Finasteride - WordPress.com
advertisement
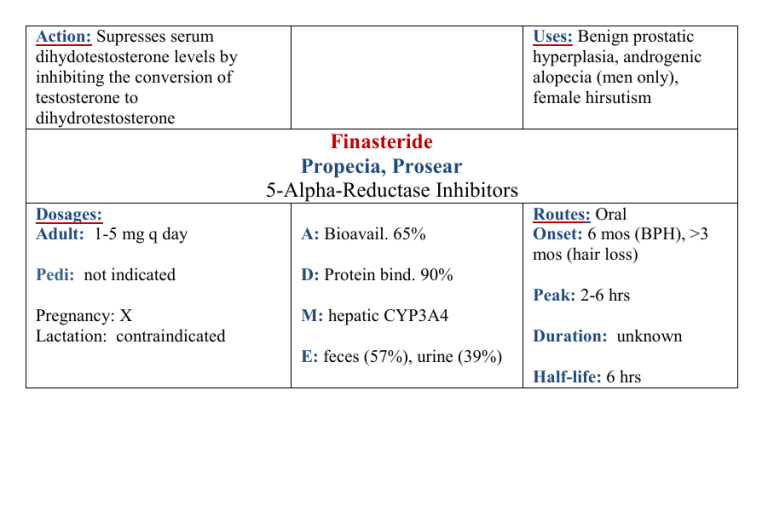
Action: Supresses serum dihydotestosterone levels by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone Uses: Benign prostatic hyperplasia, androgenic alopecia (men only), female hirsutism Finasteride Propecia, Prosear 5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors Dosages: Adult: 1-5 mg q day A: Bioavail. 65% Pedi: not indicated D: Protein bind. 90% Pregnancy: X Lactation: contraindicated M: hepatic CYP3A4 Routes: Oral Onset: 6 mos (BPH), >3 mos (hair loss) Peak: 2-6 hrs Duration: unknown E: feces (57%), urine (39%) Half-life: 6 hrs Common Side Effects: erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, breast enlargement, ejaculation disorder, breast tenderness, rash Adverse Effects: hypersensitivity reactions – rash, pruritis, uticaria and angioedema (including swelling of lips, tongue, throat and face); male breast cancer; depression Contraindications: hypersensitivity, women of childbearing potential, children Interactions: carbamazepine, clarithromycin, erythromycin base, erythromycin ethylsuccinate, erythromycin lactobionate, erythromycin stearate, isoniazid, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, nevirapine, rifabutin, rifampin, St. John’s wort Nursing Considerations: caution in liver dysfunction; sexual dysfunction continues after discontinuation of treatment; may cause decreased serum PSA; pregnant and potentially pregnant women should not handle crushed or broken tablets; report signs of male breast cancer – breast tenderness, enlargement, pain, lumps, nipple, discharge or any breast changes











