Monkemeier April 13, 2015 – April 17, 2015 Honors Biology Unit 8
advertisement

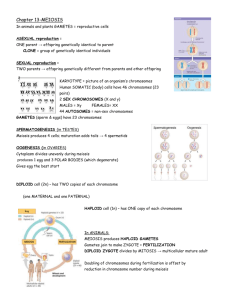
Monkemeier Honors Biology April 13, 2015 – April 17, 2015 Unit 8: Cell Reproduction Quiz 3: Meiosis Name _____________________________ Date ___________________ Unit 8: Cell Reproduction Quiz 3 Meiosis Study Guide Text References Biology 7th Edition (Campbell) Pages 238 – 250, 285 – 288 Biology 8th Edition ((Raven) Pages 205 – 218, 239 – 241, 249 – 250 1. Explain the significance of a karyotype with respect to homologous chromosomes. Autosomes. Sex chromosomes and diagnosing disorders. 2. Distinguish between autosomes and sex chromosomes. 3. Distinguish between the terms haploid and diploid. You may use humans or fruit flies to help you form your answer. 4. How are homologous chromosomes related? Be specific. How are homologous chromosomes related to the terms haploid and diploid in humans? How are homologous chromosomes inherited? 5. Explain how the gender of an organism such as a human, dog, horse or fruit fly can be determined from the karyotype of the organism. 6. Female mammals experience dosage compensation. Explain how dosage compensation relates to Barr Bodies. How does dosage compensation relate to genetic mosaics? 7. Explain how the following terms relate to karyotypes and disorders in humans: nondisjunction, trisomy, monosomy, Down’s Syndrome, Turner’s Syndrome, Klinefelter’s Syndrome. 8. Explain why meiosis and fertilization alternate in sexual life cycles. 9. Distinguish between gamete and somatic cell. 10.Outline the steps of meiosis and highlight where each of the following takes place: homologous chromosomes form tetrads, crossing over can occur, homologous chromosomes in tetrads align at equator, homologous chromosomes separate, chromosomes align at the equator, chromatids separate, nondisjunction can occur. 11.Distinguish between spermatogenesis and oogenesis in humans. Pay close attention to the differences between the processes and where each process occurs in either human males or human females. 12.Sexual Reproduction allows for the creation of new individuals via new combinations of genes known as genetic variation. Explain how each of the following contributes to genetic variation: crossing over, random alignment of tetrads at the equator, random combination of egg and sperm. 13. Explain how sexual life cycles contribute to evolution. 14. Compare and contrast the process of Mitosis with the process of Meiosis.