Individual ACT Style - Geologic Time
advertisement
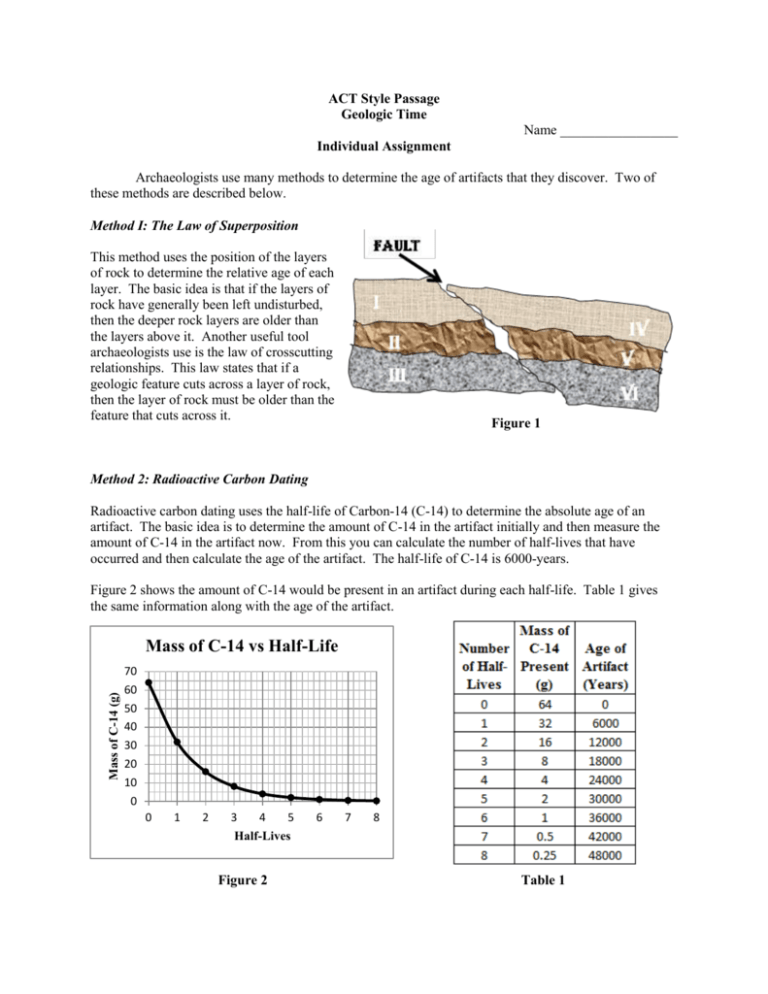
ACT Style Passage Geologic Time Name _________________ Individual Assignment Archaeologists use many methods to determine the age of artifacts that they discover. Two of these methods are described below. Method I: The Law of Superposition This method uses the position of the layers of rock to determine the relative age of each layer. The basic idea is that if the layers of rock have generally been left undisturbed, then the deeper rock layers are older than the layers above it. Another useful tool archaeologists use is the law of crosscutting relationships. This law states that if a geologic feature cuts across a layer of rock, then the layer of rock must be older than the feature that cuts across it. Figure 1 Method 2: Radioactive Carbon Dating Radioactive carbon dating uses the half-life of Carbon-14 (C-14) to determine the absolute age of an artifact. The basic idea is to determine the amount of C-14 in the artifact initially and then measure the amount of C-14 in the artifact now. From this you can calculate the number of half-lives that have occurred and then calculate the age of the artifact. The half-life of C-14 is 6000-years. Figure 2 shows the amount of C-14 would be present in an artifact during each half-life. Table 1 gives the same information along with the age of the artifact. Mass of C-14 (g) Mass of C-14 vs Half-Life 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Half-Lives Figure 2 Table 1 Analysis 1) Describe how the law of superposition can be used to determine the age of an object. Is this relative or absolute age? 2) What is the Law of Crosscutting Relationships? What geologic features in figure 1can this law be applied to? 4) Describe how radioactive carbon dating can be used to determine the age of a fossil. 5) Describe the relationship between the mass of C-14 and the number of half-lives. 6) How much C-14 is left after 3.75 half-lives? 7) A fossil starts with 64-g of C-14 and is reduced to 2-g. How old is the fossil? 8) If the fossil from #7 was found in layer V, what can you say about the age of a fossil found in layer I? Multiple Choice 1) Which of the lists below gives the correct relative ages, oldest to youngest, of layer I, II, III and the fault in figure 1. a. b. c. d. 2) If an artifact began with 64-g of Carbon-14 and now has 12-g, use figure 2 to determine the number of half-lives that have passed. a. b. c. d. 3) b. c. d. Since layer II and layer V are the same layer that was broken by the fault, the two artifacts have the same relative age. Since layer V is slightly lower than layer II, the arrowhead is slightly older than the piece of metal. Since layer V is slightly lower than layer II, the metal piece is slightly older than the arrowhead. There is really no way to tell which artifact is older since the two layers are broken by the fault. An artifact is found to be 28,000 years old. Approximately how much C-14 should be present in this artifact if it started with 64-g? a. b. c. d. 5) 2.25 3.00 1.50 3.75 An archaeologist finds a piece of metal in layer II and an arrowhead in layer V as shown in figure 1. What conclusion is valid about the relative age of these two artifacts? a. 4) III, II, I, Fault I, II, III, Fault Fault, I, II, III Fault, III, II, I 3.0-g 6.0-g 1.5-g 12-g A piece of pottery was found in layer IV and a wooden spoon was found in layer VI, as shown in figure 1. The pottery was found to have 4-g of C-14 present in it after starting with 64-g. What can be said about the age of the wooden spoon? a. b. c. d. The wooden spoon is more than 24000-years old. The wooden spoon is 24000-years old. The wooden spoon is less than 24000-years old. The wooden spoon is greater than 36000-years old.