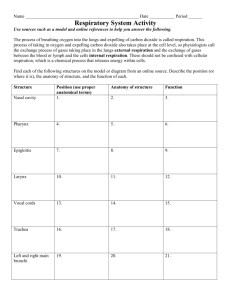
Respiratory System 1) What do each of these parts of the respiratory
advertisement

Respiratory System 1) What do each of these parts of the respiratory system do? -Lungs: Inhale and exhale air in order to bring oxygen to the body -Alveoli: Allow gas exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the surrounding blood vessels -Pleural Fluid: Lubricates the pleural membranes and prevents the lungs from sticking -Nasal Passages: Takes in and filters air -Bronchi: Divide the trachea and direct the flow of air to each of your lungs -Bronchioles: Further divide the bronchi and direct the flow of air to the alveoli -Mucus: Traps bacteria and lubricates your respiratory and digestive systems 2) Where can you find mucus within the body? The trachea, the stomach, the nasal passages, etc. 3) Explain how gas exchange happens within the alveoli. Oxygen diffuses into the arteries and veins surrounding the alveoli, and carbon dioxide diffuses out of the same blood vessels, into the alveoli 4) Describe the process of ventilation. Include all of the steps, in the correct order. Inhalation: Diaphragm contracts, the volume of the chest cavity increases, the air pressure inside of the chest cavity drops, air rushes in from outside the body, the air inflates the lungs, oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream Exhalation: Carbon dioxide diffuses into the alveoli, diaphragm relaxes, the volume of the chest cavity decreases, the air pressure inside of the chest cavity increases, air rushes out of the lungs and leaves the body. 5) Label the picture below. 6) Compare and contrast combustion and respiration. -Combustion needs the following to happen: SPARK, FUEL SOURCE, OXYGEN -Combustion produces the following: SMOKE, CO2, HEAT, LIGHT -Respiration needs the following to happen: OXYGEN, GLUCOSE -Respiration produces the following: ATP, HEAT, CO2, WATER 7) How does fermentation work? Why is respiration better for cells than fermentation? FERMENTATION OCCURS WHEN THE BODY USES SOMETHING OTHER THAN OXYGEN TO PROCESS GLUCOSE. THIS PRODUCES FAR LESS ATP THAN RESPIRATION. 8) Why is it dangerous to climb high mountains, in regards to the respiratory system? How can you train to minimize the risks? THE AIR IS THINNER AT HIGH ELEVATIONS, MEANING LESS OXYGEN IS PRESENT. A LACK OF OXYGEN TO YOUR BLOODSTREAM WILL RESULT IN PASSING OUT. TO TRAIN, YOU CAN GRADUALLY CLIMB UP AND DOWN REPEATEDLY, AT INCREASING ELEVATIONS, TO GET YOUR BODY USED TO THE ELEVEATION. THIS IS CALLED ACCLIMATIZATION. 9) Describe what an Iron Lung does, and how it is like the respiratory system. THE IRON LUNG FORCES THE PERSON INSIDE OF IT TO BREATHE THROUGH USE OF CHANGING THE VOLUME OF THE METAL CHAMBER BY USING A RUBBER DIAPHRAGM, TURNING THEM INTO A GIANT, LIVING MODEL OF A LUNG. 10) Draw the syringe model of breathing below. Label the various parts, as if they were a respiratory system. 11) Describe what the following mean. You should know how they relate to the sponge model as well. -Tidal Volume: THE VOLUME OF AIR THAT ONE CASUALLY BREATHES IN AND OUT -Vital Capacity: THE MAXIMUM VOLUME OF AIR THAT ONE CAN BREATHE OUT AT ONE TIME -Residual Volume: THE AIR REMAINING IN THE LUNGS, EVEN AFTER EXHALING ‘ALL’ STORED AIR -Total Lung Capacity: VITAL CAPACITY + RESIDUAL VOLUME: MAXIMUM AIR THE LUNGS CAN HOLD Circulatory System 12) Name the three blood vessels and describe where they carry blood. -ARTERIES: AWAY FROM THE HEART -VEINS: CARRY BLOOD TOWARD THE HEART -CAPILLARIES: CONNECT ARTERIES AND VEINS 13) Describe the components of blood below and explain what each does. -RBC’s: CARRY OXYGEN USING HEMOGLOBIN -WBC’s: FIGHT BACTERIA IN THE BLOODSTREAM -PLATELETS: CLUMP TOGETHER TO SEAL OFF WOUNDS -PLASMA: CARRIES THE OTHER THREE PARTS 14) Describe the order of blood flow through the heart. Which chambers, valves, and vessels does it flow through? Right side: (NO OXYGEN) VENA CAVA RIGHT ATRIUM TRICUSPID VALVE RIGHT VENTRICLE PULMONIC VALVE PULMONARY ARTERY LUNG Left Side: (WITH OXYGEN) PULMONARY VEIN LEFT ATRIUM BICUSPID/MITRAL VALVE LEFT VENTRICLE AORTIC VALVE AORTA REST OF THE BODY 15) Label the picture of the heart below. 16) What determines your blood type? Which blood types are the universal donor/recipient? MARKERS ON YOUR RED BLOOD CELLS (ANTIGENS) DONOR: O RECIPIENT: AB The following blood types can receive blood from: A: A,O B: B,O AB: A,B,AB,O O: ONLY O -How do the digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems work together to keep cellular respiration going? DIGESTIVE: OBTAINS GLUCOSE BY BREAKING DOWN STARCH WITH SALIVARY AMYLASE RESPIRATORY: OBTAINS OXYGEN AND SENDS IT TO THE ALVEOLI, OXYGEN THEN DIFFUSES INTO THE BLOODSTREAM CIRCULATORY: BLOOD CARRIES NUTRIENTS TO EVERY CELL IN THE BODY