Benefits & Dangers of Radioisotopes
advertisement

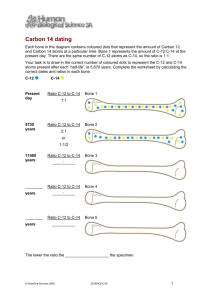
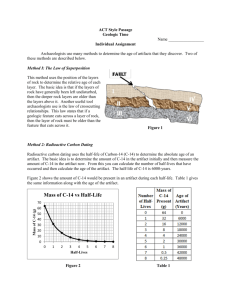
Benefits & Dangers of Radioisotopes Dating (not that kind) C-14 used to date organic (previously living) materials Living organisms incorporate C-14 into their structure, along with C-12 C-14 decays with known half-life (5730 yrs) 14 6C 14 7N + 0 -1 figure out how many half-lives occurred since died: compare amounts C-14 & C-12 ROCKS U-238 decays to Pb-206 (through many decay steps) Over time, amount U-238 as amount Pb206 – use ratio of U-238 to Pb-206 to date rocks Chemical Tracers Can detect radioactive materials and their decay products Tracer = any radioisotope used to follow path of substance in system – P-31: determine P uptake in plants – C-14: map C in metabolic processes – C-14: map organic molecules; figure out reaction mechanisms Industrial Applications Kill bacteria and spores in food and mail Medical Uses Use radioisotopes with short half-lives – quickly eliminated from body – Tracers used for medical diagnosis & treatment of cancers I-131: Diagnosis & treatment of thyroid disorders Co-60: gamma emitter – use: kill cancerous tumors Co-60 and Cs-137 – use: destroy anthrax bacilli Co-60 – use: kill bacteria in foods Tc-99: treatment of brain cancers Power Plants Use: fuel source to generate electricity No contributions to greenhouse gases No mercury contamination of atmosphere Radiation Risks Can damage normal tissue High doses can cause illness & death Can cause mutations in DNA Disposal of waste is difficult – Fuel rods are mix of many substances – Storage & transportation both problematic