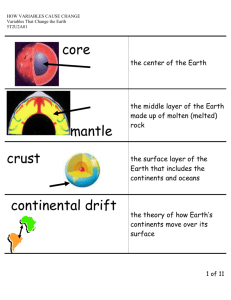
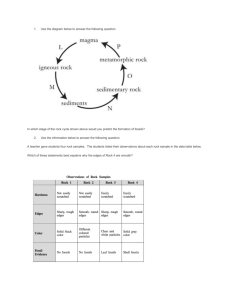
Geophysical B Final Exam Review
advertisement

Name:__________________________________________________ Geophysical B Final Exam Review Unit 6 Climate and Climate Change: 1. What is climate? How is this different from weather? 2. What are the three major factors that affect the climate of an area? 3 . 4. 5. What do scientists use the four terms listed above for? 6. List two potential causes of climate change (either cooling or warming). 7. How are human actions contributing to the warming trend we are seeing? 8. The picture to the right show Michigan’s Great Lakes. How were they formed? (include what existed here prior to the Great Lakes) Unit 7 Energy Resources and Electricity: 9. 10. 11. Which element is most commonly used in the process from question #10? 12. Fill in the table below Renewable or Nonrenewable Wind Biomass Natural Gas Nuclear Coal Geothermal Hydropower Primary or secondary energy source? One positive Aspect One Negative Aspect Solar Petroleum (Oil) 13. How does a secondary energy resource differ from a primary energy resource? Give an example of each. Unit 8 Rocks and Plate Tectonics: 14. 15. Fill in the both the bubbles and the blank arrows in the rock cycle diagram below: ___________ ______ _ WEDCC Heat and Pressure _________ _______________ ___________ _ _________ Melting and cooling 16 . 17 . 18 . 19. 20. Write a sentence that shows the relationship between the following terms and people: Alfred Wegner, Pangaea and continental drift. 21. What does the Theory of Plate Tectonics tell us? What provided proof of this theory? 22. The feature labeled A on the diagram to the right represents the ____________. At the center of this feature is a _____________________ where ________________ rises and cools to form new ocean floor. C A B 23. On the diagram to the right label younger/thinner rock and older/thicker rock. 24. Point B on the diagram represents a __________________ which is created by the subduction of an oceanic plate. What is subduction? What happens to seafloor crust at these trenches? 25. Fill in the chart below Boundary Type Arrows to show movement of plates Plates move together Type of stress Features created Continental-continental: Oceanic-continental: subduction creates trenches and volcanic mountains Oceanic-oceanic: Oceanic-oceanic: Divergent Continental-continental: Shearing 26 . 27 . 28 . 29 . 30 . 31 . 32 . 33 . 34 . 35 . 36. Deformation of earth’s crust occurs from _____________________ adjustments. When something is added to Earth’s crust it sinks ______________ into the mantle and when that additional weight it lifted/removed from the crust is will lift back __________. Unit 9: Earthquakes and Volcanoes 37. (amount of surface destruction) (amount of energy released) 38. On the diagram to the right, label the focus and the epicenter of an earthquake. 39 . 40 . 41 . 42 . 43 . 44 . 45 . 46 . 47. Describe how scientists find the epicenter of an EQ why it is necessary to have information from three locations. Use vocabulary in your response. 48. Fill in the chart below: Wave Alternate Names Speed Motion 1st to arrive, travels through solids and liquids, body wave (under Earth’s surface) Fastest Medium Surface (Love/Rayleigh) Transverse-up and down or side to side under E. Surface Love-side to side None Extra Fact Rayleigh-elliptical, rolling motion 49. Magma that is low viscosity, low gas content and is associated with quiet eruptions Magma that is high viscosity, high gas content and is associated with explosive eruptions 50. What two common locations in the U.S are located near/over hotspots? 51. How is the creation of a volcano at a hotspot different than at a subduction zone or mid-ocean ridge? 52. Fill in the chart below Volcano Type Lava type Type of Eruption Location/Example Shape/Height and how they form Hawaiian Islands Steep volcano formed by layers of ash and lava Composite Cone Felsic Cerro Negro in Nicaragua 53 . 54 . 55 . 56 . 57 . 58 . Unit 10: Hydrology 59. k. imaginary line separating two watersheds _____ 11. Divide 60. Label the following on the diagram below: zone of saturation, zone of aeration (unsaturated zone), water table and well. 61. Based on the diagram, does the position of the water table remain constant? What forms when Earth’s surface dips below the water table? 62. Label all arrows on the water cycle diagram below: 63. Below sketch the evolution of a river from young to mature to old and fill in the characteristics below: Young Overall Shape: Speed: Shape of Bed: Features: Mature Old 64. What are some ways we can prevent flooding of a river? 65 66 67 68. 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 Unit 11: Earth’s History 76. f. fossil of organisms that lived for a short geologic time span over a wide area 77. What is the difference between absolute and relative dating? Give an example of each. 78. For each statement write R for relative age and A for absolute age The rock is said to be 3 million years old _________ The law of crosscutting relationships says that any fault is younger than the rock is cuts through _________ Carbon dating _____ The law of superposition says that older rocks lie at the bottom of a rock column ______ 78. Based on the graph below, what is the half-life of Cesium? 79. Now that you have determined the half-life, define/describe what it is. 80. Fossils such as the Petoskey stone are found in what type of rock- Igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic? Why not in the other two? 81. Look at the diagram below. Which era is by far the longest? 82. Label each era below (Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic) with the main life forms that thrived during that time, if there were any, and whether or not there was a major event/mass extinction that occurred. Precambrian 83. Use the diagram to the right to name the geologic units of time from the largest to the smallest (Periods, Eras, Epochs) 84. The cenozoic era is the only one that is broken into epochs. Why is this? 85 86 88 Make sure you review your electricity TTR!!!!!