DSRIP Plan: UC San Diego Page CATEGORY 1: Infrastructure
advertisement

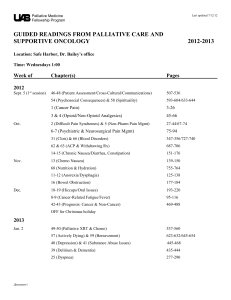
DSRIP Plan: UC San Diego Page 1 CATEGORY 1: Infrastructure Development Project Implement and Utilize Disease Management Registry Description Build disease management registry to identify, monitor, manage, and communicate with high risk patients Y1: Y2: Y3: Y4: Y5: Enhanced Interpretation Services and Culturally Competent Care Gap analysis to determine baseline of language access gaps, revise policies to assure meet JCHO, HHS and other standards, integrate cultural competency into staff training, and expand technology used in interpretation services. Y1: Y2: Y3: Y4: Y5: 5-Year Goals (1) Have registry functionality at 2 practice sites (2) create protocols for registry-driven reminders and reports for providers and nurses re: BP, LDL cholesterol, liver and renal monitoring and management in cardiovascular disease patients (1) create protocols for breast and cervical cancer screening. Metric: electronic process to correctly identify 95% of screening tests that require followup. (2) staff training so that 75% of all outpatient primary care and cardiology sites have at least 2 people trained. (1) Generate at least 2 registry based reports for each provider for care delivered outside office visit and peer comparisons for nurse-driven protocols. (2) Hold 2 sessions for primary care providers to learn from highest performing cardiovascular risk factor managers. (3) Add at least 2 specialty practices that can use registry. (1) ) Generate at least 2 registry based reports for each provider for care delivered outside office visit and peer comparisons for provider-driven protocols (e.g blood pressure control, LDL cholesterol control) (2) improve workflow to either reduce time it takes to manage registry or add more patients using same resources. (3) Expand registry functionality to have at least some registry activity for 75% of all primary care providers. (1) Deliver registries to 95% of all system practicing ambulatory care providers. (2) At least 2 registry reports to every provider. Develop organizational plan for patient and family centerdness and cultural competencies. (1) Gap analysis (2) Establish baseline of qualified health care interpreter encounters per month. (1) Increase number of qualified health care interpreter encounters per month by 10% . (2) Implement audio/video conferencing interpreter terminals in 80% of patient care areas. (3) 80% of staff trained to appropriately use health care interpreters (via video, phone, or in person.) Increase qualified health care interpreter encounters per month by 30% of baseline. Increase qualified health care interpreter encounters per month by 20% DSRIP Plan: UC San Diego Page 2 of baseline. Y1: Develop plan to establish UCSD Department of Telemedicine. Expand current centralized specialty consult Y2: (1) Telemedicine triage unit established for one specialty. (2) Pilot telemedicine to be part of routine activity in any telemedicine charting and communication tools within EMR. clinical specialty and acute care/emergency operations, and expand hours in specialty clinics, Y3: (1) Expand to at least one additional specialty. (2) Implement telemedicine partnership with at least one additional remote clinical and expand telemedicine use for emergency site (SPOKES) (3) Establish baseline number of e-consultations. evaluation services. Y4: (1) Increase e-consultations by 10%. (2) Expand to at least one additional specialty. (3) Expand to at least one additional remote clinical site. Y5: (1) Increase e-consultations by 20%. (2) Expand to at least one additional remote clinic. Y1: Gap analysis. Transition all coding from ICD-9 to ICD-10 Y2: (1) Develop project plan for organization-wide transition. (2) Asses all current info systems re: need for transition. Y3: (1) Train 100% of coding staff. (2) Update clinical document improvement tools for ICD-10. Y4: (1) 100% of records coded using ICD-10. (2) Audit at least 50% of records for accuracy. Y5: Develop and implement improvement plan based on audit. CATEGORY 2: INNOVATION AND REDESIGN Introduce Telemedicine Enhance Coding and Documentation for Quality Data Redesign Primary Care Improve and increase patient use of electronic medical record to improve access for screening and preventive services. Improve Patient Flow in the Emergency Department Analyze ED for improvement opportunities, initiate care per protocol and triage to expedite exam and treatment, expand physical patient care areas to increase capacity, and implement electronic health info exchange with pre-hospital Y1: Establish mechanism for patient self-enrollment in EMR (MyUCSDChart), without provider referral. Y2: (1) Establish baseline for patient enrollement. (2) Develop marketing strategy to encourage patient enrollment. (3) Develop protocol for automatic patient reminders. Y3: (1) Increase enrollment by 5% over baseline. (2) Develop protocols for screening alerts sent to patients. Y4: (1) Increase enrollment by 10% over baseline. (2) Develop protocols for reminders for lipid and glucose screening in CVD and diabetes screening. Y5: (1)Increase patients by 