transit into duct of vestibular aqueduct. 68. What striated muscles are connected with middle ear? Tensor muscle of tympanic membrane – is used in low, weak sounds; stapedeus muscle – holds on otostapes in case of loud sounds, not to come down into vestibule of inner ear. 69. Enumerate places of localization of balance receptors: Macula of utricle, macula of saccule in membranous labyrinth of vestibule ; anterior, posterior and lateral ampular crests in membraneous labyrinth of semicircular canaliculuses. 70. Where is lacrimal gland located? Lacrimal gland is located in the fossa of lacrimal gland in superior lateral angle of the orbit. 71. Name the narrowest place of external auditory duct: Isthmus of external auditory duct. 72. Where are hearing receptors located? Hearing receptors form «Corti organ», which is located on tympanic wall of membraneous cochlear duct. 73. In what cerebral nuclei are second neurons of conduction tract of hearing analyzer located? Anterior and posterior cochlear nuclei.