Science Chapter 8 “Earth`s History”
advertisement

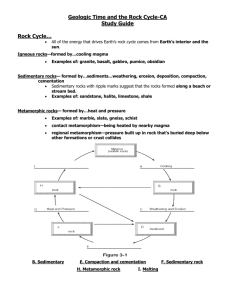
Science Chapter 8 “Earth’s History” Vocabulary: Geology erosion rock cycle lava fault unconformity half-life plate period invertebrate mass extinction theory of plate tectonics igneous rock relative age inclusion continental drift vertebrate radioactive decay sedimentary rock absolute age index fossil geologic time scale amphibian uniformitarianism metamorphic rock intrusion atom era reptile Law of superposition magma extrusion element period mammal Know the stages of the rock cycle; what happens at each stage?; what are the 3 main groups of rocks? Compare and contrast relative age and absolute age of rocks; know how geologists determine the relative age of rocks Know the clues geologists use to determine the relative age of rocks (section 2) Know the age of intrusions of rock compared to rocks they go through Know how to use relative age for faults, intrusions, extrusions, inclusions Why are index fossils used? How can fossils help geologists match rock layers? What are 2 types of fossils that are used as index fossils? What is radioactive dating used for? What rocks are best for this process? What element is used for radioactive dating? What happens during radioactive decay? Know what happens during each era on the geologic time scale; When did vertebrates and invertebrates first appear? What types of organisms existed during each era (Cambrian, Precambrian, Devonian, Mesozoic, Cenozoic, Paleozoic)? When was the mass extinction? What were the major events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras? Scientists can use the information about plates moving to do what? How fast are Earth’s plates moving? What was the super continent called? What do scientists think caused the mass extinction of dinosaurs? What did Hutton’s observations allow him to infer about geologic processes? What is the relative age of faults compared to the layers around them? When did life first appear on Earth? What is the connection between the rock cycle and plate tectonics? How old is the earth? What is the principle of uniformitarianism? Know how to calculate the half-life of an element Know how sand can end up coming out of a volcano, using the rock cycle Explain how geologists use the geologic time scale to explain Earth’s history Explain how plate tectonics, geologic time, the rock cycle, and the theory of evolution are related California State Standards: Earth and Life History (Earth Sciences) 4. Evidence from rocks allows us to understand the evolution of life on Earth. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know Earth processes today are similar to those that occurred in the past and slow geologic processes have large cumulative effects over long periods of time. b. Students know the history of life on Earth has been disrupted by major catastrophic events, such as major volcanic eruptions or the impacts of asteroids. c. Students know that the rock cycle includes the formation of new sediment and rocks and that rocks are often found in layers, with the oldest generally on the bottom. d. Students know that evidence from geologic layers and radioactive dating indicates Earth is approximately 4.6 billion years old and that life on this planet has existed for more than 3 billion years. f. Students know how movements of Earth’s continental and oceanic plates through time, with associated changes in climate and geographic connections, have affected the past and present distribution of organisms. g. Students know how to explain significant developments and extinctions of plant and animal life on the geologic time scale.