15% over baseline Y1: (1) Develop care initiation protocols, (2) establish baseline for patients who leave ED without being seen, and (3) establish ED wait time baseline. Y2: (1)Decrease % patients who leave ED without being seen by 5% (2) Develop health info exchange link with pre-hospital and community clinic care. (3) Reduce ED wait time for admitted patients by 5%. DSRIP Plan: UC San Diego Page 3 care Y3: (1) Decrease % patients who leave ED without being seen by 10% (2) Reduce ED wait time by 10% Y4: (1) Decrease % patients who leave ED without being seen by 15% (2) Reduce ED wait time by 15% Y5: (1) Maintain 15% below baselines for ED leavers (2) Maintain 15% below baseline for ED wait time Y1: (1) Develop criteria and mechanism for automatic triggers for palliative Increase number of patients receiving palliative care consult and (2) establish baseline for palliative care consults care by expanding teams, creating automated Y2: (1) Increase palliative care consults by 25% over baseline (2) establish triggers to identify patients needing palliative baseline of patients who died in hospital and received palliative care care, monitor patient transitions from ICU or consult code status changes to increase appropriate Y3: (1) Increase palliative care consults by 50% over baseline (2) Increase transitions to palliative care, and monitor and palliative care consults among patients who died in hospital by 5% evaluate cost and symptom impacts Y4: (1) increase palliative consults by 75% (2) Increase palliative care consults among patients who died in hospital by 10% Y5: (1) increase palliative consults by 100% (2) Increase palliative care consults among patients who died in hospital by 15% Use of Palliative Care Programs Conduct Medication Management Establish medication management program for high risk patients Implement/Expand Care Transition Programs Improve transition from inpatient to outpatient care and prevent readmissions, improve followup, and increase and improve use of collaborative and electronic medical records and health information technology for effective transitions and continuity of care Y1: Develop plan. Y2: (1) Develop criteria and identify targeted patient populations. (2) Implement program via written plan to provide medication reconciliation as part of transition from acute to ambulatory care Y3: Increase number of patients that consistently receive medication management by 100% Y4: Increase number of patients that consistently receive medication management by 200% Y5: Increase number of patients that consistently receive medication management by 300% Y1: (1) Develop staffing and implementation plan. (2) Develop care transition protocols for community with patients and families during and post-discharge (3) Designate team to manage project. Y2: (1) Identify top chronic conditions and patient characteristics characteristic of readmission (2) Create patient stratification system to enable resources to be targeted to highest risk patients (3) Pilot care transitions process for patient/family communications and interdisciplinary rounds on 2 wards (4) Achieve completion of discharge summaries within 48 hours of discharge in 80% of hospital medical services discharges (5) Establish baseline percent of medical surgical inpatients discharged to home who are assigned a medical home. DSRIP Plan: UC San Diego Page 4 Y3: (1) Pilot care transitions protocols on 4 wards (2) Establish hospitalbased case manager process for discharged patients who have top chronic conditions, to include standardized discharge instructions and education and provide additional coaching as needed (3) Achieve completion of discharge summaries within 48 hours of discharge in 80% of all medical and general surgical patients (4) assess and establish linkages with community-based organizations to create support network for targeted discharged patients (5) increase percent of medical inpatients discharged to home who are assigned a medical home by 15%. Y4: (1) Achieve completion of discharge summaries within 48 hours of discharge in 90% of all medical and general surgical patients (2) increase percent of medical inpatients discharged to home who are assigned a medical home by 30%. Y5: (1) Share learnings with peer organization audiences in at least two venues (2) increase percent of medical inpatients discharged to home who are assigned a medical home by 50%. Implement Real-Time Healthcare Associated (HAI) Systems Establish HAI surveillance system that is integrated with electronic medical records system, includes prompting tools for physicians, and provides just-in-time education tools and resources for clinicians when HAIs are identified. Improve Severe Sepsis Detection and Management implement Sepsis Management and Resuscitation Bundle Reduce avoidable harm or deaths due to severe sepsis to patients receiving inpatient services Y1: (1) Develop real-time intervention system in EMR to track patients with organisms known to increase HAI risk. (2) Develop electronic system for real-time feedback to clinicians re potential HAI events (3) Implement prompts for prevention and risk identification for CLIP and daily line necessity. Y2: (1) Expand