electronic supplementary information
advertisement

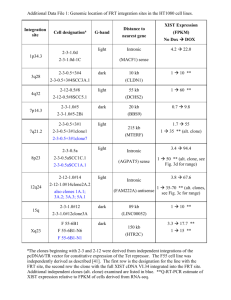
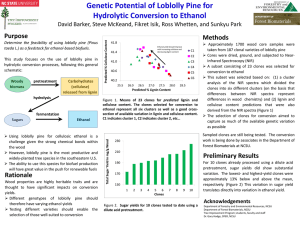
RAC1 GTPASE-DEFICIENT HELA CELLS PRESENT REDUCED DNA REPAIR, PROLIFERATION AND SURVIVAL UNDER UV OR GAMMA IRRADIATION Gisele Espinha, Juliana H. Osaki, Yuli T. Magalhaes and Fabio L. Forti* Laboratory of Signaling in Biomolecular Systems, Department of Biochemistry, Institute of Chemistry, University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo-SP, Brazil Av. Prof. Lineu Prestes, 748 - Bl.09i, Sl.922 CEP: 05508-900 - Cidade Universitária - São Paulo-SP, Brazil *Corresponding author: Fabio Luis Forti, PhD Av. Prof. Lineu Prestes, 748 - Bl.09i, Sl.922 CEP: 05508-900 - Cidade Universitária - São Paulo-SP, Brazil Phone: 55-11-3091-9905 / Fax: 55-11-3091-2186 E-mail address: flforti@iq.usp.br ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutively active HeLa-Rac1 clones behave in an opposite manner to HeLa-Rac1-N17 deficient clones. A) HeLa-Rac1-V12 clones exhibit high basal levels of Rac1-GTP that are still slightly increased by gamma or UV radiation. B) Gamma and UV treatments are able to increase stress fiber formation in HeLa cells but not in the dominant-negative HeLaRac1-N17 clones, which exhibit higher levels of stress fibers. Quantification of fluorescence intensity was performed by the LSM Software (Zeiss) after normalization of all parameters (laser intensity, detector gain, pinhole, etc.) to the control condition and after maintenance for all other treatments, in approximately 100 cells (see the exact number over the bars) from three independent experiments. Supplementary Figure 2 Constitutively active HeLa-Rac1-V12 clones exhibit high basal levels of Rac1-GTP that can be directly correlated to a fast and efficient DDR, comparable to in HeLa cells, by measuring H2AX protein phosphorylation for both treatments, either by immunofluorescence at 1 h (A) or by western blot in kinetic experiments up to 6 h after gamma or UV irradiation, using a specific antibody against phospho-H2AX-Ser139 (B).