chp_18_due_by_sunday_01-20-13_6pm
advertisement

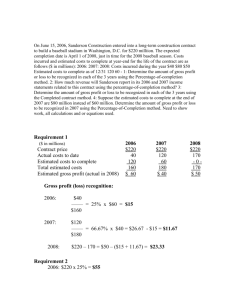
1. Jansen Corporation shipped $18,400 of merchandise on consignment to Gooch Company. Jansen paid freight costs of $1,760. Gooch Company paid $720 for local advertising, which is reimbursable from Jansen. By year-end, 63% of the merchandise had been sold for $21,900. Gooch notified Jansen, retained a 9% commission, and remitted the cash due to Jansen. Prepare Jansen’s entry when the cash is received. (Round answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 1,525. Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually.) Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit (To record the cash remitted to Jansen.) (To record the cost of inventory sold on consignment.) Cash Inventory on Consignment = [$21,900 – $720 – ($21,900 x 9%)] = $19,209 = [63% x ($18,400 + $1,760)] = $12,701 2. Turner, Inc. began work on a $7,723,000 contract in 2012 to construct an office building. During 2012, Turner, Inc. incurred costs of $1,702,140, billed its customers for $1,333,000, and collected $978,300. At December 31, 2012, the estimated future costs to complete the project total $3,455,860. Prepare Turner’s 2012 journal entries using the percentage-of-completion method. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. For costs incurred use account Materials, Cash, Payables.) Account Titles and Explanation No. Debit Credit (1) (To record costs incurred.) (2) (To record billings.) (3) (To record collections.) (4) (To recognize revenue.) Construction in Process = [($1,702,140 ÷ 5,158,000) x $2,565,000] = $846,450 Revenue from Long-Term Contracts = ($7,723,000 x 33%) = $2,548,590 3.Gordeeva Corporation began selling goods on the installment basis on January 1, 2012. During 2012, Gordeeva had installment sales of $110,000; cash collections of $67,100; cost of installment sales of $77,000. Prepare the company’s entries to record 1) installment sales, 2) cash collected, 3) cost of installment sales, 4) deferral of gross profit, and 5) gross profit recognized, using the installment-sales method. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually.) No. Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 4.On June 3, Hunt Company sold to Ann Mount merchandise having a sales price of $11,000 with terms of 3/10, n/60, f.o.b. shipping point. An invoice totaling $120, terms n/30, was received by Mount on June 8 from the Olympic Transport Service for the freight cost. Upon receipt of the goods, June 5, Mount notified Hunt Company that merchandise costing $600 contained flaws that rendered it worthless. The same day, Hunt Company issued a credit memo covering the worthless merchandise and asked that it be returned at company expense. The freight on the returned merchandise was $28, paid by Hunt Company on June 7. On June 12, the company received a check for the balance due from Mount. (a) Prepare journal entries for Hunt Company to record all the events noted above under each of the following bases. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually.) 1. Sales and receivables are entered at gross selling price Date Account Titles and Explanation 6/3 6/5 6/7 6/12 Debit Credit 2. Sales and receivables are entered net of cash discounts. Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit 6/3 6/5 6/7 6/12 (b) Prepare the journal entry under basis (2), assuming that Ann Mount did not remit payment until August 5. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually.) Account Titles and Explanation (a) 1. 2. 6/12 6/3 6/5 (b) 8/5 Debit Credit Sales Discounts Sales Revenue Accounts Receivable (Ann Mount) (3% x $10,400) [$11,000 – (3% x $11,000)] [$600 – (3% x $600)] $312 $10,670 $582 Sales Discounts Forfeited (3% x $10,400) $312 5. (Recognition of Profit, Percentage-of-Completion) In 2012 Gurney Construction Company agreed to construct an apartment building at a price of $1,200,000. The information relating to the costs and billings for this contract is shown below. 2012 2013 Cost incurred to date $280,000 $600,000 Estimated costs yet to be incurred 520,000 200,000 Customer billings to date 150,000 500,000 Collection of billings to date 120,000 320,000 (a) Assuming that the percentage-of-completion method is used. (1) Compute the amount of gross profit to be recognized in 2012 and 2013. 