Liquid Water Ice Water Vapor
Name: ____________________________________________________ Block: _________ Date: _______________________
Study Guide Due: Test Dates:
A day – ________
B day – ________
A day – ________
B day – ________
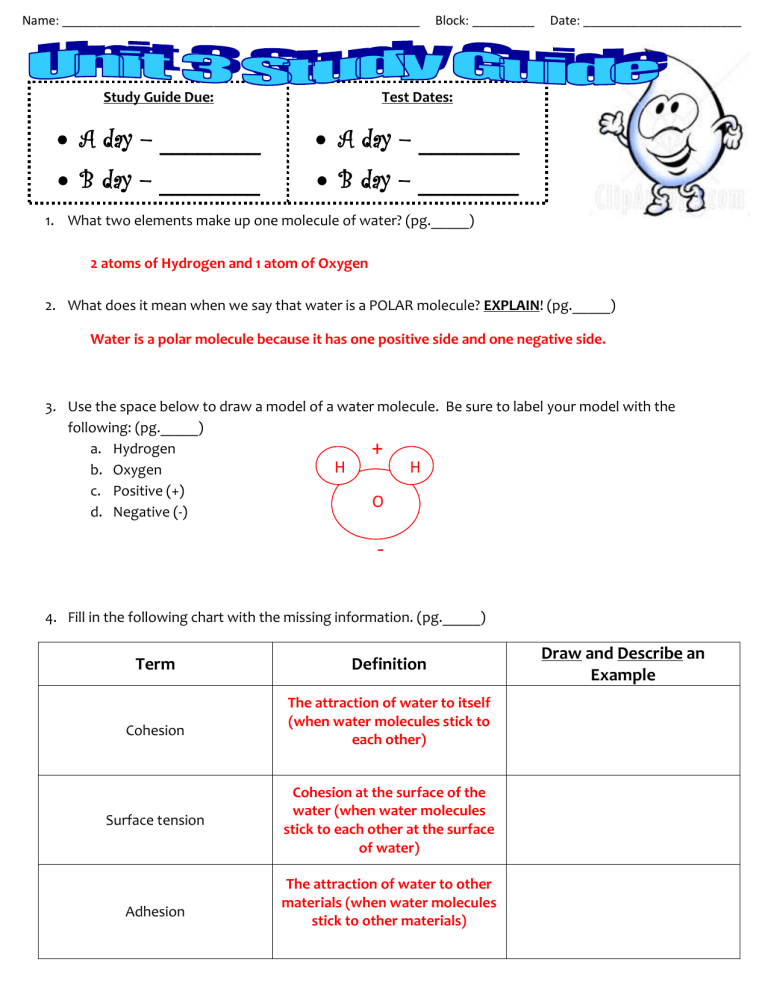
1.
2 atoms of Hydrogen and 1 atom of Oxygen
2.
What does it mean when we say that water is a POLAR molecule? EXPLAIN! (pg._____)
Water is a polar molecule because it has one positive side and one negative side.
3.
Use the space below to draw a model of a water molecule. Be sure to label your model with the following: (pg._____) a.
Hydrogen + b.
Oxygen
H H c.
Positive (+) d.
Negative (-)
O
-
4.
Fill in the following chart with the missing information. (pg._____)
Term
Draw and Describe an
Example
Cohesion
Surface tension
Adhesion
Definition
The attraction of water to itself
(when water molecules stick to each other)
Cohesion at the surface of the water (when water molecules stick to each other at the surface of water)
The attraction of water to other materials (when water molecules stick to other materials)
5.
To the right is an example of surface tension in action. EXPLAIN what is happening. (pg._____)
The water molecules are sticking together very tightly at the surface. The weight of the paper clip is being supported by the water’s surface tension. The top layer of the water behaves as if it was an elastic or stretchy skin. This is surface tension. Surface tension is caused by the attraction of water molecules to other water molecules.
6.
Capillary action is what causes tall redwood trees to be able to receive water all the way at the top.
What properties of water allow this to happen? (pg._____)
Cohesion and adhesion working together; adhesion is when the water sticks to the inside of the tree and cohesion is when water molecules stick to each other. When these properties happen at the same time it allows the water to “climb” up the tree.
7.
Why is water considered the universal solvent? (pg._____)
Water is considered the universal solvent because it can dissolve more substances than any other compound.
8.
What property of water allows it to dissolve so many things? (pg._____)
Water is a polar molecule which allows it to stick to and dissolve so many different substances.
9.
In the boxes provided, draw pictures of the arrangement of water molecules as a liquid, solid, and gas.
(pg._____) a.
Circle the box where the molecules are moving the fastest!!!
solid liquid
10.
Fill in the following chart with the correct temperatures. (pg._____)
Water
Freezes at:
Boils at:
0 o C
100 o C
gas
11.
The following chart shows water changing from one state to another. For each example, write “adding heat” or “removing heat” to describe how the water is changing from one state to the other.
(pg._____)
Phase Change Adding Heat or Removing Heat?
Ice Liquid water Adding heat
Water vapor Liquid water Removing heat
Liquid water Ice Removing heat
Liquid water Water vapor Adding heat
12.
Match the property with the correct phase or phases of water. (pg._____)
Choices: Liquid Water Ice Water Vapor
(You can choose more than one)
Takes the shape of the container
The water molecules are moving the slowest
Liquid water (& water vapor)
Ice
The molecules can move freely and bounce off each other
Water molecules are moving the fastest
Liquid water & water vapor
Water vapor
Water molecules have the largest temperature range (0 -100 ˚C) in this phase.
Liquid water
13.
The glass of water to the right shows two phases of water, which two phases do you see? (pg._____) liquid water & solid ice
14.
In the glass of water shown to the right, the ice is floating on top of the water.
Which phase of water appears to be LESS dense than the other? (pg._____)
The ice is less dense than the water; that’s why the ice is floating.
15.
Using your answer from question #14, EXPLAIN WHY that phase is LESS dense than the other. (pg._____)
Ice is less dense than liquid water because as water freezes it expands and forms a rigid geometric pattern (hexagonal chain). This creates more space between the molecules than in the liquid phase. This space causes the ice to become less dense and float on liquid water.