I Want to Be Like You-oo-oo!! Oh, oobee

I Want to Be Like You-oo-oo!!
Oh, oobee-doo
I wanna be like you-u-u
I wanna walk like you
Talk like you, to-oo-oo-oo
You'll see it's true
An element like me-e-e
Can learn to be a gas….like you toooo-oo
(badly modified from Disney’s ‘Jungle
Book’)
Criteria for Write-Up
Introduction:
How is the periodic table arranged?
What are the in-common properties of the periods (rows)
What are the in-common properties of the groups (columns)
Why are we interested in the valence electrons associated with each of the elements
Does the periodic table provide us with any patterns when it comes to valence electrons?
What are ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity and effective nuclear charge?
What patterns do we see in each of the above trends
Results:
Alkali Metals
What differences were observed in both the physical properties and reactivity of the alkali metals?
Arrange the alkali metals in order of reactivity and apply a scale of 1-6 for each of the metals
Lithium
Sodium
Potassium
Rubidium
Cesium
Alkali Metal
Alkaline Earths: pH_Conductivity
Alkali Metal Compound
Mg(OH) s
Ca(OH) s pH properties Reactivity (1-6)
Conductivity
Alkaline Earth : Solubility a.
Barium chloride solution, BaCl
2
, b.
Ammonium oxalate solution, Na
2
C
2
O
4 c.
Calcium chloride solution, CaCl
2 d.
Potassium iodate solution, KIO
3 e.
Magnesium chloride solution, MgCl
2 f.
Sodium carbonate solution, Na
2
CO
3 g.
Strontium chloride solution, SrCl
2 h.
Sodium sulfate solution, Na
2
SO
4 i.
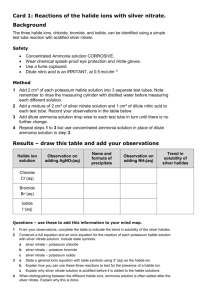
Add 1 mL of an alkaline earth metal chloride solution to each well in a horizontal row, as follows:
• magnesium chloride to wells A1–A5
• calcium chloride to wells B1–B5
• strontium chloride to wells C1–C5
• barium chloride to wells D1–D5 ii.
Add 1 mL of testing solution to each well in a vertical column, as follows:
• potassium iodate to wells A1–D1
• sodium sulfate to wells A2–D2
• ammonium oxalate to wells A3–D3
• sodium carbonate to wells A4–D4
Halogens: physical properties
Halogens
Chlorine (Cl
2
)
Bromine (Br
2
)
Iodine (I
2
)
Physical State
Halide Salt
Potassium Chloride (KCl)
Potassium Bromide (KBr)
Potassium Iodide (KI)
Toggle setting on probe
Halogens: Single displacement Reactions between halogens and halide salts
Test Tube
Halogen
Sodium Halide Solution
Evidence of a reaction
(color change?)
1
Cl
2
NaBr
2
Cl
2
NaI
3
Br
2
NaCl
Color
Conductivity
4
Br
2
NaI
I
5
2
I
6
2
NaCl NaBr
Discussion:
Describe any trends you observed among the Alkali metals, Alkaline Earths and Halogens in each of the above categories of exploration.
Provide in-depth explanations for what might account for any patterns you observed going down a group or across the period (looking at conductivity values for the IIA and VII elements might be helpful here). Include the following in your explanation:
Differences in atomic size
Differences in ionization energy
Differences in electronegativity
Differences in effective nuclear charge
Write complete and balanced equations for the double displacement reactions you observed in the reaction plates when you were looking at solubility.
→
→
→
→
→
→
→
→
→
→
Write complete and balanced equations for the single displacement reactions you observed in the test tubes.
→
→
→
→
→
→