2012 2013 Gross profit recognized (2) Prepare journal entries for 2013. Description/Account Materials, Cash, Payables, etc. $ 2014 $785,000 -01,200,000 940,000 $ Debit Credit Cash Construction Expense (b) For 2013, show how the details related to this construction contract would be disclosed on the balance sheet and on the income statement. Income Statement (2013) $ Balance Sheet (12/31/13) $ $ (a) (1) Gross profit recognized 2012 2013 $140,000 $160,000 Gross profit recognized in 2012: Contract price Costs: Costs to date Estimated additional costs Total estimated profit Percentage completion to date ($280,000/$800,000) Gross profit recognized in 2012 Gross profit recognized in 2013: Contract price Costs: Costs to date Estimated additional costs Total estimated profit Percentage completion to date ($600,000/$800,000) Total Gross profit recognized Less: Gross profit recognized in 2012 Gross profit recognized in 2013 (2)Journal entries for 2013. Description/Account Construction in Process ($600,000 - $280,000) Materials, Cash, Payables, etc. Accounts Receivable ($500,000 - $150,000) Billings on Construction in Process Cash ($320,000 - $120,000) Accounts Receivable Construction Expense Construction in Process Revenues from Long-Term Contract * 1,200,000 × [($600,000 – $280,000) ÷ $800,000] Income Statement (2013) (b) Gross profit on long-term construction project Balance Sheet (12/31/13) Current assets: Receivables- construction in process Inventories-construction in process totaling ($900,000 ** less billings of $500,000) * $180,000 = $500,000 – $320,000 **Total cost to date $600,000 2012 Gross profit 140,000 160,000 2013 Gross profit $900,000 6. (Gross Profit Calculations and Repossessed Merchandise) $1,200,000 $280,000 520,000 800,000 400,000 35% $140,000 $1,200,000 $600,000 200,000 800,000 400,000 75% 300,000 140,000 $160,000 Debit 320,000 Credit 320,000 350,000 350,000 200,000 200,000 320,000 160,000 *480,000 $160,000 * $180,000 $400,000 Basler Corporation, which began business on January 1, 2012, appropriately uses the installment-sales method of accounting. The following data were obtained for the years 2012 and 2013. 2012 2013 Installment Sales $750,000 $840,000 Cost of installment sales 510,000 588,000 General & administrative expenses 70,000 84,000 Cash collections on sales of 2012 310,000 300,000 Cash collections on sales of 2013 -0400,000 (a) Compute the balance in the deferred gross profit accounts on December 31, 2012, and on December 31, 2013. Deferred Gross Profit Account 2012 Installment Sales 2013 Installment Sales Balance, December 31, 2012 $ Balance, December 31, 2013 $ $ A 2012 sale resulted in default in 2014. At the date of default, the balance on the installment receivable was $12,000, and the repossessed merchandise had a fair value of $8,000. Prepare the entry to record the repossession. (List multiple debit/credit entries from largest to smallest amount, e.g. 10, 5, 2.) Description/Account Debit Credit (b) (To record the default and the repossession of the merchandise) (a) (b) Deferred Gross Profit Account 2012 Installment Sales Balance, December 31, 2012 $140,800 Balance, December 31, 2013 $44,800 Balance, December 31, 2012 Deferred Gross Profit Account-2012 Installment Sales Gross profit on installment sales-2012 ($750,000 - $510,000) Less: Gross profit realized in 2012 ($310,000 × 32%) Balance at 12/31/12 Balance, December 31, 2013 Deferred Gross Profit Account-2012 Installment Sales Balance at 12/31/12 Less: Gross profit realized in 2013 on 2012 sales ($300,000 × 32%) Balance at 12/31/13 Deferred Gross Profit Account-2013 Installment Sales Gross profit on installment sales-2013 ($840,000 - $588,000) Less: Gross profit realized in 2013 on 2013 sales ($400,000 × 30%) Balance at 12/31/13 2013 Installment Sales $132,000 $240,000 (99,200) $140,800 $140,800 (96,000) $44,800 $252,000 (120,000) $132,000 Description/Account Repossessed Merchandise Deferred Gross Profit ($12,000 × 32%) Loss on Repossession [$8,000 - ($12,000 - $3,840)] Installment Accounts Receivable (To record the default and the repossession of the merchandise) Debit 8,000 3,840 160 Credit 12,000 7. Shanahan Construction Company has entered into a contract beginning January 1, 2012, to build a parking complex. It has been estimated that the complex will cost $849,000 and will take 3 years to construct. The complex will be billed to the purchasing company at $1,411,000. The following data pertain to the construction period. 2012 Costs to date 2013 2014 $382,050 $602,790 Estimated costs to complete 466,950 246,210 $862,000 –0– Progress billings to date 328,000 529,000 1,411,000 Cash collected to date 305,000 497,000 1,411,000 (a) Using the percentage-of-completion method, compute the estimated gross profit that would be recognized during each year of the construction period. Gross profit recognized in 2012 $ Gross profit recognized in 2013 Gross profit recognized in 2014 $ $ (b) Using the completed-contract method, compute the estimated gross profit that would be recognized during each year of the construction period. Gross profit recognized in 2012 Gross profit recognized in 2013 $ $ Gross profit recognized in 2014 $ 2012 $1,411,000 2013 2014 Contract price $1,411,000 $1,411,000 Less estimated cost: Costs to date 382,050 602,790 862,000 Estimated cost to complete 466,950 246,210 — Estimated total cost 849,000 849,000 862,000 Estimated total gross profit $562,000 $562,000 $549,000 $382,050 2012: x $562,000= $252,900 $849,000 $602,790 2013: x $562,000= $399,020 $849,000 Less 2012 recognized gross profit 252,900 Gross profit in 2013 $146,120 2014: Estimated total gross profit for 2014 Less 2012–2013 recognized gross profit Gross profit in 2014 Total billings $1,411,000 Total cost (862,000) Gross profit recognized in 2014 $549,000 $549,000 399,020 $149,980