HAI EMR system to other areas such as ICU, non-ICU, or specialty care, and generate report (2) Develop electronic system for real-time education to clinicians (3) Expand prevention and risk identification prompts to include urinary catheter necessity Y3: Expand HAI system to all inpatients. Y4: Initiate chlorhexidine bathing in non-ICU adults with central lines, urinary catheters, or recent surgery Y5: Measure HAI rate for urinary catheter associated infections CATEGORY 4: URGENT IMPROVEMENT IN CARE Y1: Participate in San Diego Patient Safety Collaborative on Sepsis to learn and share best practices. Y2: (1) Implement the Sepsis Resuscitation Bundle: (2) Report at least 6 months of data to SNI for baseline / benchmarks; (3) Report the results to the state. Y3: (1) achieve TBD% compliance with sepsis resuscitation bundle; (2) share Central Line Associated Blood Stream Infection (CLABSI) Prevention Surgical Site Infection DSRIP Plan: UC San Diego Page 5 data and practices with SNI for benchmarking across public hospitals; (3) Report results to the state Y4: (1) achieve TBD% compliance with sepsis resuscitation bundle; (2) share data and practices with SNI for benchmarking across public hospitals; (3) Report results to the state Y5: (1) achieve TBD% compliance with sepsis resuscitation bundle; (2) share data and practices with SNI for benchmarking across public hospitals; (3) Report results to the state Y1: Implement the Central Line Insertion Practices (CLIP) improve compliance with central line insertion Y2: (1) Report at least 6 months of data collection on CLIP to SNI for bundle baseline / benchmarks; (2) Report at least 6 months of data collection Reduce avoidable harm or deaths and costs of on CLABSI to SNI baseline / benchmarks; (3) Report CLIP results to the care due to central-line associated blood stream state infections Y3: (1)achieve TBD% compliance with CLIP; (2) share data and practices with SNI; (3) report CLIP and CLABSI results to State Y4: (1) achieve TBD% compliance with CLIP; (2) reduce central line bloodstream infections by TBD%; (3) share data and practices with SNI; (4) report CLIP and CLABSI results to State Y5: (1) achieve TBD% compliance with CLIP; (2) reduce central line bloodstream infections by TBD%; (3) share data and practices with SNI; (4) report CLIP and CLABSI results to State Y1: Redesign and implement antibiotic delivery documentation within the improve surgical site infection prevention inpatient EMR Y2: (1) Report at least 6 months of data collection on SSI to SNI for baseline/benchmarks; (2) Report result to state (3) Achieve 92% compliance in SCIP Core Measures: post-operative glycemic control in CT surgery and urinary catheter removal by post op day 2 (4) Achieve 85% compliance with combined SCIP Core Measure for ambulatory antibiotic administration. Y3: (1) Reduce the rate of surgical site infection for Class 1 and 2 wounds by X (2) share data and practices with SNI (3) Report results to the state (4) Achieve 93% compliance in SCIP Core Measures: post-operative glycemic control in CT surgery and urinary catheter removal by post op day 2 (4) Achieve 90% compliance with combined SCIP Core Measure for ambulatory antibiotic administration. Y4: (1) Reduce the rate of surgical site infection for Class 1 and 2 wounds by X (2) share data and practices with SNI (3) Report results to the state (4) Achieve 95% compliance in SCIP Core Measures: post-operative glycemic control in CT surgery and urinary catheter removal by post op Hospital-acquired Pressure Ulcer (HAPU) Prevention DSRIP Plan: UC San Diego Page 6 day 2 (4) Achieve 95% compliance with combined SCIP Core Measure for ambulatory antibiotic administration. Y5: (1) Reduce the rate of surgical site infection for Class 1 and 2 wounds by X (2) share data and practices with SNI (3) Report results to the state (4) Maintain or exceed 95% compliance in SCIP Core Measures: postoperative glycemic control in CT surgery and urinary catheter removal by post op day 2 (4) Maintain or exceed 95% compliance with combined SCIP Core Measure for ambulatory antibiotic administration. Y1: Implement wound ostomy nurses documentation of skin assessment in Improve prevention of pressure ulcers using EMR evidence-based recommendations from the Y2: (1) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI to foster national Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel shared learning and benchmarking across the California public hospitals; (2) Report hospital-acquired pressure ulcer prevalence results to the state. Y3: (1) Achieve hospital-acquired pressure ulcer prevalence of less than 1.1%; (2) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI; (3) Report hospital-acquired pressure ulcer prevalence results to the state Y4: (1) Maintain hospital-acquired pressure ulcer prevalence of less than 1.1%; (2) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI (3) Report hospital-acquired pressure ulcer prevalence results to the state Y5: (1) Maintain hospital-acquired pressure ulcer prevalence of less than 1.1%; (2) Share data, promising practices and findings with SNI (3) Report hospital-acquired pressure ulcer prevalence results to the state