Remake Your Classroom - 21st Century Competencies Wiki
advertisement
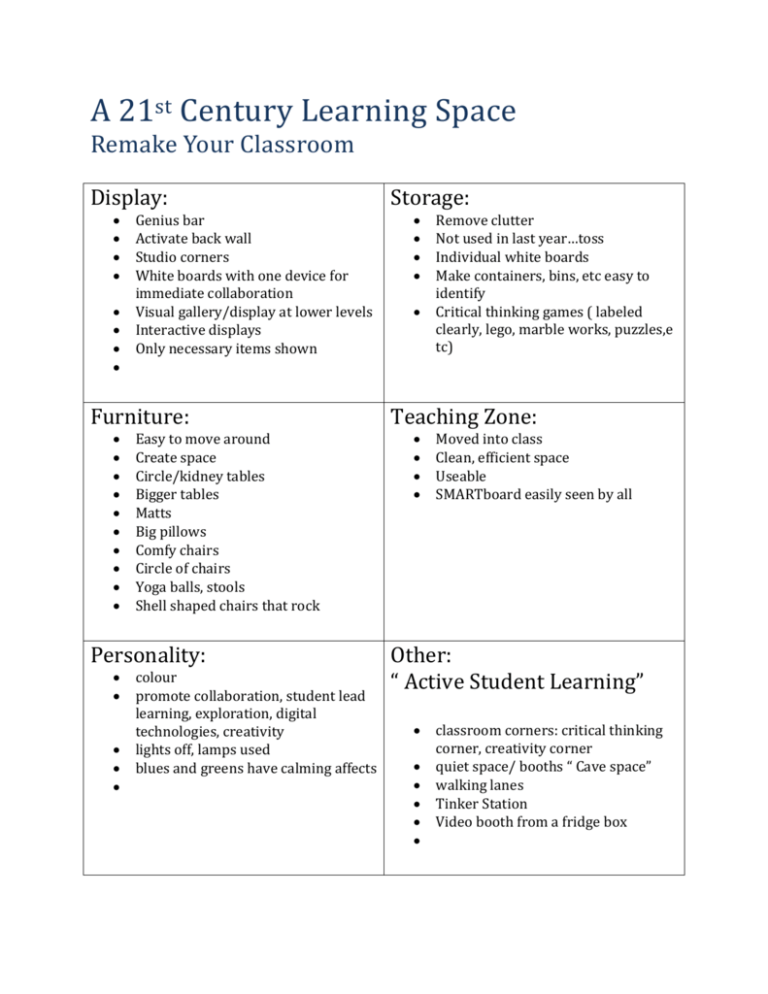
A 21st Century Learning Space Remake Your Classroom Display: Genius bar Activate back wall Studio corners White boards with one device for immediate collaboration Visual gallery/display at lower levels Interactive displays Only necessary items shown Furniture: Easy to move around Create space Circle/kidney tables Bigger tables Matts Big pillows Comfy chairs Circle of chairs Yoga balls, stools Shell shaped chairs that rock Personality: colour promote collaboration, student lead learning, exploration, digital technologies, creativity lights off, lamps used blues and greens have calming affects Storage: Remove clutter Not used in last year…toss Individual white boards Make containers, bins, etc easy to identify Critical thinking games ( labeled clearly, lego, marble works, puzzles,e tc) Teaching Zone: Moved into class Clean, efficient space Useable SMARTboard easily seen by all Other: “ Active Student Learning” classroom corners: critical thinking corner, creativity corner quiet space/ booths “ Cave space” walking lanes Tinker Station Video booth from a fridge box Questions to Consider: 1. What are your key routines and activities? 2. When are classroom successes amplified? 3. When are challenges seen by physical environment? 4. How do your students learn best? 5. Identify THREE priorities you would like to transform. ( Example: peer to peer learning, environment of trust and comfort, flow and mobility, teaching zone efficiency, storage, student furniture) 6. Decide what you feel is already working: ( keep class motos, beliefs, displays, etc) 7. What isn’t working in your classroom and brainstorm ways to tackle this issue. 8. What supplies and materials do students use most often? Brainstorm the best ways to store them. 9. Adapted from TheThirdTeacher+, http://www.edutopia.org/blog/steps-to-redesign-your-classroom-melanie-kahl ( December, 2103). Mrs. Farrell’s Classroom Makeover Displays: Take down anything that is not being used Move useable displays/etc to eye view for students Try to group displays by grades ( gr. 2 displays together and grade1 displays together) Try to use neutral colours, and use colours purposefully Create a Wonder Wall Activate the back wall bulletin board ( student writing continuum, exemplars, student gallery, RAN chart,etc) Furniture: New lower white shelves for students materials, books, etc Get rid of big shelf by lockers Use two bookshelves to create “ booth” Use puzzle pieces for teacher zone Carpet piece and cushions for collaboration station Lamps Artificial plants Personality: A place where students lead their learning in a collaborative, creative, and innovation way Storage: Baskets for reading books in classroom Baskets ( 9) for student duotangs for subjects Go through cupboards, filing cabinet, binder shelf to see what doesn’t need to be at school or kept Think about how you would like to be able to use your desk ( what is most important for efficiency) Stations: Collaboration station Teacher zone Presentation station The booth Walking lane Note: Label the stations Student Materials: 21st Century Learning Spaces 20th Century Classroom vs. the 21st Century Classroom USA 1960’s typical classroom – teacher-centered, fragmented curriculum, students working in isolation, memorizing facts. A classroom at the School of Environmental Studies, aka th Zoo School, in Minneapolis. A perfect example of real-life, relevant, project-based 21st century education. Time-based Outcome-based Focus: memorization of discrete facts Focus: what students Know, Can Do and Are Like after all t details are forgotten. Lessons focus on the lower level of Bloom’s Taxonomy – knowledge, comprehension and application. Learning is designed on upper levels of Blooms’ – synthesis analysis and evaluation (and include lower levels as curricu is designed down from the top.) Textbook-driven Research-driven Passive learning Active Learning Learners work in isolation – classroom within 4 walls Learners work collaboratively with classmates and others around the world – the Global Classroom Teacher-centered: teacher is center of attention and provider of information Student-centered: teacher is facilitator/coach Little to no student freedom Great deal of student freedom “Discipline problems" – educators do not trust students and vice versa. No student motivation. No “discipline problems” – students and teachers have mutu respectful relationship as co-learners; students are highly motivated. Fragmented curriculum Integrated and Interdisciplinary curriculum Grades averaged Grades based on what was learned Low expectations High expectations – “If it isn’t good it isn’t done.” We expec and ensure, that all students succeed in learning at high levels. Some may go higher – we get out of their way to let them do that. Teacher is judge. No one else sees student work. Self, Peer and Other assessments. Public audience, authe assessments. Curriculum/School is irrelevant and meaningless to the students. Curriculum is connected to students’ interests, experiences, talents and the real world. Print is the primary vehicle of learning and assessment. Performances, projects and multiple forms of media are use learning and assessment Diversity in students is ignored. Curriculum and instruction address student diversity Literacy is the 3 R’s – reading, writing and math Multiple literacies of the 21st century – aligned to living and working in a globalized new millennium. Factory model, based upon the needs of employers for the Industrial Age of the 19th century. Scientific management. Global model, based upon the needs of a globalized, high-te society. Driven by the NCLB and standardized testing mania. Standardized testing has its place. Education is not driven the NCLB and standardized testing mania.