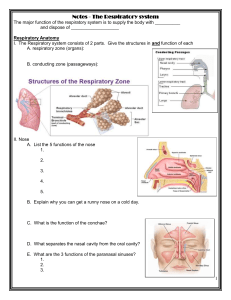
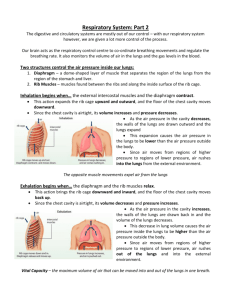
Steps in respiration
advertisement

Biology 30 - Ch. 11 Gas Exchange Notes Respiration Larger organisms need specialized organs to bring in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide for body tissues. Land-dwelling animals have lungs for gas exchange (aquatics species have gills). Function of respiration—humans cannot go more than 5–6 minutes without breathing. All cells must capture ___________; needed to _____________________. Must dispose of _________________ generated through ______________ _____________________________________. Respiratory system also: _________________________________________________________. _________________________________________________________. _________________________________________________________. _________________________________________________________. Structure of respiratory system _________________________________________________________. _________________________________________________________. Conducting passageways - ___________ branching into ______________, then ________________ and ending in tiny thin-walled air sacs called ________________. ___________________________. Lungs, containing some of the elements just listed and more. The Nose & Nasal Cavity The air enters the nose through the _______________. The entrance to the nostrils is lined with _______________ which ______________________ entering the nasal cavity. The walls of the nasal passage are lined with ________________________ which produces _________________________. Both of these trap foreign particles and remove them from the body. The mucous _______________, and large numbers of ________________ ___________. The nasal cavity prepares the air for passage to the lungs by ___________________________________________. A benefit you don’t get when you breathe through your mouth. The Pharynx & Larynx Air travels from the nasal cavities to the _____________. This opening is covered and protected during swallowing by the ________________. 1 Biology 30 - Ch. 11 Gas Exchange Notes Air travels from the pharynx into the ______________________. The vocal cords are 2 membranes stretched across the larynx which make sounds as air passes across them. The larynx is covered during swallowing by the _____________________ Trachea This is a tube that runs from the ___________________________. The walls are embedded with _________________________ to keep the ___________________________. The trachea is lined with a __________ _________________which traps foreign particles and moves the mucous into the pharynx where it is usually swallowed. The Lungs The Trachea branches into ________________ just before it enters the lungs. These bronchi then form further branches called bronchial tubes, then bronchioles which end in sacs called alveoli. The _____________ are where _______________________ takes place. The lungs fill most of the space in the thoracic cavity. They are separated from the abdominal cavity by ____________________ __________________________. Each lung is completely covered by a 2 layered membrane called the ___________________. One layer covers the lung while the other is in contact with the diaphragm and other organs in the chest cavity. These layers are ___________________________________ the lungs and allow them to move. Steps in respiration: _________________________________ refers to physical movement of air into and out of lungs; operates in respiratory cycle consisting of: ____________________—movement into lungs. ____________________—movement of air out of lungs. ______________________ between lungs and external environment control stages of respiratory cycle. No movement of air when _______________________________________ (as at start of breath). Contractions of ____________________________, sometimes aided by _________________________, ____________________; _______ in pressure brings in air (inhalation). 2 Biology 30 - Ch. 11 Gas Exchange Notes When respiratory muscles __________, elastic fibers in lung tissue recoil, ____________ thoracic cavity and ________________________________ within (exhalation). Exchange of gases during breathing Takes place at _______________, which is closely linked with _________ ________________________________________________ ______________________________ refers to exchange of gases across ________________________ surfaces. Oxygen moves down its concentration gradient from alveoli into capillaries. In capillaries, oxygen diffuses into RBCs and is tightly bound to ________________________, producing oxygenated blood. Pumping by heart moves oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. Carbon dioxide in blood leaves capillaries and diffuses into alveoli down its concentration gradient, to be expelled during upcoming exhalation. ___________________ refers to two-way diffusion of gases between _________________________ taking place along a concentration gradient. Cells bathed in interstitial fluid release carbon dioxide, which then diffuses to venous capillaries. Independently, oxygen moves from arterial side of capillary beds into interstitial fluid and diffuses into surrounding cells. Summary: Transport of ________________________________ Oxygen moving across alveolar-capillary interface is bound to hemoglobin. Carbon dioxide moving from interstitial fluid to veins enters RBCs (93% of it) or remains in plasma (7% only) This is a great animation on respiration: http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/esm/esm_krogh_biology_3/ch28/animation s/chapter_28/Present/Activities/28_2/28_2_1a.swf Diseases of the respiratory system Asthma – Severe allergic reaction that causes wheezing coughing, etc.. The bronchioles in the lungs spasm, thus constricting airflow. Bronchitis – a bacterial or viral infection that causes the bronchioles to swell and clog with mucous. More common in smokers. Emphysema – a condition where lungs lose their elasticity and damage to the alveoli also occurs. This decrease respiratory surface area and causes difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, etc. Smoking increases the risk of emphysema. 3




![The Breathing System Key Terms [PDF Document]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008697551_1-df641dd95795d55944410476388f877c-300x300.png)