Unit 5 - Roman Empire

Roman Influences
From Republic to Empire
Unit 5 -- Section 2 - The Empire
Key Terms
Emperor
Census
Tariffs
Gladiators
People to Know
Augustus
Marcus Aurelius
Diocletian
Constantine I
Theodocius
Alaric
Rule of Augustus
27 BCE Octavian becomes first Roman emperor.
Renames himself Caesar Augustus (“the revered one”)
Augustus
- He was very clever and disguised his power by making the empire look like a republic.
- Kept assemblies and government officials
- Careful to make senators feel honored
Strength
He strengthened his authority in two ways.
Had every soldier swear allegiance only to him
Gave him complete control of the military
Built up his imperial household
Chose people because of talent NOT birth
Gave slaves and freedmen a chance to be part of the government.
Vision on Expansion
Only wanted borders that were easy to protect
Not interested in gaining new territory but did much to increase the quality of life in - the existing empire.
Visions for Rome
Wanted to make Rome more beautiful
Wrote strict laws
Set up a fire brigade and police force
Encouraged learning by building Rome’s first library
Made Roman citizenship available to people in the provinces.
Took census in order to count people in the empire.
Reorganized government so that it ran well for 200 years!
Gave Rome a new sense of patriotism.
Pax Romana
Peace of Rome
Lasted 200 years
Prosperous period
Civilization spread
Cultures mixed
Trade
With peace came increased trade
The same coins were used throughout the empire
There were no tariffs (taxes on goods brought into the country)
Trade routes were made safe by clearing pirates out of the Mediterranean.
Luxury items such as marble, granite, amber, Chinese silk.
Increased trade meant more business for the Romans.
Law
Daily Life
Early in the empire about 1 million people under Roman rule.
Rome suffered many of the same problems we face today.
Air pollution, crime in the streets, little work, and high taxes.
Family
Twelve Tables were rewritten.
New laws were written to ensure fairness for members of the empire that were not
Romans, and lived in the provinces.
Judges were helped by special lawyers and legal writers called juris prudentes, they were used to help write and interpret the new laws.
Under the new laws, a person was innocent until proven guilty.
All important
12 years old boys and girls went to school together !
Both wealthy and poor went to school.
Poor went to work after and wealthy began their formal education.
At 12 years, girls ended their formal education.
Wealthy received private lessons
Fall of the Empire
The Pax Romana ended after 200 years.
After, conditions continually worsened in Rome
By 476 CE there was no empire left
Instead most of western Europe turned into a group of Germanic kingdoms.
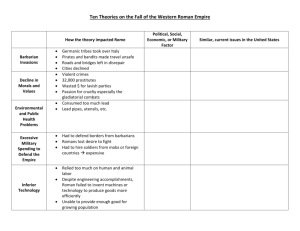
Reasons for Decline
There were many!
Political weaknesses
No written rule about who would inherit the throne once the emperor died.
Between 96 and 180 CE all emperors were adopted.
Marcus Aurelius
Became emperor in 161
Kind, intelligent, devoted to duty
His son Commodus was completely the opposite
Commodus
Aurelius died in 180
Commodus was cruel and hated by all Romans
Strangled by his own bodyguards
The Pratorian Guard (bodyguards) sold the throne to the highest bidder.
This set a terrible precedent
For 100 years, legion fought legion in order to put their emperor on the throne.
By 284 Rome had 37 different emperors.
Most were murdered by the army or the Praetorian Guard
Economic Reasons
Soldiers wages were too high
Too much money was needed for the military payroll
Rome began to suffer from inflation
Period of ever increasing prices
Gold was no longer available due to lack of new conquests.
Less gold used in coins, therefore, the value of money was decreasing.
People began to barter (or exchange goods without money
Foreign Enemies
While Roman politician fought each other, Rome’s frontiers fell under attack by invaders.
Germanic tribes began to raid Gaul and Greece.
Diocletion
Tried very hard to save the empire
Ruled from 284 to 305
Fortified frontiers
Set maximum prices for goods in order to keep prices down.
Established Rule by Divine Right
Emperors powers came from the gods, not the people
In order to solve the problem of succession, and to answer the question of who would be Emperor of the newly divided East and West, Diocletian created what has become known as the system of
"Tetrarchy", or "rule of four", whereby a senior emperor would rule in the East and another senior emperor would rule the West, and each would have a junior emperor.
By 292, Diocletian had the system in place and chose the Eastern Empire for himself and gave Maximian the Western Empire.
The imperial power was now divided between two people. The two men established separate capitals, neither of which was at Rome.
Constantine I
312 – 337 CE
In 306, Constantine started a civil war in the west, which he won in 312, and took the eastern half by 324, thus ruling as a united Empire until his death in 337. However, by 395 the division occurred again and the two halves would never be reunited.
Reforms
Issued orders in order to keep people from leaving jobs.
Sons had to follow father’s trade.
Sons of farmers had continue farming
Sons of ex-soldiers had to serve in the army
Despite the best efforts of Diocletion and Constantine, the empire began to crumble in the west.
In 330 CE, Constantine moved the capital from a dying Rome to a new city in the East.
Named in Constantinople. (Present day Turkey now Istanbul)
The End of the Empire
Neither Diocletian nor Constantine could save the empire.
German attacks increased
Theodosius
After Constantine’s division of the empire by moving the capital from Rome to
Constantinople, Theodosius reunited the eastern and western portions of the empire.
Theodosius was the last emperor of both the Eastern and Western Roman Empire. After his death, the two parts split permanently.
Huns
Of all the Barbarian invasions, the Huns were the most damaging.
Huns were the most devastating groups
Came from Outer Mongolia
Invented stirrups for horses! Stability in combat.
Led by Attila (405 to 452)
By 400 CE Rome was very weak
In 410 CE the Germanic chieftain Alaric ( king of the Visogoths) and his soldiers invaded
Rome o Burned records o Looted the treasury
Roman Senate told the Roman people : “You can no longer rely on Rome for finance or direction. You are on your own.”
Odoacer
Odoacer (435 – 493), also known as Odovacar was King of Italy (476 - 493), and deposed the last Western Roman Emperor.
Crowning himself king of Italy in 476 is considered as the official end of the entire Western
Roman Empire.